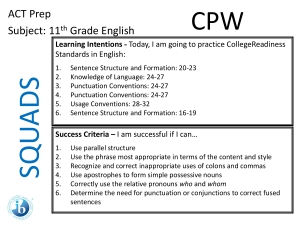
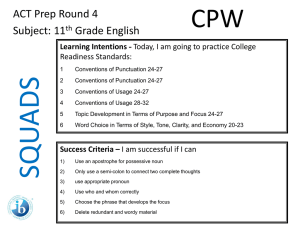
Chinese Context and the Monitoring and Evaluation Framework of
advertisement

Chinese Context and the Monitoring and Evaluation Framework of the 11th Five-Year Plan Xu Lin Director General Department of Fiscal and Financial Affairs, NDRC China’s Five-Year Plan and Its M&E China’s Five-Year Plan for Economic and Social Development is a key strategy document of the Chinese government It decides on the development priorities of the country in the five-year period covered. First Five-Year Plan was prepared in 1953 11th Five-Year Plan just began, covering 2006-2010 No M&E activity for the Plan till the 10th Five-Year Plan Mid-Course Review of the 10th Five-Year Plan Initiated by the Strategic Planning Department of NDRC, which is also the Plan maker. The objective was to find out if any 10th Five-Year Plan targets were not appropriate anymore and if any implementation measure were not effective and need improvement. Informal and experimental in scope; used available data Based on local government’s and Ministries’ midterm reviews and experts’ independent opinions. Mid-Course Review of the 10th Five-Year Plan (continued) The Review was done from nine aspects: Macro-regulatory targets Industrial structure, Development of western region, Urbanization, Science, technology and education, Natural environment, Reform of the economic system, Opening up to the outside world, People’s lives. Mid-Course Review of the 10th Five-Year Plan (continued) The Review identified five major problems Unhealthy pattern of the economic growth, relying overly on investment and export Insufficient development of the tertiary industry Insufficient policy guidance and incentives for developing western region The slow progress of urbanization The unbalance between economic and social development Contributed to the new thinking on people-centered development concept and the 11th Five-Year Plan Country Context for M&E M&E now a priority of the government Prime Minister Wen Jiabao called on government departments at various levels to “establish accountability system and undertake M&E activities”. China’s 11th Five-Year Plan (2006-2010) Major shift from previous GDP-focused development approach Based on scientific concept of development – “People-centered development, which is comprehensive, coordinated and sustainable, for the promotion of overall harmonic development of economy, society and human beings.” China’s 11th Five-Year Plan (2006-2010) (continued) Five balances as the guiding principles: balancing urban and rural development coastal and inland development economic and social development man and nature development domestic development and opening up to the outside world China’s 11th Five-Year Plan (2006-2010) (continued) For the first time, contained an M&E indicator matrix with 22 indicators, 8 of them with quantitative targets and 14 with benchmarks; The “benchmark” indicators are the country’s anticipated development indicators. They will rely mainly on the market force to help the realization of them. The government should create a favorable to try to help realize these benchmarks. The “target” indicators are the indicators that the government is responsible for and obligated to achieve. They are the requirements by the central government for local governments and central government department/agencies. The central government will guarantee the meeting of these targets. China’s 11th Five-Year Plan (2006-2010) (continued) The Plan has also for the first time contained specific text discussions on the importance of M&E work and explicitly committed to carry out a mid-course evaluation on the 11th FYP, which will then be subject to the review of the standing committee of the National People’s Congress (NPC). M&E of China’s 11th Five-Year Plan: Objectives To monitor the implementation progress of the Plan to find out where the country is To evaluate the implementation effectiveness of the Plan to find out why the targets and benchmarks are or are not being achieved The lessons learned will guide the implementation process of the 11th five-year plan in the later part of the five-year period. M&E of China’s 11th Five-Year Plan: Methodologies Internationally Recognized Ten Steps Model --Readiness assessment, --Agreeing on outcomes to M&E --Selecting key performance indicators to monitor --Setting baselines and gathering data on indicators --Selecting Targets ... Consultations with both international and domestic experts 6. Monitoring and Evaluation of China’s 11th Five-Year Plan: Framework Five-balances as the guiding Principle 3 to 4 goals for each Balance About 80 candidate monitoring indicators 7. Monitoring and Evaluation Framework of China’s 11th Five-Year Plan: Core Indicators 22 core indicators 8 obligatory 14 anticipated 8. Monitoring and Evaluation Framework of China’s 11th Five-Year Plan: Input Indicators Two Types of Input information for each Balance Info. on input activities: government policies and regulations Info. on input indicators: government expenditure composition and distribution 9. Monitoring and Evaluation Framework of China’s 11th Five-Year Plan: Going Forward Refining and finalizing the indicators Deciding on targets or benchmarks Institutional setups: organizational structure, legal framework etc. Mid-course evaluation Thank you! mid-term evaluation of the 11th Plan, scheduled for mid-2008. The mid-term evaluation will also be a test for the M&E framework, allowing for lesson learning and corrections as well as improvements, and pointing out to additional needs in terms of statistical data and indicators