Level 1
advertisement

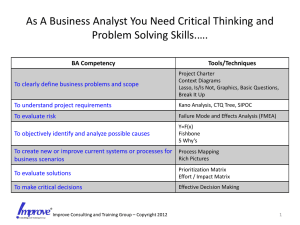
For today’s audio You can use your computer’s microphone and speakers OR Call: (530) 881-1212 Meeting ID: 893-795-560# on your telephone Reminders This session is being recorded. If you have considerable background noise, please mute your line and do not put us on hold. Participant Engagement Phone lines will remain open. Polls Facilitator will ask you directly to answer questions. Use the chat box for comments or questions. Setting Strategic Priorities Brought to you by: CiMH and Laree Kiely, PhD The Kiely Group www.kielygroup.com Your Presenters Donna Wigand Laree Kiely If it feels like this, it’s about time and it’s about time!! The Essence of Prioritizing is: To make the most amount of impact and progress toward the organization’s goals with the least amount of effort • Skopec and Kiely, Taking Charge The Essence of Prioritizing is: To make the most amount of impact and progress toward the organization’s goals with the least amount of effort • Skopec and Kiely, Taking Charge and The Essence of Prioritizing is: To make the most amount of impact and progress toward the organization’s goals with the least amount of effort • Skopec and Kiely, Taking Charge and To be ready for whatever is coming!! Simple Prioritization • At a simple level, you can prioritize based on time constraints, on the potential profitability or benefit of the task you're facing, or on the pressure you're under to complete a job. Simple Prioritization • At a simple level, you can prioritize based on time constraints, on the potential profitability or benefit of the task you're facing, or on the pressure you're under to complete a job: • Prioritization based on project value or profitability is probably the most commonly-used and rational basis for prioritization. Whether this is based on a subjective guess at value or a sophisticated financial evaluation, it often gives the most efficient results. Simple Prioritization • At a simple level, you can prioritize based on time constraints, on the potential profitability or benefit of the task you're facing, or on the pressure you're under to complete a job: • Prioritization based on project value or profitability is probably the most commonly-used and rational basis for prioritization. Whether this is based on a subjective guess at value or a sophisticated financial evaluation, it often gives the most efficient results. • Time constraints are important where other people are depending on you to complete a task, and particularly where this task is on the critical path of an important project. Here, a small amount of your own effort can go a very long way. Simple Prioritization • And it's a brave (and maybe foolish) person who resists his or her boss's pressure to complete a task, when that pressure is reasonable and legitimate. Tactical Activities Must Align to Strategic Goals and Outcomes What is your typical daily pattern? What is your typical daily pattern? • Do the hard, most important, thinking stuff at your peak time of the day What is your typical daily pattern? • Do the hard, most important, thinking stuff at your peak time of the day • Save the easier stuff for when you are at your lowest physical or mental energy Make a List Why am I doing this? • To what does it contribute? Leading the Change to Priority-Based Activities Becoming a “why” culture: • The “why” Always the “why” • Why the “why”? • A focus on curiosity versus certainty • Questions rather than answers • And the “who” Always the “who” 5 Levels of “Why” • Ask “why” 3 to 5 times to get to the core issue • Or “click down” on one of their words • Use their words to gather more meaning • When they start to struggle with the answer, you are close to the core • Practice SILENCE—Let them think • If you go down the wrong path, back up and start down another Prioritization Matrices Michael Brassard, who wrote The Memory Jogger II in 1994 said a prioritization matrix is said to: • Quickly surface basic disagreements so that they may be resolved up front. • Force a team to focus on the best things to do, not everything they could do, dramatically increasing the chances for implementation success. • Limit hidden agendas by surfacing the