Persuasive text Notes
advertisement

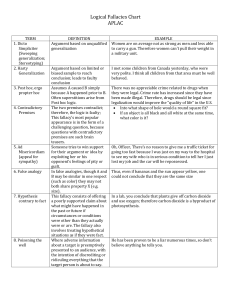
Persuasive Text AUTHORS REACH THEIR CONCLUSIONS THROUGH ANALYZING THE EVIDENCE EACH PRESENTS Persuasive Text text written with the intent to persuade or convince the reader of something Analyze • • Rhetorical fallacy - an argument that is not sound but may still be convincing Logical fallacy - depends upon faulty logic Logical Fallacies include: Loaded term Caricature Leading question False assumption Incorrect premise Loaded term a term or phrase that has strong emotional overtones and that is meant to evoke strong reactions beyond the specific meaning tax relief instead of tax cut, or death tax instead of estate tax Student Enrichment instead of Student Detention Extra Practice instead of Extra Work Getting Even instead of Revenge Caricature a distortion of characteristics or defects of a person or thing, either in a picture or in words Caricature came from www.google.com images. Leading question A question worded to suggest the desired response What do you think of the horrible effects of homework? What makes you think you can cheat on your homework? Why do you like to waste money? Why did you commit the crime? False assumption Flawed ideas that emerge when a reader pieces information together solely by inference and fails to consider other possible interpretations SEE PDF Incorrect premise A faulty idea that is used as the foundation of an argument If the streets are wet, it has rained recently. (Premise) The streets are wet. (premise) Therefore it has rained recently. (conclusion) This argument is logically valid, but quite demonstrably wrong, because its first premise is false - one could hose down the streets, the local river could have flooded, etc The kid is sweaty because he is dirty (Premise) The kid is sweaty (premise) Because he is dirty. (conclusion) This argument is logically valid, but quite wrong, because its first premise is false – The student could of just finished going for a run, It could be hot outside, etc.