TIPSE & TIN
advertisement

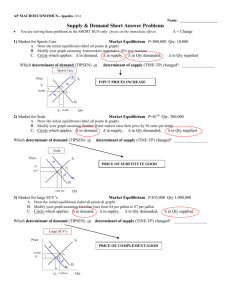
Supply and Demand in Action The Motion of a “Free Market” Equilibrium occurs when Demand = Supply T-Shirts Price -------------- E1 ------------- P1 S1 Q1 D1 Qty Key Terms for S&D Unit Goods which can “replace” other goods SubstituteSoda & Water Compliment- Px good A Goods which “go together” Px good A Gas & Cars => Demand good B (are needed to use the other) => Demand good B Changes in Demand • When a Determinant of Demand (TIPSE) changes the entire demand curve will shift left or right • A “shift” in a demand curve is called a change in demand • • Right shift is an increase in demand Left shift is a decrease in demand Hybrid Cars Price D1 D2 Qty Determinants of Demand (TIPSE) • • • • • Tastes Incomes Population Substitute/Complement Price Expectations If TIPSE changes => Draw a New D-Curve! Example: Event: Change in Demand The price of bottled water increases Market for Soda TIPSE ↓ Price Price Substitute ↑ ↓ Demand ↑ D1 D2 Qty Worksheet Side #1 Changes in Supply • When a Determinant of Supply (TIN) changes the entire supply curve will shift left or right • A “shift” in a supply curve is called a change in supply • • Right shift is an increase in supply Left shift is a decrease in supply T-Shirts Price S1 S2 Be careful! a “down” shift in supply is an increase in supply Qty Determinants of Supply (TIN) • Technology • Input Prices • Number of Sellers If TIN changes => Draw a New S-Curve! Example: Event: Change in Supply IBM enters the Soda market Market for Soda Price S1 S2 TIN ↓ # of Sellers ↑ ↓ Supply ↑ Qty Worksheet Side #2