criteria as a necessary part of the process. • Increase the chance of follow-through because consensus is sought at each step in the process (from criteria to conclusions). • Reduce the chances of selecting someone’s pet project. Prioritization Matrices To be used when: • There are many tactical activities and there isn’t enough time to do them all • We are being given tasks to do from multiple sources • Resources are limited • Tasks are competing • We don’t know why we are doing what we are doing Make a list of everything… …That you do or need to do or will be doing • Big and small • One time only and repetitive Level 1: The Urgent Versus Important Matrix Where do you spend the largest percentage of your time? Level 1: The Urgent Versus Important Matrix Level 2: The High Versus Low Model HIGH IMPACT Do first: biggest impact, easiest HARDER EASIER Do last: lowest impact, hardest LOW IMPACT Strategic Priorities Must Accomplish Strategic Goals and Outcomes For leaders, it is critical that our work is adding up, not just stacking up • Organization’s purpose: why do we exist • For whom do we exist? THE ARCHITECTURE OF STRATEGY Why do you exist? For whom? How do you define success? THE VALUE CLUSTER YOU Immediate consumer Intermediate consumer Etc. Etc. Ultimate consumer The Value Chain YOU Immediate consumer Intermediate consumer Etc. The Value Cluster Etc. Ultimate consumer What’s Coming? The big ticket items • The Triple Aim • Payment reform • Meaningful use • Other unknowns?? Prioritization Matrices: Complexity Level 3 Criteria Method Steps: 1. Agree on the ultimate goal to be achieved in a clear, concise statement Complexity Level 3 Criteria Method Steps: 1. Agree on the ultimate goal to be achieved in a clear, concise statement 2. Create the list of criteria Complexity Level 3 Criteria Method Steps: 1. Agree on the ultimate goal to be achieved in a clear, concise statement 2. Create the list of criteria 3. For each criterion, we assign a value of 1 (lowest) to 5 (highest) Complexity Level 3 Criteria Method Steps: 1. Agree on the ultimate goal to be achieved in a clear, concise statement 2. Create the list of criteria 3. For each criterion, we assign a value of 1 (lowest) to 5 (highest) 4. See which total is highest and that should inform how you spend your time Complexity Level 3 Criteria Method Steps: 1. Agree on the ultimate goal to be achieved in a clear, concise statement 2. Create the list of criteria 3. For each criterion, we assign a value of 1 (lowest) to 5 (highest) 4. See which total is highest and that should inform how you spend your time 5. Decide how this will manifest itself on a daily, weekly, monthly calendar for each person involved Complexity Level 3 Criteria Method Steps: 1. Agree on the ultimate goal to be achieved in a clear, concise statement 2. Create the list of criteria 3. For each criterion, we assign a value of 1 (lowest) to 5 (highest) 4. See which total is highest and that should inform how you spend your time 5. Decide how this will manifest itself on a daily, weekly, monthly calendar for each person involved 6. Then treat like a project plan with due dates and responsible people Complexity Level 3 Criteria Method Project #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 Criterion Criterion Criterion Criterion Criterion Criterion 1 2 3 4 5 6 TOTAL Complexity Level 3 Criteria Method Example Project Family members involved Costs money Amount of time Stress level Complexity Involves outside help TOTAL #1 Packing to move 5 1 5 4 4 1 20 #2 Getting new house ready 1 3 3 3 3 1 14 #3 Closing out bills to old house 1 1 2 1 1 1 7 #4 Buying new furniture 4 5 2 1 2 2 16 #5 Unpacking in new house 5 2 5 5 5 1 23 1=Low; 5=High HELPS WITH SEQUENCING AND SETTING ASIDE THE APPROPRIATE AMOUNT OF TIME AND RESOURCES Complexity Level 4 Weighted Criteria Method • Carpenter Model: An electronic version of his template and description of how to use it is available at: http://www.isixsigma.com/index.php?option=com_k2&v iew=item&id=253:prioritization-matrix-is-made-easierwith-a-template&Itemid=224 • The Carpenter model is a more complex model to use. You can always create your own version of his model, using different weights or values. CRITERIA WEIGHT 