Lecture Summary
advertisement

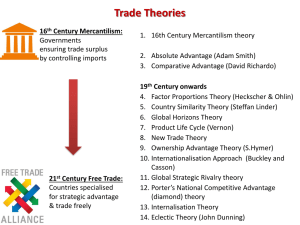
Lecture Highlights - Roles of MNC The global ones are mainly high tech companies Many are financial institutions or owned by powerful people Key Role is providing FDI, usually via: • M&A • Equity holding • Financial Restructuring + impacts on locations, regionally or globally Code of Conduct Principles on how they comply to good governance principles relating to Human Rights Labour Equality Environment Sustainability Anti Corruption Why MNCs invest in FDI? Country Attractiveness Marketing Factors Trade Barriers Profit Attractions Cost Factors Investment Supporting Host Country Cost-Benefits Host Country Costs • Industrial dominance • Exploitation of raw materials and cheap labour • • • Bribery and corruption Interference in political matters Technological dependence • • Disturbance of economic plans Cultural change • Interference by home government through MNC • Degree of government control may be less than intended Host Country Benefits • Improves Gross Domestic Product via repatriation of profits, royalties & fees • Increases export opportunities • Political advantages • Job losses • • Net effect on imports & exports Creating competitors Allegations against MNCs 1. Control of technology transfer prices Inappropriate technology introduction to host country 2. Skip the country when regulation sets in 3. MNC control systems exert neo-colonist relationship with host country POOR Corporate Social Responsibility 4. Expose country sensitive information in global intelligence networks 5. Produce products that do not create or contribute social value to host country 6. Undermining national labour interests 7. Avoid paying taxes 8. Give best jobs to own boys, especially in HQ circles Code of Conduct Principles on how they comply to good governance principles relating to Human Rights Labour Equality Environment Sustainability Anti Corruption Lecture Highlights - Trade Theories 1. 16th Century Mercantilism theory 2. Absolute Advantage (Adam Smith) 3. Comparative Advantage (David Richardo) 19th Century onwards 4. Factor Proportions Theory (Heckscher & Ohlin) 5. Country Similarity Theory (Steffan Linder) 6. Global Horizons Theory 7. Product Life Cycle (Vernon) 8. New Trade Theory 9. Ownership Advantage Theory (S.Hymer) 10. Internationalisation Approach (Buckley and Casson) 11. Global Strategic Rivalry theory 12. Porter’s National Competitive Advantage (diamond) theory 13. Internalisation Theory 14. Eclectic Theory (John Dunning) Individual /Pair Presentation The Rise of Bangladesh’s Textile Trade Case Study Bangladesh's textile industry – 1.51 m https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CxKlnkp9SvQ Ethnical Textiles – 3.31m https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A3xrXC9wcZg https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hcYYLmcxavA Source: The Hindu, Dec 20, 2012 Martin Jacques - When China Rules the World – 10.04 m https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Og8zBhDDkEQ 1. Why was the shift to a free trade regime in the textile industry good for Bangladesh? 2. Who benefits when retailers in the US source textiles from low-wage countries suh as Bangladesh? 3. What international trade theory or theories best explain the rise of Bangladesh as a textile exporting powerhouse? 4. How secure is Bangladesh ‘s textile industry from foreign competition? What factors could ultimately lead to a decline? The Benefits During Lecture, we saw the POSITIVES: 1. 2. 3. 4. Capital Formation Technology Transfer Regional & Sectoral Development Internal Competition & Entrepreneurship 5. Favourable Effect on Balance of Payments 6. Increased Employment Bangladesh's textile industry – 1.51 m https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CxKlnkp9SvQ At What Costs? At Whose Costs? Bangladesh has the advantage of not being China The argument focus is Cost Advantage Bangladesh Low cost factors China China Is the largest world’s exporter sunk FDI But still MNC have concerns of increasing cost factors Martin Jacques - When China Rules the World – 10.04 m https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Og8zBhDDkEQ The long version – 1.34 hrs https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3G1EyvRZmOs The Costs During Lecture, we saw the NEGATIVES: 1. Industrial dominance 2. Exploitation of raw materials + cheap labour 10. Technology transfer may be too expensive or inappropriate (eg old) 11. Can move out when country regulates 3. Bribery and corruption 4. Interference in political matters 5. Technological dependence 6. Disturbance of economic plans 12. Products are for overseas markets and may not benefit local social needs or value 7. Cultural change 13. MNC’s home country’s labour /employment interests are undermined 8. Interference by home government 14. Avoid taxes through MNC 9. Degree of government control may 15. Best jobs given to MNC’s privileged people be less than intended Ethnical Textiles – 3.31m https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A3xrXC9wcZg https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hcYYLmcxavA