Ch14
Production and Costs
13
CLICKER QUESTIONS
© 2013 Pearson
Production and Costs
14
CLICKER QUESTIONS
© 2013 Pearson
Checkpoint 14.1
Checkpoint 14.3
Checkpoint 14.4
Checkpoint 14.2
© 2013 Pearson
CHECKPOINT 14.1
Question 1
Which of the following is an example of an implicit cost?
A. wages paid to employees
B. interest paid to a bank on a building loan
C. the cost of the firm using capital that is owned by the entrepreneur of the firm
D. dollars paid to a supplier for materials used in production
E. liability insurance payments made only once a year
© 2013 Pearson
CHECKPOINT 14.1
Question 2
For a business, opportunity cost equals ____________.
A. the cost of labor and materials
B. the implicit costs of the business
C. all of the firm's costs including its normal profit and its economic profit
D. the cost of all the factors of production the firm employs
E. the firm ’s explicit costs
© 2013 Pearson
CHECKPOINT 14.2
Question 3
If 5 workers can wash 30 cars a day and 6 workers can wash 33 cars a day, then the marginal product of the 6th worker equals ________.
A. 30 cars a day
B. 33 cars a day
C. 5 cars a day
D. 5.5 cars a day
E. 3 cars a day
© 2013 Pearson
CHECKPOINT 14.2
Question 4
Increasing marginal returns occur when the _________.
A. average product of a worker is less than the average product of the previous worker
B. marginal product of a worker exceeds the marginal product of the previous worker
C. average product of labor is at a maximum
D. marginal product of labor exceeds the average product of labor.
E. marginal product of labor is at a maximum
© 2013 Pearson
CHECKPOINT 14.2
Question 5
Average product increases if _________.
A. marginal product increases
B. average product exceeds marginal product
C. marginal product is less than average product
D. marginal product exceeds average product
E. total product increases
© 2013 Pearson
CHECKPOINT 14.3
Question 6
Jay set up his hot dog stand near the business district. His total variable cost includes the _______.
A. annual insurance for the hot dog stand
B. cost of buying the hot dog stand
C. cost of the hot dogs and condiments
D. interest he pays on the funds he borrowed to pay for advertising
E. revenue he gets when he sells his first hot dog each day
© 2013 Pearson
CHECKPOINT 14.3
Question 7
One reason the ATC curve is U-shaped is that _____.
A. returns from labor increase regardless of the number of workers employed
B. returns from labor eventually decrease as more workers are employed
C. the price of the good fall as output of the good increases
D. the average fixed cost increases as more output is produced.
E. the variable cost decreases as more output is produced
© 2013 Pearson
CHECKPOINT 14.3
Question 8
If the wage rate paid to workers increases, then _____.
A. the AFC curve shifts upward
B. the AVC curve doesn ’t change, but ATC shifts upward
C. the MC curve remains the same, but the AVC curve shift upward
D. both the MC curve and the AVC curve shift upward
E. both the AFC curve and the ATC curve shift upward
© 2013 Pearson
CHECKPOINT 14.4
Question 9
Economies of scale occur whenever ________.
A. marginal cost decreases as output increases
B. output is increased by increasing all inputs by the same percentage and total cost increases by smaller percentage
C. marginal product increases as labor increases with capital unchanged
D. a firm increases its plant size and labor by the same percentage, but its output increases by a larger percentage
E. marginal product increases as the firm increases its plant size
© 2013 Pearson
CHECKPOINT 14.4
Question 10
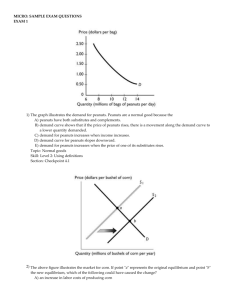
The figure shows four ATC curves of a firm. If the firm produces 3,000 units per day, in the long run, it will use the plant size that corresponds to _______.
A.
ATC
1
B.
ATC
2
C.
ATC
3
D.
ATC
4
E. either ATC
1
© 2013 Pearson or ATC
4