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 X 0.20 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.20 0.80 0.01 2 Service costs 5.00 X 0.20 0.20 0.10 0.20 5.00 10.70 0.08 3 Ease of use: administration 10.00 5.00 X 1.00 1.00 0.20 10.00 27.20 0.20 4 Ease of use: user 10.00 5.00 1.00 X 5.00 5.00 10.00 36.00 0.27 Conforms to open web 5 standards 10.00 10.00 1.00 0.20 X 0.20 1.00 22.40 0.17 6 Scalable 10.00 5.00 5.00 0.20 5.00 X 5.00 30.20 0.23 Directory-based access 7 controls 5.00 0.20 0.10 0.10 1.00 0.20 X 6.60 0.05 0.00 0.00 X 0.00 0.00 133.90 1.00 Little to no customization 1 necessary Complexity Level 4 Weighted Criteria Method 8 CRITERIA #8 8 X 9 CRITERIA #9 COLUMN TOTALS 9 TOTAL DECIMAL VALUE 50.00 25.40 7.40 1.80 12.20 5.90 31.20 0.00 0.00 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 X 10.00 5.00 5.00 20.00 0.44 2 EMG 0.10 X 10.00 5.00 15.10 0.33 3 SUN 0.20 0.10 X 10.00 10.30 0.22 4 NEXID 0.20 0.20 0.10 X 0.50 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 X 0.00 0.00 0.00 45.90 1.00 Little to no customization necessary 1 MicroLog 5 SELECTION #5 X 6 SELECTION #6 X 7 SELECTION #7 X 8 SELECTION #8 X 9 SELECTION #9 COLUMN TOTALS 0.50 0.50 15.10 20.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 TOTAL DECIMAL VALUE Complexity Level 4 Weighted Criteria Method Complexity Level 5: Full Analytical Criteria Method Full Analytical Criteria Method Full Analytical Criteria Method Managing Multiple, Sometimes Competing, Demands • Being given tasks from above – Enlisting their help – Your strategic assessment • Delegating tasks to people deeper in the organization – Helping them decide – Up-leveling their skill sets Delegate: The Authority Scale Levels of AUTHORITY and AUTONOMY Level 7: Team/Individual researches, determines options, chooses option, acts, and does not report to manager Level 6: Team/Individual researches, determines options, chooses option, acts, reports only failure to manager Level 5: Team/Individual researches, determines options, chooses option, acts, reports results to manager Level 4: Team/Individual researches, determines options, chooses option, manager gives final approval Level 3: Team/Individual researches, determines options, makes recommendation, manager decides Level 2: Team/Individual researches, suggests options, manager chooses Level 1: Team/Individual researches, manager decides The Overall Job Expectancy Scale Most Independent Level 6: Act independently, no need to report Level 5: Act independently, report routinely Level 4: Act independently, report immediately Level 3: Recommend action, do whatever directed Level 2: Ask what to do Level 1: Wait to be directed Least Autonomous “Whatever you can do, or dream you can, begin it. Boldness has genius, power, and magic in it” -goethe- Bottom Line: One of the main reasons we have managers who oversee us is to help us with prioritization. Why might that be the case? The same goes for the people you supervise Making Best Use of Your Time and Resources • Prioritization is the essential skill you need to make the very best use of your own efforts and those of your team. It's also a skill that you need to create calmness and space in your life so that you can focus your energy and attention on the things that really matter. • It's particularly important when time is limited and demands are seemingly unlimited. It helps you to allocate your time where it's most-needed and most wisely spent, freeing you and your team up from less important tasks that can be attended to later... or quietly dropped. • With good prioritization (and careful management of reprioritized tasks) you can bring order to chaos, massively reduce stress, and move towards a successful conclusion. Without it, you'll flounder around, drowning in competing demands. Why does it matter? Because time is a precious resource Since every activity you do needs to align with your organization’s purpose, goals and objectives, start by always asking: How does this? Priority 1 Priority 2 Priority 3 Priority 4 Help us get here? How does this? Priority 1 Priority 2 Priority 3 Priority 4 Agency’s Strategic Goals …to ultimately get us here: …to ultimately get us here: Thank You!! Let us know how we can help CiMH and The Kiely Group