Tammy Murphy
Physical Science
D. Phillips, Spring 2011
EMPACTS Project
The most important goal for the adult learner
is to be able to use and apply the skill of
converting within the metric system that is
learned in an academic setting and be able to
apply it to real-life situations.
Developed new ways to present how to
convert units within the metric system to the
adult learner.
Expanded on the knowledge of measurement
that the learner already understood.
Increased the student’s ability to apply this
knowledge to real-life situations.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Digital Camera
Phone (Texting and calling)
Computer
Internet
E-mail
Microsoft Power Point
Microsoft Word
The teacher will use the PowerPoint
presentation to explain the Metric System.
The first activity on the presentation is the
Manipulative Activity.
(This is the 1st slide on the classroom presentation…)
The decimal measuring system based on the meter, liter,
and gram as units of length, capacity, and weight or
mass
The metric system is in use by 95% of the world
The metric system is universally used in the sciences
The only country in the world that does not utilize the
metric system is the United States
(2nd slide of the classroom presentation…)
There are three basic units of metric measure
that the adult learner will use in real-life
situations:
meter (m) - length
gram (g) - mass or weight
liter (L) - volume
(3rd slide of the classroom presentation…)
Many disciplines use the metric system, such as
pharmacology, chemistry, nursing and
astronomy. For example, the average distance
between the moon and the earth is 384,403
kilometers (238,857 miles). When nurses
calculate how much an infant takes from a
bottle, they do it in cubic centimeters. Thirty cc's
equals about an ounce.
(4th slide of classroom
presentation…)
Ladder Method
1
2
KILO
1000
Units
HECTO
100
Units
3
DEKA
10
Units
DECI
0.1
Unit
Meters
Liters
Grams
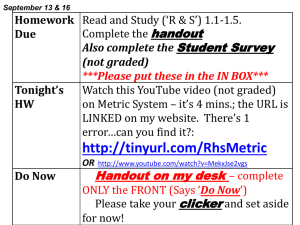
How do you use the “ladder” method?
1st – Determine your starting point.
2nd – Count the “jumps” to your ending point.
3rd – Move the decimal the same number of
jumps in the same direction.
CENTI
0.01
Unit
MILLI
0.001
Unit
4 km = _________ m
Starting Point
Ending Point
How many jumps does it take?
4. __. __. __. = 4000 m
1
2
3
(5th slide of classroom presentation…)
An easy way to remember the metric units of measure is
to remember the sentence:
King Henry died ___ drinking chocolate milk!
(Poor guy!!!)
kilo- (1000)
hecto- (100)
deka- (10)
deci- (0.1)
centi- (0.01)
milli- (0.001)
Manipulative Activity
(6th slide of classroom
presentation)
Try these conversions using the ladder method.
1000 mg = _______ g
1 L = _______ mL
160 cm = _______ mm
14 km = _______ m
109 g = _______ kg
250 m = _______ km
Compare using <, >, or =.
56 cm
6m
7g
698 mg
(7th slide of classroom
presentation)
Independent Practice
Write the correct abbreviation for each metric unit.
1) Kilogram _____
4) Milliliter _____
7) Kilometer _____
2) Meter _____
5) Millimeter _____
8) Centimeter _____
3) Gram _____
6) Liter _____
9) Milligram _____
Try these conversions, using the ladder method.
10) 2000 mg = _______ g
15) 5 L = _______ mL
20) 16 cm = _______ mm
11) 104 km = _______ m
16) 198 g = _______ kg
21) 2500 m = _______ km
12) 480 cm = _____ m
17) 75 mL = _____ L
22) 65 g = _____ mg
13) 5.6 kg = _____ g
18) 50 cm = _____ m
23) 6.3 cm = _____ mm
14) 8 mm = _____ cm
19) 5.6 m = _____ cm
24) 120 mg = _____ g
After the students have completed the
Independent Practice “Metric Conversions
Worksheet ” the teacher will ask about the
process by which they knew how to complete
the worksheet. The teacher will use this
group discussion as an assessment tool to
assess each student’s understanding of
metric conversion.
Compare using <, >, or =.
63 cm ___ 6 m
536 cm ___ 53.6 dm
5 g ___ 508 mg
1,500 mL ___1.5 L
43 mg ___ 5 g
(8th slide of classroom presentation)
3.6 m ___ 36 cm
•
Review worksheets
•
Review “Ladder System” of metric
conversions
•
Students will demonstrate how to convert
metric units
Presented “Metric conversions for the adult
learner” to Ms. Phillip’s PHSC M/W class on
Wednesday, April 20, 2011.
The adult student learners in this class were
very cooperative and learned a new skills that
they will be able to apply to real-world
situations.
•
Success = observing student progress and their
understanding of the concepts taught
•
Successful due to feedback from manipulative
activity
•
The independent practice reflected their
comprehension of the subject matter
Demonstrating “Ladder
System” to adult
learner classroom
•
Students did well on all of the activities
•
Students were able to use the “ladder system” to
convert units of metric measures
•
Students were able to work independently to make
their own comparisons and convert metric
measures
•
Group collaboration
•
Interacting with teachers
•
Becoming proficient within my topic
•
Group efficiency with time and organization
•
Improving teaching abilities and gaining
experience in the classroom
•
Improving technology skills
This lesson plan can be used in any adult
learner classroom to teach metric
conversions and
Dictionary.com, n.d. Retrieved April 25, 2011 from
http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/metric+system
Ehow.com, n.d. Retrieved April 25, 2011 from
http://www.ehow.com/how_5864935_use-metric-systemreal-life.html
Michigan Department of Labor and Economic Growth. n.d.
Retrieved May 10, 2011, from http://www.michigan.gov
The Science Spot, n.d. Retrieved May 10, 2011, from
http://sciencespot.net/Pages/classmetric.html#Anchor14210
The Science Spot, n.d. Retrieved May 10, 2011, from
http://sciencespot.net/Media/metric_metconv.ppt
A big thank you to Ms. Phillips and her
Physical Science M/W adult learner class for
allowing me to present a lesson on metric
conversions. I had a lot of fun teaching this
lesson!