What is a project? - Swansea University
advertisement

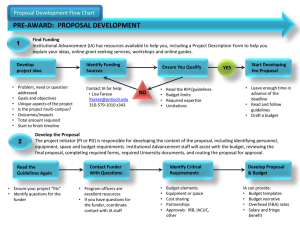
Project Management Framework Ciaran Whyte Risk Administrator Planning & Strategic Projects Unit May 2010 Project Management Framework OR..... Ciaran Whyte Agenda Objectives of Seminar What is a project? What is PMF? PRINCE2 Project Management Framework Project Lifecycle Stage 1 – Scoping and Approval Project Governance Stage 2 – Project Planning Stage 3 – Start Up the Project Stage 4 – Deliver the Project Stage 5 – Close the Project Stage 6 – Post Project Review Objectives of Seminar At the end of the seminar you should - • Know what the Project Management Framework is • Know what the stages in a project life cycle area • Within each stage know what steps to take • Realise that a Project Manager’s job is not really for dummies! Project management challenges How the funder explained it External partners understanding Project team’s understanding Admin Depts perception How HoS/HoD described it How it was documented What was delivered How SMT described it Perception from other Schools What the funder really needed What is a project? Definite beginning and definite end Reached when project objectives met or project terminated “a temporary endeavour undertaken to create a unique product or service” Product or service is different from all other products or services What is PMF? “Project Management Framework provides a basic structure for understanding project management as it is deployed at Swansea University” Application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to meet project requirements PRINCE2 Directing A Project Directing a Project Starting Up a Project Controlling a Stage Starting Up a Project Controlling a Stage Initiating a Project Initiating a Project Managing Stage Boundaries Managing Stage Boundaries Managing Product Delivery Managing Product Delivery Planning Planning Closing a Project Closing a Project The Project Lifecycle Project Stages Planning Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Scoping & Approval Project Planning Start Up the Project Identify need & scope of project Write business case Identify owning HOS/D Secure planning resources Agree governance SMG Research approval Create project plan Prepare full bid Conduct risk review Plan all resources Negotiate agreements Secure SMT approval Delivery Close Post Stage 4 Stage 5 Stage 6 Deliver the Project Close the Project Post Project Review Initiate contracts Execute project plans Secure all resources Manage exceptions Deliver outputs Engage PM Manage contract delivery Setup finances Project Steering Group control Secure funders approval Project Assurance Review (if requested) Submit Claims to funder SMT Monitoring Reports Funder/PWC Audits (if requested) Close contracts Close finances Write Project Completion Report Release resources Review benefit delivery Identify follow-up projects Stage 1 – Scoping and Approval define Scope Initiation document Scope Planning Business Case Project Definition High Level Project Plan Ensure project includes ALL the work required AND ONLY the work required to complete successfully Scope Definition Scope Verification Breakdown to lower levels Key stakeholders SMG Research approval Stages 1-3 – Other things to do what standards apply Quality Planning stakeholder needs roles, resps and reporting Organisation Planning what, how much & when get the team Staff Acquisition specify & identify potential sources Communications Planning Procurement Planning Solicitation Planning Risk Identification Risk Evaluation Risk Mitigation Pre-RA check to assess risk level Risk Assessment Review for high risk projects Project Governance •Direction & guidance •Provide resources •Secure funding •Liaison to Exec groups •Approve outputs •Resolve issues •Manage risks •Policy decisions •Scope changes •Contingency University Senior Management Team (SMT) SMT Owner External Project Steering Group “owns” Project Appoints chair Project Steering Group Direct Management Responsibilities Administrative Departments School Resources Sub-Group Management Finance Infrastructure Budget Building/ICT - Head of School(s) - Principal Investigator (PI) - Project Manager (PM) - Key SU stakeholders External Suppliers or Partners Delegate accountability to chair of sub-group R&D Business Marketing Academic Activity External/Outputs Communications Stage 2 – Project Planning establish dependencies MS Project Activity Sequencing specify activities determine -people -kit -materials to perform each activity Activity Definition Resource Planning Activity Duration Estimating task schedule Schedule Development estimate work periods Cost Estimating Translate to £s Pull together & document with ALL assumptions Project Plan Development Cost Budgeting allocate to periods Stage 2 – Project Planning Stage 3 – Start Up the Project Negotiating and receiving funding Carry out initiation tasks Secure resources Initiate contracts Finance systems setup Engage project manager Handle changes Revisit Stages 1 & 2 if scope or plan changes Stage 4 – Deliver the Project CONTROL EXECUTION perform all activities in project plans Collect information status – current position against plan progress – achievements forecasts - prediction Document Steering Group Highlight Report External reports to Funder Major Project Monitoring Report Issue Log / Risk Register Meetings Steering Group Meeting Sub-Group Meetings Project Team Meetings Claim Meetings Stage 4 – Other activities “health check” Project Assurance Review Quality Assurance Team Development Information Distribution timely provision to stakeholders enhance performance Solicitation Source Selection getting quotes / bids choosing supplier Scope Verification Scope Changes Contract Administration Risk Monitoring requests assess impact & estimate cost approvals Schedule Control Cost Control Quality Control managing supplier delivery review risks & track actions conduct sampling & agree actions to eliminate unsatisfactory performance Stage 4 – Project Assurance Review 1. Are all stakeholders fully committed and effectively involved? 2. Will the project deliver the desired outputs and costs, and is tracking ongoing and meaningful? 3. Is the project plan accepted and maintained and is there confidence in reporting and estimates to complete? 4. Are the project team high performing with clear roles and responsibilities? 5. Is the scope realistic and are the project boundaries being clearly managed? 6. Are all risks being mitigated? 7. Does the project help or endanger Swansea University’s reputation, finances or staff development? Stage 5 – Close the Project Close contracts verify completed successfully final invoices Close financial systems Project Completion Report plan versus actual with variances explained – finances – milestones – outputs – resources lessons learned – what went well? what went badly? recommendations archiving of project files Release resources Celebrate achievements! Stage 6 – Post Project Review SMT Owner appoints independent reviewer Review achievement of benefits Review management of project Lessons learned Identify potential follow-up projects And if it all goes wrong...