fmtr - jccornell.net
advertisement

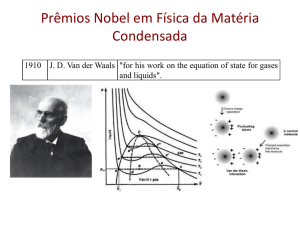
Muscles, Flight, and Temperature Regulation in Insects John Cornell Oxygen Consumption in some Animals Animal budgerigar resting flying ml O2/g/hr Animal ml O2/g/hr 4.5 - 3.3 21.9 Calypte rest hovering 10 42.4 pidgeon resting flying 0.9 11.9 Selaphorus rest hovering 14 85 shrew 7 - 11 Homo sapiens V02 max bats Lepidoptera rest flight 0.4 - 0.7 40 - 100 Schistocerca rest flying 0.6 10 - 30 5 2 Drosophila rest flight (Prosser, 1973) 1.7 21 Homo sapiens http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/ids_104_musclenerve_path/student_musclenerve/normal2.html Neurogenic (Synchronous) Muscles Pringle (1957) Okanagana vanduzeei an endothermic cicada Josephson & Young (1985) Pringle (1957) Okanagana vanduzeei Josephson & Young (1985) Tymbal muscle of Okanagana vanduzeei Josephson & Young (1985) Josephson & Young (1985) Josephson, Young (1987) Josephson, Young (1987) Myogenic (Asynchronous) Muscles Pringle (1957) (Josephson, Malamud, Stokes (2000) Josephson, Malamud, Stokes (2000) Josephson, Malamud, Stokes (2000) Flight Douglas (1981) Indirect wing muscles Pringle (1957) Insect wing movements from Wikipedia Chapman (1971) Vibrating halteres act like gyroscopes in dipterans Chapman (1971) Dragonfly direct wing muscles Chapman (1971) Wing beat frequencies in asynchronous flyers are determined in part by the resonant frequency of the wings. Forcipomyia sp. normal wing beat frequency 1046 Hz Forcipomyia sp. with clipped wings Sotavalta (1953) 2200 Hz Pringle (1957) Temperature Regulation Defined by source of heat Endotherm Exotherm Endotherm/Exotherm Type of temperature regulation Homeothermic Poikilothermic Heterothermic Method of regulation Physiological Behavioral Physiological/behavioral Dormant state Hibernation Torpor Heinrich (1974) Bombus vosnesenkii Bombus vosnesenskii Kammer & Heinrich (1974) Bombus vosnesenskii (Heinrich & Kammer (1973) Bombus vosnesenskii Heinrich & Kammer (1973) Heinrich (1974) Heinrich (1996) Kammer & Heinrich (1974) . Neoconocephalus triops http://www.texasento.net/triops.htm Neoconocephalus robustus Heath & Josephson (1970) Manduca sexta Manduca sexta Kammer (1980) What can you do with heat? Heinrich (1974) Heinrich (1996) Heinrich (1996) Literature Cited Chapman, R.F. (1971) The insects: structure and function. American Elsevier Publishing Company, Inc., New York. Douglas, M.M. (1981) Thermoregulatory significance of thoracic lobes in the evolution of insect wings. Science 211, 84-86. Heath J. E. & Josephson, R/K. (1970) Body temperature and singing in the katydid, Neoconocephalus robustus (Orthoptera, Tettigonidae). Biol. Bull, 272-285. Heinrich, B. (1974) Thermoregulation in endothermic insects. Science 185, 747-756. Heinrich, B. (1996) The thermal warriors: strategies of insect survival. Harvard University Press, Cambridge Mass Heinrich, b. & Kammer, A.E. (1973) Activation of the fibrillar muscles in the bumblebee during warm-up, stabilization of thoracic temperature and flight. J. exp. Biol., 58, 677-688. Kammer, A.E. (1981) Physiological mechanisms of thermoregulation in Insect thermoregulation, Bernd Heinrich, Editor. John Wiley & Sons, New York. Kammer, A. E. & Heinrich, B. (1974) Metabolic rates related to the muscle activity in bumblebees. J. exp. Biol., 61, 219-227. Josephson, R.K. (1987) Fiber Ultrastructure and contraction kinetics in insect fast muscles. (1987) Amer. Zool. 27, 991-1000. Josephson, R.K., Malmud, J.G. & Stokes, D.R. (2000) Asynchronous muscle: a primer. J. exp. Biol. 203, 2713-2722. Josephson, R.K. & Young, D. (1985) J. exp. Biol., 118, 185-208. Pringle, J.W.S. (1957) Insect flight. Cambridge University Press Prosser, C.L. (1973) Chapter 5, Oxygen: Respiration and metabolism. in Comparative Animal Physiology, third edition. C.L Prosser, Editor. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia Sotavalta, O. (1953) Recordings of high wing-stroke and thoracic vibration frequency in some midges. Biol. Bull. 104, 439-444. The End