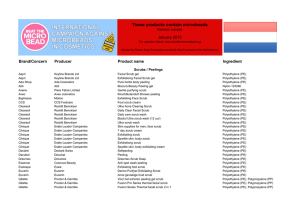
SMAC Project
advertisement

Product Overview Manufacture of product Product Description Product Uses Exposure Potential Health Information Environmental Information Physical Hazard Information Regulatory Information Additional Information Polyethylene resins are polymers of ethylene or co-polymers of ethylene and an alpha-olefin monomer such as butene, hexene or octene. Polyethylene is not known to occur naturally and are considered to be safe for humans and environment in known intended uses CAS No: 25087-34-7 Ethylene/Butene-1 Copolymer CAS No: 25213-02-9 Ethylene/Hexene-1 Copolymer CAS No: 9002-88-4 Ethylene Homopolymer EQUATE manufactures Polyethylene using UNIPOL gas phase process wherein ethylene and comonomer react as gases at low pressure, in presence of catalyst using fluidiaized bed conditions to produce granular products. EQUATE produces Polyethylene in Kuwait Polyethylene resins are odorless white granules or pellets. HDPE resin is made from ethylene and hex ene-1 while LLDPE resin is made from ethylene an d butene-1 The molecular structure of HDPE is a repeating (-CH2-CH2-)n with a slight degree of branching. Th e molecular structure of LLDPE is mostly linear cop olymer backbone with some short chain branching. Resins are classified by Melt Index, Molecular weig ht and branching. The Melting Point of HDPE is 133 C The Melting Point of LLDPE is 125 C Typical use of Polyethylene resins are the following -Film: Industrial and Consumer packaging -Injection Molding: Household articles -Blow Molding: Container for chemicals -Pipes: Transporting water and liquids -Wire & Cable: Telecom and power cables -Sheet: Geomembrames -Others: Resellers, Compounders & Distributors Raffia Injection Molded Crates Carry bags HIC Bottles Large Drums Non pressure pipes Agriculture Carry bags Heavy duty sacks Drip Irrigation Food Packaging Packaging Workplace Exposure Employees producing or processing polyethyle ne can be exposed to resin dusts and irritating fumes while processing polymer resin Spilled polyethylene pellets pose slipping hazard Good ventilation, use of proper PPE and good house keeping minimize these exposure hazard In workplace processing of polyethylene, contact with dusts and fumes may cause eye, skin and respiratory irritation Contact with hot molten material may cause severe thermal burns. Inhalation of smoke under fire condition is considered as hazardous Swallowing of polyethylene pellets may cause chocking Polyethylene film can cause asphyxiation hazard if misused to cover the face Use of proper PPE and good house keeping minimize these exposure hazard Polyethylene resins are expected to be inert to environment Polyethylene will float in water and can be widely distributed, it is non bio-degradable Pellets may represent a chocking hazard for if ingested by waterfowl or aquatic life The best way to handle PE waste is to recycle the same . Established waste handling management practices, such as “3R” should be followed Spilled Polyethylene may cause slipping hazard Pneumatic conveying of granular material can generate combustible dust Polyethylene will burn if overheated to high temperatures and can cause thick fumes Processing should be done in well ventilated place and precautions should be taken to prevent build up of charges Good house keeping practices can avoid spill problem Property Value Appearance Opaque translucent solid, non-pyrophoric Odor Odorless Melting Point 118 – 135 C Specific Gravity 0.910 – 0.970 Autofalammability 260 – 410 C Solubility Insoluble in water Soluble in some organic solvents Stability Stable, non-reactive under normal conditions All EQUATE Polyethylene grades meet national a nd international regulatory requirements. Thus all EQUATE polyethylene grades are Food Contact a pproved. For all EQUATE Polyethylene grades Safety Data Sheet, Technical Data Sheet and Handling Guidelines exists Risk Characterization and Risk Management procedures to identify and mitigate product risk are practiced in EQUATE EQUATE conducts business risk review for new markets and identify/eliminate misuse of products All EQUATE PE grades are not recommended f or the following: in any commercial or developmental application which is intended for contact with human internal body fluids or body tissues, regardless of the length of time involved in any cardiac prosthetic device application, regardless of the length of the time involved, including, without limitation, pacemaker leads and devices, artificial hearts, heart valves, intra-aortic balloons and control systems, and ventricular bypass assisted devices; as a critical component in any medical device that supports or sustains human life specifically by pregnant women or in any applications desig ned specifically to promote or interfere with human reproduction. All requests for regulatory compliance should be a ddressed to EQUATE R&D. Safety Data Sheets are available in www.equate.com Polyethylene product data sheets are availabl e in www.equate.com