Bodies of Water
advertisement

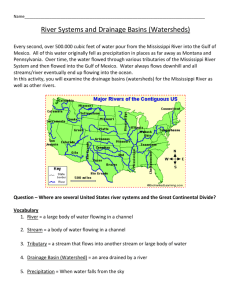
Bodies of Water What are some of the different bodies of water in the United States? • Identify and locate major bodies of water in the United States • Explain why many cities in the United States are located near rivers. Lesson Vocabulary inlet – any area of water extending into the land from a larger body of water. gulf – are large inlets. sound – is a long inlet that separates offshore islands from the mainland. tributary – a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or river. river system – is made up of rivers and tributaries. A siver system drains and carries water away from the land around it. drainage basin – the land drained by a river system is its drainage basin. fall line – is a place where the land drops sharply. Chapter 1, Lesson 3 Places to Know Gulf of Mexico Great Lakes Great Salt Lake Mississippi River Inlets and Gulfs Chapter 1, Lesson 3 Our Largest Lakes How do the Great Lakes and the Great Salt Lake differ? The Great Salt Lakes contain freshwater. The Great Salt Lake contains salt water. Some people consider the Great Salt Lake a sea – an inland body of water containing salt. Chapter 1, Lesson 3 Bodies of water in the United States Inland and Ocean What are some major inland bodies of water? What are some major ocean inlets? What rivers are part of the Mississippi River system? Chapter 1, Lesson 3 tributary – a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or river. river system – is made up of rivers and tributaries. A river system drains and carries water away from the land around it. drainage basin – the land drained by a river system is its drainage basin. Rivers The Mississippi and its tributaries create the largest river system in the United States. Chapter 1, Lesson 3 The Chesapeake Bay Chapter 1, Lesson 3 What is the difference between a river and a river system? A river system drains, or carries water away from, the land around it. Rivers and Cities Many US cities were founded near a river, so these cities could be reached by boat, long before roads and railroads connected these to other cities. Rivers were vital for city transport, trade, and defense. Examples: New York City (The Hudson River) St. Louis (Mississippi River) Albany (Hudson River) Richmond (James River) Augusta (Savannah River) Portland (Columbia River) Hartford (Connecticut River) Louisville (Ohio River) Chapter 1, Lesson 3 Fall Line – a place where the land drops sharply, causing rivers to form waterfalls or rapids. People once used fastmoving water to power machines. We now use it to make electricity. The Continental Divide of North America How do rivers east and west of the Continental Divide differ? Eastern rivers flow into the Atlantic Ocean or Gulf of Mexico. Western rivers flow into the Pacific Ocean. Summary 1.3 - The United States has different bodies of water. Its largest lakes are the Great lakes. Rivers drain land and are often used for transportation. The Continental Divide separates rivers that flow into the Atlantic from rivers that flow into the Pacific.