File - Social Studies
advertisement

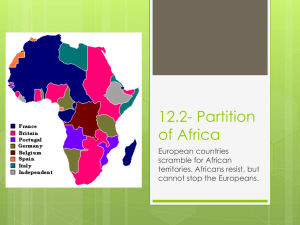
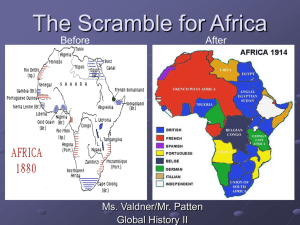
Case Study #2 Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) Outline Geography History Dictators Civil War Conflict Minerals Geography Brainstorm: What do you think the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) looks like? Geography Geography Second largest country in Africa ¼ the size of the USA Geography Located on the equator Midpoint between the poles Average temperature: 25 ° C Geography Congo River • Deepest river in the world • 3rd largest river in the world • 9th longest river in the world Geography Mt. Nyiragongo • Active volcano in the DRC • One of the most active in the world • One of the least studied because of the constant warfare in the region History Before we go into the history of the Democratic Republic of the Congo… we need to go back and review the history of globalization… History Phases of Globalization (Dominant Western Perspective) Phase One (2,000 BC - 1400): The Spread of Trade • Goods and ideas were spread by caravans, horses, & walking • Rise of Asian power • Land and sea routes are important (i.e. Silk Road) Phase Two (1400 - 1950): Discovery and Expansion • Helped by advances in shipping • Started with Christopher Columbus sailing to the Caribbean • Rise of European expansion & imperialism • Widespread industrialization with the Industrial Revolution Phase Three (1950 - present): Widespread Interconnectedness • Includes economic, social, political • Rapid growth of world markets • Instant communications • Rise of China and India as economic powers History Phases of Globalization (Dominant Western Perspective) Phase One (2,000 BC - 1400): The Spread of Trade • Goods and ideas were spread by caravans, horses, & walking • Rise of Asian power • Land and sea routes are important (i.e. Silk Road) Phase Two (1400 - 1950): Discovery and Expansion • Helped by advances in shipping • Started with Christopher Columbus sailing to the Caribbean • Rise of European expansion & imperialism • Widespread industrialization with the Industrial Revolution Phase Three (1950 - present): Widespread Interconnectedness • Includes economic, social, political • Rapid growth of world markets • Instant communications • Rise of China and India as economic powers During this second phase, the “Age of Discovery,” Europeans started exploring Africa… History ACTIVITY Draw three scenes – one for each of the phases of globalization. Draw the symbols, people, landscapes, and anything else you think you might see/have seen during each of the phases of globalization History The Scramble for Africa During the Age of Discovery, we saw Europeans establish settlements and trade posts along the coast of the African continent but there was little interest in the interior of Africa for many years…. What Changed? Why did people go to the interior? History The Scramble for Africa Trade • Increased European demand for raw materials unavailable in Europe, especially copper, cotton, rubber, cocoa, diamonds, and tea • As trade increased, Africa offered cheap materials, limited competition, and abundant raw materials Industrial Revolution • Industrialisation brought about rapid advancements in transportation and communication, especially in the forms of steam navigation, railways, and telegraphs Medical Advances • An effective treatment for malaria enabled vast expanses of the tropics to be accessed by Europeans Strategic Areas • Gathering strategic military bases and trade route access (often good bargaining items) The Suez Canal The first interior place to be thoroughly explored History The second place to be thoroughly explored… THE CONGO History Exploring the Congo King Leopold II of Belgium • King Léopold II of Belgium sparked the scramble for Africa • Why? He wanted more resources • Went to Africa and claimed the Congo region • Why? Rich in ivory and rubber – needed rubber for increasing amounts of tires… • Brutal ruler – villages had quotas for production and if they didn’t meet them, they would get their hands cut off • Used Propaganda - did not let knowledge of his atrocities get out and bribed publishers to write positive stories Is this Propaganda? Propaganda Things that are used to persuade people to accept a cause or a position by presenting only one side of an argument Congo labourers who failed to meet rubber collection quotas were often punished by having their hands cut off Leopold is rumored to have killed up to 16 million Congolese Indigenous people A father in the Congo looks at the severed hand and foot of his five year old daughter What do you think this cartoon is symbolizing? What do you think this cartoon is trying to say? Do you think Belgium was the ONLY Empire that wanted resources from Africa…? History The Scramble for Africa Was a period of invasion, occupation, colonization and annexation of African territory by European powers between 1881 and World War I in 1914 History The Scramble for Africa Berlin Conference (1884-1885): A conference among the world’s imperial powers to split up Africa… no African representatives were given a voice… or territory…. History Berlin Conference Fake Reason: “Humanitarianism“ • • • Real Reason: Establish Rules of Competition • • Condemnation