Mentoring and Coaching
advertisement

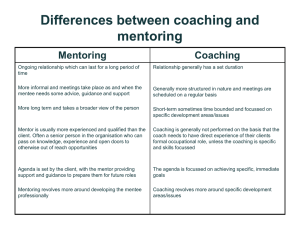
Mentoring and Coaching Fasset: October 2013 1 Welcome Note • Welcome to Mentoring and Coaching Workshop. • Purpose: Teach you skills and knowledge that will enable you to effectively mentor and coach others. • Will be introduced to • mentoring and coaching-related terminology, • mentoring and coaching-related documents, • role-players in the mentoring and coaching processes (and their functions) and • the steps in the mentoring and coaching processes. Mentoring and Coaching 2 Welcome Note (cont.) • Workshop (and Learner Guide) consists of learning units. • Learning units include activities. • Mentoring and coaching-related templates in the relevant learning units. • Workshop is non-credit bearing. Mentoring and Coaching 3 Content Learning Unit 1: Mentoring-related concepts Learning Unit 2: Steps in the mentoring process Learning Unit 3: Initiate the mentor-mentee relationship Learning Unit 4: Define the mentor-mentee relationship Learning Unit 5: Plan the education, training and development of the mentee Learning Unit 6: Review the planned education, training and development of the mentee Learning Unit 7: Perform continuous mentoring-related activities Mentoring and Coaching 4 Content Learning Unit 8: Coaching-related concepts Learning Unit 9: Steps in the coaching process Learning Unit 10: Initiate the coach-learner relationship Learning Unit 11: Identify the task that the learner must be able to perform Learning Unit 12: Prepare the learner for the coaching Learning Unit 13: Conduct the coaching sessions Mentoring and Coaching 5 Activity 1 1. Find a partner and discuss the following questions with him/ her. Record your joint response to the questions in the space provided. 1.1 Why do you mentor employees in your organisation? 1.2 Who (i.e. what employees) do you mentor? 1.3 How and when do you mentor employees? Mentoring and Coaching 6 Learning Unit 1: Mentoringrelated concepts Mentoring and Coaching 7 7 What is mentoring? • caring relationship • a person with more experience (i.e. the Mentor) • works with a less experienced person (i.e. the mentee) • to promote the professional and personal development of mentee Mentoring and Coaching 8 Who mentors? • A Mentor Mentoring and Coaching 9 Who is mentored? • a mentee (or protégé) Mentoring and Coaching 10 What are the advantages of mentoring? Advantages to Mentors Advantages to Advantages to mentees Creates opportunity for Mentors to share their experience and thus ‘enriches’ Mentors. Creates opportunity to be recognised. It provides an opportunity to do something different (than normal duties). Mentoring and Coaching Provides professional recognition and affirmation. Reduces isolation. Provides meaningful learning experiences and an opportunity for personal and professional growth. 11 organisations Improves integration of new employees. Increases communication, networking and openness/ transparency in organisations. Improves employee satisfaction. Enhances career development. Creates a learning culture. Learning Unit 2: Steps in the mentoring process Mentoring and Coaching 12 12 Steps in the mentoring process Initiate the mentor-mentee relationship (Learning Unit 3) Define the mentor-mentee relationship (Learning Unit 4) Plan the education, training and development of the mentee (Learning Unit 5) Review the planned education, training and development of the mentee (Learning Unit 6) Perform continuous mentoring-related activities (Learning Unit 7) Mentoring and Coaching 13 Learning Unit 3: Initiate the mentor-mentee relationship Mentoring and Coaching 14 14 Steps in the mentoring process Initiate the mentor-mentee relationship (Learning Unit 3) Define the mentor-mentee relationship (Learning Unit 4) Plan the education, training and development of the mentee (Learning Unit 5) Review the planned education, training and development of the mentee (Learning Unit 6) Perform continuous mentoring-related activities (Learning Unit 7) Mentoring and Coaching 15 What should the HR/ Training Department do to initiate the mentor-mentee relationship? • Identify Mentor and mentee Mentoring and Coaching 16 Step 1 Who can be a Mentor? • Senior professional employees (e.g. Accountants, Engineers, Technicians, HR Consultants, etc.). • Senior trade workers (e.g. Carpenters, Mechanics, Electricians, etc.). • Senior employees from other occupations (e.g. clerical workers, etc.). • Supervisors and Managers. • Employees from the HR/ Training Department. Mentoring and Coaching 17 What characteristics should a Mentor have? • Leadership – The Mentor should be able to influence the mentee to achieve certain objectives. • Self-knowledge – The Mentor should be aware of his/her likes, dislike and beliefs. • Commitment to the development of people – The Mentor should be willing to develop and motivate others. • The ability to act as sponsor, teacher, ‘insider’, encourager and