File
advertisement

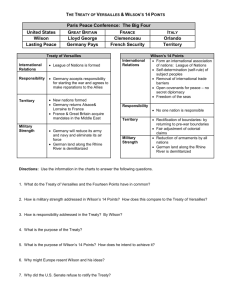
Were the Peace Treaties (1919-1923) fair? What were the motives and aims of the Big Three at Versailles? Why did all the victors not get everything they wanted? What was the impact of the peace treaty on Germany up to 1923? Could the treaties be justified at the time? The Big Three: summarise your reading to describe what these 3 men want David Lloyd George Georges Clemenceau Woodrow Wilson LEADER WILSON LLOYD GEORGE CLEMENCEAU COUNTRY ATTITUDE TOWARDS GERMANY MAIN AIMS REACTION Source analysis 1) Study source 1 on page 7 2) Answer questions 1 – 2 making sure you can explain your reasons referring to examples from the picture. 3) Study source 2 and 3 on page 8 a) In what ways are the sources different? b) In what ways are they similar? c) Can you give reasons why they may be different? (look at the audience) Homework: Due Wednesday 10th September Who said what? Use the task on page 11 to explain which of the leaders would have said what and to whom? You could design it like: Statement Who? How do I know? A Wilson to Lloyd George Because Wilson wanted SD and Lloyd George wanted to protect his empire Woodrow Wilson I’ll have my fourteen points please! Prediction Problems I predict for making the Treaty of Versailles are…… “The conduct of Germany is almost unexampled in human history . . . Not less than seven million dead lie buried in Europe . . Because Germany saw fit to gratify her lust for tyranny by resort to war . . .Justice is the only possible basis for the settlement of the accounts of this terrible war.” Clemenceau’s speech to the Paris Peace Conference 1919 Who said this? Germany must pay to the last penny. We want a peace which will be just not vindictive. Above all we want to protect the future against a repetition of the horrors of this war. 1918 – Lloyd George The world must be free from democracy. We have no selfish ends to serve. We require no conquest, no dominion. We seek no indemnities for ourselves, no material compensation. 1917 – Woodrow Wilson Now think . . . • How do Clemenceau’s views differ from Woodrow Wilson’s and Lloyd George’s? • Look back at your 14 points – tick off which ones Wilson achieved in the Treaty of Versailles. Answer the exam question below The Versailles Treaty created disagreement and hostility. (a)What did Wilson hope to achieve from the peace settlement of 1919–20? [4] Two explained points Peer Marking • Look at the mark scheme in front of you. • Look through your partner’s answer and decide what you would give them. • Write down: – What they did well – What they could do better Example exam question: Why did Clemenceau and Lloyd George disagree over how to treat Germany? [6] Two reasons explained in detail! Task: Read through the sheets highlight any points that you think are important for answering this question Peer Marking • Look at the mark scheme in front of you. • Look through your partner’s answers and decide what you would give them. • Write down: – What they did well – What they could do better Germany accepts full responsibility for war. German army cut to 100,000 soldiers (that’s really small) German Navy only allowed six battle ships No air force League of nations was set up. It was hoped that countries would talk rather than fight Germany had to pay money (reparations) of 6600 million pounds Article 231 of the treaty said ‘Germany accepts responsibility for causing all the loss and damage’ Germany was required to pay compensation for all the damage caused No submarines Read the statements above and separate them into Land, Army, Money, Blame. Reactions to the Treaty • Read through your views of the treaty. • Create a speech in pairs to explain how you feel about the treaty after it is signed! Think! What problems could arise from this situation? An ‘Unhappy Compromise’? Did do they do the best they could at the time? Was Germany punished too harshly?