of the slave trade Prohibition of the sale of alcoholic beverages and firearms in certain regions Expressed concern for missionary activities No nation was to stake claims in Africa without notifying other powers of its intentions. No territory could be formally claimed prior to being effectively occupied. Real Life • The competitors ignored the rules when convenient Why are we learning this? History: Activity Mission: Re-organize the classroom – what do you think we should do? Rules: Get into groups of five Read your handout & follow the directions Submit your proposal for the new classroom design History: Activity Debrief: How did you feel during this activity? Why did you compete with the other groups to claim the furniture? Do you think this was a fair way to claim the furniture? What might have been a better way? If unclaimed furniture remains, who should get it? Did anyone ask me how I thought the classroom should be designed? How does this activity compare to the Scramble for Africa? History: Activity Reflection The scramble for African territories among European powers was like… Create an analogy, finish the response, and create a drawing of the analogy MY ANALOGY!?! Does it work? The scramble for African territories among European powers was like… A game of Hungry Hungry Hippos! History: Worksheet In groups of two, analyze the worksheet “The Quest for Empire: Analyzing European Motives” For each source, determine the motivation for empire building (Gold, Glory, God) and provide an explanation for your choice Dictators After WWII, many imperial powers pulled out of Africa… This created a power-vacuum In many African countries, imperialist powers were replaced by home-grown dictators WHY? Dictators Power Vacuum? After WWII, the United Nations was created Maintain peace & promote cooperation Created a charter that did not fit with imperialism and owning nations… Dictators UN Charter: “…To develop friendly relations among nations based on respect for the principle of equal rights and self-determination of peoples, and to take other appropriate measures to strengthen universal peace…” Dictators Independence (June 30, 1960) A President & PM were put in place but there was unrest… Mobutu Sese Seko led a coup financed by the USA and Belgium (he opposed communism and they wanted to stop the spread of communism) Dictators Mobutu Mobutu declared himself head of state Elections were held where he was the only candidate Embezzled government funds and took international loans and placed them in his personal bank account Dictators Brainstorm! What do you think the word “dictator” means? What about “dictatorship?” Dictators Dictator: A ruler who has complete control over a nation Dictatorship: A type of government where a single person rules with absolute power. Civil War Rwandan Civil War: Tutsis v. Hutus Tutsis were in control of the Rwandan government 1.2 million Hutus fled to the Congo – killed Tutsis in the Congo Rwanda and Ugandan armies invaded the Congo… overthrew Mobutu and Laurent-Kabila was the new leader Civil war continued… Kabila was assassinated and his son, Joseph Kabila took over Joseph called for multilateral help from the UN Civil War Multilateral Assistance – United Nations Created a “United Nations Organization Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (MONUC)” Negotiated a cease-fire agreement Oversaw the country’s first free and fair elections – Joseph Kabila won Fighting still continues as different forces (rebel forces, Rwanda, etc.) try to gain control of the Congo’s rich resources March 2013: The UN has given the peace-keeping organization orders to “neutralize” and “disarm” rebel groups in the resourcerich east of the country… To date, over 5 million people have died… Conflict Minerals What’s so valuable about Congo’s resources? Conflict Resources Brainstorm! What is everything you can think of that is related to cell phones? Conflict Resources Brainstorm! What is everything you can think of that is related to guns? Conflict Resources How do you think these might be related? Conflict Minerals Conflict Minerals Documentary: Blood in the Mobile Conflict Minerals Calculating the TRUE cost of a cell phone Questions to Research & Answer: 1. 2. 3. 4. How are our cell phones linked to minerals in the Congo? Why are the Congo’s minerals called “conflict minerals?” How have conflict minerals have damaged Congo’s environment? Answer the following questions about life in the Congo: a) Describe the life a mine worker in the Congo. b) Where does the Congo rank on the Human Development Index? Explain what this index is and why you think the Congo might have its ranking. c) How many people are killed each month in the Congo because of conflict minerals? d) How has rape been used as a weapon in the Congo? 5. Is there any legislation in place to protect the Congo and its people? (Hint: Look into the Dodd-Frank law on conflict minerals) 6. Look up the term “sustainable prosperity.” Do you think the Congo’s conflict minerals are an example of sustainable prosperity? Why or why not? Quiz Review Terms to know: Phases of Globalization (Age of Discovery) Scramble for Africa Berlin Conference Annexation King Leopold Rubber War Propaganda Humanitarianism Dictator/Dictatorship United Nations Conflict minerals