supporter, counsellor and advisor to the mentee. Mentoring and Coaching 18 Who can be a mentee? • New employees (including professionals and trade workers) who just completed education-type training interventions i.e. qualifications. • Less experienced (and usually younger) employees who are earmarked for accelerated development. • Employees who are busy with training interventions (e.g. qualifications, skills programmes, short courses, etc.). Mentoring and Coaching 19 What should the HR/ Training Department do to initiate the mentor-mentee relationship? (cont.) • ‘Pair’ Mentor and mentee Step 2 • Orientate Mentor and mentee Mentoring and Coaching 20 Step 3 Learning Unit 4: Define the mentor-mentee relationship Mentoring and Coaching 21 21 Steps in the mentoring process Initiate the mentor-mentee relationship (Learning Unit 3) Define the mentor-mentee relationship (Learning Unit 4) Plan the education, training and development of the mentee (Learning Unit 5) Review the planned education, training and development of the mentee (Learning Unit 6) Perform continuous mentoring-related activities (Learning Unit 7) Mentoring and Coaching 22 What should the Mentor discuss during the meeting? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v3MnGaheXdY&feature =player_embedded Mentoring and Coaching 23 What should the Mentor discuss during the meeting? • The purpose of the meeting. • The agreement to the mentor-mentee relationship. • The purpose and benefits of mentoring. • The mentee’s background and work experience. • The Mentor’s background and work experience. • The mentee’s previous mentor-mentee relationships. Mentoring and Coaching 24 What should the Mentor discuss during the meeting? (cont.) • The roles and responsibilities of role-players involved in the mentoring process. • The structuring of the mentor-mentee relationship. • The questions, inputs and/ or concerns of the mentee. Mentoring and Coaching 25 Learning Unit 5: Plan the education, training and development of the mentee Mentoring and Coaching 26 26 Steps in the mentoring process Initiate the mentor-mentee relationship (Learning Unit 3) Define the mentor-mentee relationship (Learning Unit 4) Plan the education, training and development of the mentee (Learning Unit 5) Review the planned education, training and development of the mentee (Learning Unit 6) Perform continuous mentoring-related activities (Learning Unit 7) Mentoring and Coaching 27 Activity 2 1. Read the Learner Guide section allocated to you. Mentoring and Coaching 28 Activity 2 (cont.) 2. Conduct an ‘IDP-planning meeting’ with ‘your mentee’ to plan the education, training and development of the mentee. (One person will play the role of ‘the Mentor’ and another person will play the role of ‘the mentee’ during the ‘IDP-planning meeting’. ‘The Mentor’ has to discuss relevant aspects with ‘the mentee’ and ‘the mentee’ has to provide inputs during the ‘IDP- planning meeting’.). Also complete ‘your mentee’s’ Individual Development Plan (IDP) (available on the next pages) during and after the ‘IDP-planning meeting’. Mentoring and Coaching 29 Activity 2 (cont.) 3. Observe the ‘IDP-planning meeting’ that takes place between ‘the Mentor’ and ‘the mentee’. (The purpose of the ‘IDP-planning meeting’ is to plan the education, training and development of the mentee.) Make notes on the effectiveness of the meeting by using the Observation checklist provided on the next page(s). 4. As a group, discuss the effectiveness of the meeting that took place. Mentoring and Coaching 30 Learning Unit 6: Review the planned education, training and development of the mentee Mentoring and Coaching 31 31 Steps in the mentoring process Initiate the mentor-mentee relationship (Learning Unit 3) Define the mentor-mentee relationship (Learning Unit 4) Plan the education, training and development of the mentee (Learning Unit 5) Review the planned education, training and development of the mentee (Learning Unit 6) Perform continuous mentoring-related activities (Learning Unit 7) Mentoring and Coaching 32 What should the Mentor discuss during the IDP-review meeting? • The purpose of the IDP-review meeting and the Individual Development Plan (IDP). • The progress in terms of the planned education, training and development-type training interventions. • The questions, inputs and/ or concerns of the mentee. • The mentee’s review of the IDP-review meeting as well as the mentee’s agreement to his/ her revised IDP. Mentoring and Coaching 33 Learning Unit 7: Perform continuous mentoring-related activities Mentoring and Coaching 34 34 Steps in the mentoring process Initiate the mentor-mentee relationship (Learning Unit 3) Define the mentor-mentee relationship (Learning Unit 4) Plan the education, training and development of the mentee (Learning Unit 5) Review the planned education, training and development of the mentee (Learning Unit 6) Perform continuous mentoring-related activities (Learning Unit 7) Mentoring and Coaching 35 Activity 3 1. Read the Learning Guide section/ card allocated to your group. When done, conduct a group discussion in terms of the questions below. Record your joint response to the questions in the space provided. 