Charging by Friction, Conduction, and Induction
advertisement
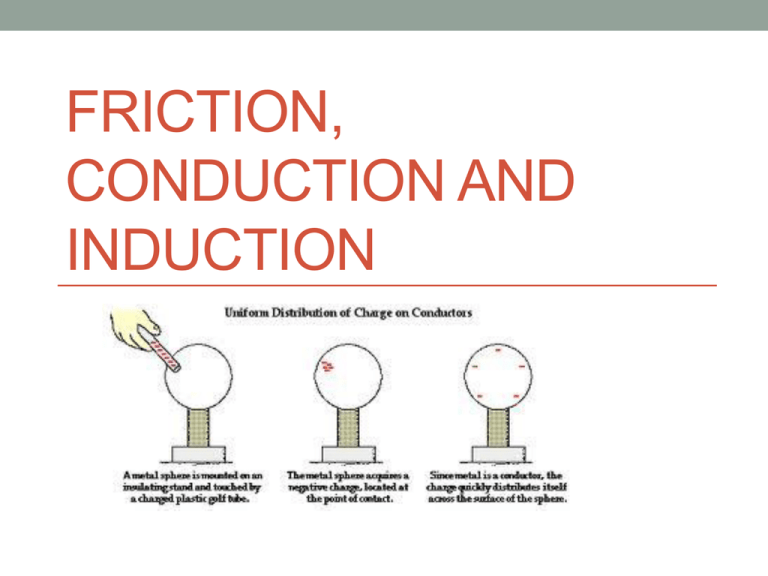
FRICTION, CONDUCTION AND INDUCTION How do you charge an object? • There are three ways to charge an object: 1. Charge by Friction 2. Charge by Conduction 3. Charge by Induction How do you measure “charge” • The unit of measure for electrical charge is the Coulomb (C). In equations it is symbolized by a “q” • Eg: q = 900C • One Coulomb is equal to the charge of 6.25 X 1018 electrons (-) or protons (+). • That is to say, one Coulomb has 6.25 X 1018 electrons. Charging Objects • Most objects start out electrically neutral, but by CHARGING an object you create an imbalance in the number of electrons and protons; the object is then charged and is either positive or negative. • You can charge an object through: • Friction – the transfer of electrons from one object to the other • Conduction – by having two objects TOUCH each other and transfer electrons from one object to the next. • Induction – By inducing electrons to move from one object to the other. Charging by Friction • When two neutral objects are rubbed against each other, one object may pull electrons away from the other creating one positive object and one negative object. Electrostatic Series: All objects begin neutral & can positively or negatively charged become A positively charged object has more positives than negatives A negatively charged object has more negatives than positives Electrostatic Series: • Electrostatic series is a list that ranks objects’ ability to take negative charges Rubber Ebonite Polyethylene Cotton Silk Wool Glass Acetate Fur / Hair Items at top take negatives Items at bottom lose negatives Items at top take negatives Your cat rubs against a rubber balloon. What will be the charge on the balloon? Your cat’s fur? Rubber Rubber Ebonite Polyethylene Cotton Silk Wool Glass Acetate Fur / / Hair Fur Hair Rubber balloon becomes negative Negatives Cat’s fur becomes positive Items at top take negatives In a lab, you take a piece of neutral wool & neutral polyethylene & rub them together. What will be their charges? Rubber Ebonite Polyethylene Polyethylene Cotton Silk Negatives Wool Wool Glass Acetate Fur / Hair Polyethylene balloon becomes negative Wool becomes positive In a lab, you rub a piece of cotton & ebonite together. Then you rub a piece of silk & wool together. You then bring the charged piece of cotton & the charged piece of silk together. What will happen? + + Rubber Ebonite Polyethylene Cotton Silk Wool Glass Acetate Fur / Hair Cotton is + Silk is - They would ATTRACT You rub your hair with a balloon. Explain using words & pictures, why your hair “sticks up”. 1st Hair & balloon are both neutral 2nd Rubber balloon takes negative charges from the hair. So, balloon becomes negatively charged & hair becomes positively charged 3rd Since hair is positive & like charges repel, hair sticks up!!! _ +_ _ + + _+ + _ Charging by Conduction • An object can be charged by touching it with another object that already has a charge. The resulting object will then have the same charge but weaker in strength than the original object. Charging by Conduction • This image shows how a positive charged object alters the charge on the globe via conduction. Charging by Conduction • This image shows how a negative charged object alters the charge on the globe via conduction Charging by Induction • Objects do not touch (one is charged, one is neutral) • Proximity of the charged object causes (induces) the charges in the neutral object to separate. Charging by Induction • This image shows how a negative charged object alters the charge on the globe via induction. Charging by Induction • This image shows how a positive charged object alters the charge on the globe via induction. • Two types of charges – positive (+) & negative (-) • “Opposites Attract” • “Like Repel” • Items at the top of the electrostatic series list take negative charges • Only negative charges move • Three methods to charge an object: friction, conduction, induction. These three methods are what cause static electricity.