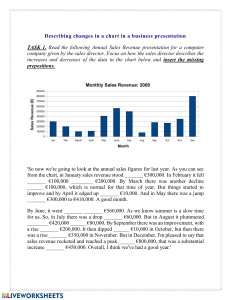
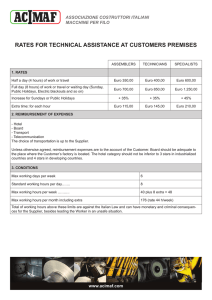
Chapter 14
advertisement

Chapter 14 Supranational Cooperation in the European Union 14.1 Introduction • Passports are needed to travel outside of the United States • Passports are needed when traveling between Countries • Supra – Latin prefix for “above” or “over” • EU – brings countries closer together/no need for passport (easier to live and work in) • 27 member countries Intro Continued • EU – removes boarders • Common form of money (Euro) • EU works hard to accomplish common goals (What goals) • Still remember they are separate countries 14.2 The Geographic Setting • • • • Centripetal Forces – bring things together Centrifugal Forces – away from one another Historically Europe has been torn apart by war Common Market – created in 1952, reduce or remove tariffs & rules of trade • European Union – 1993 formed • Nationalism – feelings of pride and loyalty toward one’s nation 14.2 Continued • EU works toward: 1.Promoting peace and prosperity/economic well-being 2.Creating jobs 3.Promote citizen’s rights 4.Preserve the Environment 5.Promote Freedom, Security, and Justice for members 14.3 Economic Cooperation in the EU Economic Forces that Unite the EU • Common Market (Single Market): 1.People have more choices 2.Prices on goods are lower 3.Workers can travel between countries to find work 4.Common Currency (Euro) adopted in 2002 – don’t have to exchange money • EU works to create jobs, develop resources, and make improvements like roads for trade 14.3 Continued Economic Forces that Divide the EU • All members don’t always agree on spent money and issues they face • Major Issues: 1.Western Europe cost of living is higher and paid more than Central and Eastern 2.EU spends more money on Central & Eastern to help bring their standard of living up 3.West fear of losing jobs to East, companies move East because it saves money 14.3 Continued Issues Continued: • Immigrants move to higher wage countries, natives come resentful • Not all EU countries adopted the Euro • Some countries were not allowed to adopt the Euro until they have stable economies • Economic benefits outweigh the costs 14.4 Political Cooperation in the EU • The EU encourages Political Cooperation EU political system: • has a common government • does not replace countries individual governments • operates above the individual governments • All members participate 14.4 Continued Unite Europe - EU Government works in 2 way: 1. Bring members together to focus on issues they all share 2. Encourages Europeans to think of themselves as citizens of Europe • EU Citizenship operates above home country • Gives certain benefits 14.4 Continued EU Political Bodies: 1.Council of the European Union – main decision making body (leaders from each country) 2.European Commission – executive body, proposes new laws, handle daily business 3.European Parliament – elected by citizens, pass laws, approve budget 14.4 Continued Divides Europe: • Countries expected to give up power to EU • Follow decisions even if they don’t agree • Population grows, so have differences – too many cultures and countries to please • National Identity fades away in the eyes of some members 14.5 Cultural Cooperation in the EU How EU Promotes Cultural Identity • Flag, European Anthem (played without words), Europe Day (May 9th) • Cultural Programs rotate featured city witch highlights cities culture, language programs 14.5 Continued Forces Working Against a European Cultural ID • Multiple Languages – info translate into 20 languages and all documents • National pride • Traditions – Ex) Czech food cooked slow, EU rules states no food served over 2 hours old