1.1 What is the role of the Mentor as a sponsor/ teacher/ ‘insider’/ encourager and supporter and counselor and advisor? Mentoring and Coaching 36 Activity 3 (cont.) 1.2 Do you think the role of the Mentor as a sponsor/ teacher/ ‘insider’/ encourager and supporter and counselor and advisor is important in your organisation? Why do you say so? 1.3 Do you/ Mentors in your organisation currently fulfill the role as sponsor/ teacher/ ‘insider’/ encourager and supporter and counselor and advisor? Why do you say so? Mentoring and Coaching 37 Steps in the mentoring process Initiate the mentor-mentee relationship (Learning Unit 3) Define the mentor-mentee relationship (Learning Unit 4) Plan the education, training and development of the mentee (Learning Unit 5) Review the planned education, training and development of the mentee (Learning Unit 6) Perform continuous mentoring-related activities (Learning Unit 7) Mentoring and Coaching 38 Content Learning Unit 1: Mentoring-related concepts Learning Unit 2: Steps in the mentoring process Learning Unit 3: Initiate the mentor-mentee relationship Learning Unit 4: Define the mentor-mentee relationship Learning Unit 5: Plan the education, training and development of the mentee Learning Unit 6: Review the planned education, training and development of the mentee Learning Unit 7: Perform continuous mentoring-related activities Mentoring and Coaching 39 Content Learning Unit 8: Coaching-related concepts Learning Unit 9: Steps in the coaching process Learning Unit 10: Initiate the coach-learner relationship Learning Unit 11: Identify the task that the learner must be able to perform Learning Unit 12: Prepare the learner for the coaching Learning Unit 13: Conduct the coaching sessions Mentoring and Coaching 40 Activity 4 1. Find a partner and discuss the following questions with him/ her. Record your joint response to the questions in the space provided. 1.1 Why do you coach employees in your organisation? 1.2 Who (i.e. what employees) do you coach? 1.3 How and when do you coach employees? Mentoring and Coaching 41 Learning Unit 8: Coachingrelated concepts Mentoring and Coaching 42 42 What is coaching? • a training method whereby • a less-skilled person (i.e. the learner) is • guided (on a one-on-one basis) • by a skilled person (i.e. the Coach) • to implement specific skills and knowledge • to be able to perform a certain task and sub-tasks according to certain performance standards/ assessment criteria Mentoring and Coaching 43 Who coaches? • A Coach Mentoring and Coaching 44 Who is coached? • a learner Mentoring and Coaching 45 What are the advantages of coaching (as a training method)? • It is cost-effective and costs less to develop and implement than other training methods. • It is a flexible training method and can easily be modified. • It can easily be tailored to meet the needs and personal learning styles of individual learners. • It results in standardisation of procedures in the organisation. Mentoring and Coaching 46 Learning Unit 9: Steps in the coaching process Mentoring and Coaching 47 47 Steps in the coaching process Initiate the coach-learner relationship (Learning Unit 10) Identify the task that the learner must be able to perform (Learning Unit 11) Prepare the learner for the coaching (Learning Unit 12) Conduct the coaching sessions (Learning Unit 13) Mentoring and Coaching 48 Learning Unit 10: Initiate the coach-learner relationship Mentoring and Coaching 49 49 Steps in the coaching process Initiate the coach-learner relationship (Learning Unit 10) Identify the task that the learner must be able to perform (Learning Unit 11) Prepare the learner for the coaching (Learning Unit 12) Conduct the coaching sessions (Learning Unit 13) Mentoring and Coaching 50 What should the HR/ Training Department do to initiate the coach-learner relationship? • Identify Coach and learner Mentoring and Coaching 51 Step 1 Who can be a Coach? • Senior professional employees (e.g. Accountants, Engineers, Technicians, HR Consultants, etc.). • Senior trade workers (e.g. Carpenters, Mechanics, Electricians, etc.). • Senior employees from other occupations (e.g. clerical workers, etc.). • Supervisors and Managers. • Employees from the HR/ Training Department. Mentoring and Coaching 52 Who can be a learner? • New employees (including professionals and trade workers) who just completed education-type training interventions i.e. qualifications. • Employees who are busy with training interventions (e.g. qualifications, skills programmes, short courses, etc.) • Learners who are busy with Learnerships. Mentoring and Coaching 53 What should the HR/ Training Department do to initiate the coach-learner relationship? (cont.) • ‘Pair’ Coach and learner Step 2 • Orientate Coach and learner Mentoring and Coaching 54 Step 3 Learning Unit 11: Identify the task that the leaner must be able to perform Mentoring and Coaching 55 55 Steps in the coaching process Initiate the coach-learner relationship (Learning Unit 10) Identify the task that the learner must be able to perform (Learning Unit 11) Prepare the learner for the coaching (Learning Unit 12) Conduct the coaching sessions (Learning Unit 13) Mentoring and Coaching 56 What should the Coach do to identify the task that the learner must be able to perform? • Identify document(s) to be compiled i.e. Task summary Step 1 • Consult various sources Step 2 • Identify • task that learners must be able to perform after coaching • related sub-tasks of task • Use verbs and nouns (objects) to describe task and sub-tasks that learners must be able to perform • Record identified task and sub-tasks on Task summary Mentoring and Coaching 57 What is a task? An action that the learner must be able to perform/ what the learner must able to (physically) do (after the coaching). Mentoring and Coaching 58 Examples of a task • Milk (verb) a cow (noun). • Overhaul (verb) an engine (noun). • Fit and wear (verb) safety equipment (noun). • Compile (verb) a budget (noun). Mentoring and Coaching 59 What are sub-tasks? Smaller steps or sub- steps of a task. A smaller action that the learner must be able to perform/ what the learner must able to (physically) do (after the coaching). Mentoring and Coaching 60 Examples of sub-tasks (for ‘milk a cow’) • Fetch (verb) the cow (noun). • Prepare (verb) the cow (noun) for milking. • Milk (verb) the cow (noun). • Clean (verb) the work area and equipment (noun). • Store (verb) the milk (noun). Mentoring and Coaching 61 What are possible sources that the Coach could consult to identify the task and sub-tasks? • An (observation) checklist or logbook (developed by the HR/ Training Department) that apply to the task. • The unit standard that the coaching will be based upon i.e. the unit standard that the learner will achieve after the coaching (and assessment). • The job description of the learner. • Operating manuals that apply to the task. • Organisational procedures that apply to the task. Mentoring and Coaching 62 What should the Coach do to identify the task that the learner must be able to perform? (cont.) Step 3 • Consult various sources • Identify • performance standards/ assessment criteria that apply to task that learner must be able to perform after coaching • Record identified performance standards/ assessment criteria on Task summary Mentoring and Coaching 63 What are performance standards/ assessment criteria? Specify how a task has to be performed. Indicates how much, how and to what level of complexity a learner has to perform a task. Mentoring and Coaching 64 Examples of a performance standards/ assessment criteria • Budget is compiled as per organisational template. • Accurate calculations are reflected. • Equipment is stored as per organisational procedures for safety and house-keeping. • Tools are used as per organisational procedures for safety. • Safety requirements are met. Mentoring and Coaching 65 What are possible sources that the Coach could consult to identify the performance standards/ assessment criteria? • An (observation) checklist or logbook (developed by the HR/ Training Department) that apply to the task. • The unit standard that the coaching will be based upon i.e. the unit standard that the learner will achieve after the coaching (and assessment). • The job description of the learner. • Operating manuals that apply to the task. • Organisational procedures that apply to the task. Mentoring and Coaching 66 Activity 5 1. Identify the task and sub-tasks that the (your) learner must be able to perform after the coaching. Use the template provided on the next page(s) to reflect the identified information. 2. Identify the performance standards/ assessment criteria that apply to the task. Use the template provided on the next page(s) to reflect the identified information. Mentoring and Coaching 67 Learning Unit 12: Prepare the learner for the coaching Mentoring and Coaching 68 68 Steps in the coaching process Initiate the coach-learner relationship (Learning Unit 10) Identify the task that the learner must be able to perform (Learning Unit 11) Prepare the learner for the coaching (Learning Unit 12) Conduct the coaching sessions (Learning Unit 13) Mentoring and Coaching 69 What should the Coach discuss during the pre-coaching meeting? • The purpose of the pre-coaching meeting and the Coaching plan. • The agreement to the coach-learner relationship. • The purpose and advantages of coaching. • The learner’s background and work experience. • The training needs of the learner. • The work environment of the learner. • Coaching session date(s), times and venue(s). Mentoring and Coaching 70 What should the Coach discuss