Chapter 6, Section 7
advertisement

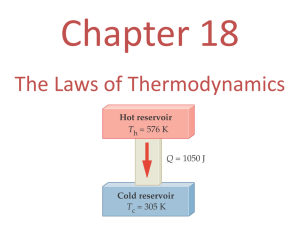
Chapter 6, Section 7 Laws of Thermodynamics: Too Hot, Too Cold, Just Right HW: 6.7 PTG, pg. 676, #1-9 • LO: – Explain the 3 Laws of Thermodynamics as they relate to conservation of energy • SC: – Assess experimentally the final temperature when two liquids of different temperatures are mixed – Assess experimentally the final temperature when a hot metal is added to cold water – Calculate the heat lost and heat gained of two objects after they are placed in thermal contact – Discover if energy is conserved when two objects are placed in thermal contact and reach equilibrium temperature – Explain the concept of entropy as it relate to objects placed in thermal contact. • Do Now: – Write LO and SC on new left side page – WDYS/WDYT: pg 664 • Agenda: – Do Now – Investigate – Summary Investigate #1-3 • #1-complete in your notebook • #2-3 Create a data table in your notebook to record all data. • #3 b-c Construct graph and use to answer questions Investigate #4-5 • Plan experiment, check procedures with teacher. • Conduct experiment Investigate #6 • Read Physics Talk, Specific Heat, pg 66667 • Complete #6 a-c Summary • Discuss how this experiment proves the law of conservation of energy. HW: 6.7 PTG, pg. 676, #1-9 • LO: – Explain the 3 Laws of Thermodynamics as they relate to conservation of energy • SC: – Assess experimentally the final temperature when two liquids of different temperatures are mixed – Assess experimentally the final temperature when a hot metal is added to cold water – Calculate the heat lost and heat gained of two objects after they are placed in thermal contact – Discover if energy is conserved when two objects are placed in thermal contact and reach equilibrium temperature – Explain the concept of entropy as it relate to objects placed in thermal contact. • Do Now: – What does Conservation of Energy mean to you? Explain your answer • Agenda: – – – – Do Now Physics Talk Practice Problems Summary Physics Talk • What did you observe in your experiment? • Equal amounts of hot and cold water produced a final temp half way between the initial temps of both • When you changed the amounts of hot or cold water the final temp was somewhere between the two initial temps, but closer to the temp of the water with the larger mass. Physics Talk • What is the Law of Conservation of Energy? • The total energy in a system is conserved, energy can neither be created or destroyed • Start=End • The cold water gained thermal energy through the transfer of heat, then the hot water must have lost and equal amount of thermal energy. Physics Talk • What equation can we use to show the Law of Conservation of Energy? Mass of water? 1mL=1g 50mL=50g Physics Talk • What is specific heat? • Energy is conserved whether the cool water is mixed with hot water or hot metal. • The heat energy (J) required to raise the temp of mass (1g) for a substance by 1°C. Physics Talk • What is the equation for specific heat? Physics Talk • Sample Problem Physics Talk • Conservation of Energy…Again! • Energy is not created or destroyed! • It can change from one from to another, but the total amount remains the same in a closed system! • Example: From GPEKE Physics Talk • What is the difference between Temperature, Heat, and Thermal Energy? • Temperature is the measure of average kinetic energy of molecules. – High Temp--> more KE Physics Talk • What is the difference between Temperature, Heat, and Thermal Energy? • Heat is the energy transferred from one place to another due to temperature differences. – Transfers from High heat to low heat Physics Talk • What is the difference between Temperature, Heat, and Thermal Energy? • Thermal energy is a type of energy that results from the motion of atoms (related to temperature) – Increase thermal energy, increase temperature – Depends on the mass and temperature of the water – 100g of hot water > 100g of cold water because of the difference in temp – A swimming pool with 10,000kg cold water > 1kg hot water due to mass Physics Talk • What is thermodynamics? • The study of the relationships between heat and other forms of energy transformation of one form into another. • There are 3 laws of thermodynamics. Physics Talk • Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics • If 2 objects have the same temperature as a third object, then the two objects must also have the same temperature. • If A=C, and B=C, then A=B Physics Talk • First Law of Thermo Dynamics • Conservation of energy related to hot and cold objects. • Hot Coffee (90°C) + Cold Milk (5°C) Coffee cools (10°C) slightly, Milk warms a lot (75°C)until they are at the same temperature (80°C) • Could be calculated with the equation if you know the mass of the coffee and milk. Physics Talk • Second Law of Thermodynamics • In irreversible processes, entropy or disorder always increases. • Time is irreversible • Thermal energy is transferred from hot objects to cold objects and NEVER goes from cold to hot spontaneously. Physics Talk • Second Law of Thermodynamics • Energy is only transferred from hot objects to cold objects until they reach an equilibrium temperature. • There is NO SUCH THING AS COLD ENERGY! Physics Talk • Second Law of Thermodynamics (con’t) • Due to Entropy. – Related to the degree of disorder of molecules. – Solids are more organized (ordered) than liquids which are more ordered than liquids. – To go from solidliquidgas the object must gain thermal energy, increasing entropy. Physics Talk • Example of Entropy Checking Up Questions • Pg. 672, #1-4 Vocabulary Boxes • Complete for all vocab words in Chapter 6, Section 7. Essential Questions • Pg. 675 – What does it mean? – How do you know? – Why should you care? Physics To Go • 6.7 PTG, pg. 676, #1-9