during the pre-coaching meeting? (cont.) • The resources that are required during the coaching sessions. • The special needs and learning barriers of the learner as well as actions to address the special needs and learning barriers of the learner. Mentoring and Coaching 71 What should the Coach discuss during the pre-coaching meeting? (cont.) • The rules that will apply during the coaching sessions. • What to do to prepare for the coaching sessions. • The questions, inputs and/ or concerns of the learner. • The learner’s review of the pre-coaching meeting as well as the learner’s agreement to his/ her Coaching plan. Mentoring and Coaching 72 Learning Unit 13: Conduct the coaching sessions Mentoring and Coaching 73 73 Steps in the coaching process Initiate the coach-learner relationship (Learning Unit 10) Identify the task that the learner must be able to perform (Learning Unit 11) Prepare the learner for the coaching (Learning Unit 12) Conduct the coaching sessions (Learning Unit 13) Mentoring and Coaching 74 What should the Coach do to conduct the coaching sessions? • Identify document(s) to be compiled i.e. Coaching report Step 1 (including Observation checklist) • Consider phases of coaching session Step 2 • Per coaching session, identify • most appropriate sequencing of phases of coaching session i.e. identify sequence in which phases should be applied during coaching session Mentoring and Coaching 75 What are the phases of a coaching session? • An ‘explanation by the Coach’ phase. • A ‘demonstration by the Coach’ phase. • A ‘checking the knowledge and understanding of the learner’ phase. • A ‘demonstration by the learner (practice)’ phase. • A ‘feedback to the learner’ phase. Mentoring and Coaching 76 What options are available in terms of the sequencing of phases of a coaching session? Option 1 Option 2 Option 3 Option 4 Demonstration by the Coach Explanation by the Coach Demonstration by the learner (practice) Checking the knowledge and understanding of the learner Explanation by the Coach Demonstration by the Coach Feedback to the learner Demonstration by the learner (practice) Checking the knowledge and understanding of the learner Checking the knowledge and understanding of the learner Demonstration by the Coach Explanation by the Coach Demonstration by the learner (practice) Demonstration by the learner (practice) Explanation by the Coach Demonstration by the Coach Feedback to the learner Feedback to the learner Checking the knowledge and understanding of the learner Checking the knowledge and understanding of the learner (Final) Demonstration by the learner Final demonstration by the learner Demonstration by the learner (practice) Demonstration by the learner (practice) (Final) Feedback to the learner (Final) Feedback to the learner (Final) Feedback to the learner Feedback to the learner Mentoring and Coaching 77 What factors should the Coach consider to identify the most appropriate sequencing of phases? • The learning style of the learner. • The safety risk of the task and related sub-tasks. • Waste factors. • The availability of time. • The experience of the learner. Mentoring and Coaching 78 What should the Coach do to conduct the coaching sessions? (cont.) Step 3 • Demonstrate a friendly and open approach throughout the coaching session Step 4 • Conduct the identified first phase of the coaching session (as per the identified sequence of phases) (e.g. the ‘explanation by the Coach’ phase) Step 5 - 8 • Conduct the identified next phase of the coaching session (as per the identified sequence of phases) Mentoring and Coaching 79 Activity 6 1. Select two people from your group to conduct a role-play. (One person will play the role of ‘the Coach’ and another person will play the role of ‘the learner’ during a ‘coaching session’ during the role-play. ‘The Coach’ has to conduct one of the phases of a ‘coaching session’ during the role-play.). (If applicable) ‘The Coach’ has to complete ‘the learner’s’ Coaching report (including Observation checklist) (available on the next pages) during and after the ‘coaching session’. Mentoring and Coaching 80 Activity 6 (cont.) 2. Observe the phases of the ‘coaching session’ that takes place between ‘the Coach’ and ‘the learner’. (The purpose of the ‘coaching session’ is to coach the learner.) Make notes on the effectiveness of the ‘coaching session’ by using the Observation checklist provided on the next page(s). 3. As a group, discuss the effectiveness of the ‘coaching session’ that took place. Mentoring and Coaching 81 Steps in the coaching process Initiate the coach-learner relationship (Learning Unit 10) Identify the task that the learner must be able to perform (Learning Unit 11) Prepare the learner for the coaching (Learning Unit 12) Conduct the coaching sessions (Learning Unit 13) Mentoring and Coaching 82 Thank You For more information please contact the Fasset Call Centre on 086 101 0001 or visit www.fasset.org.za 83