Folk culture - Ms. Stephens` Class
advertisement

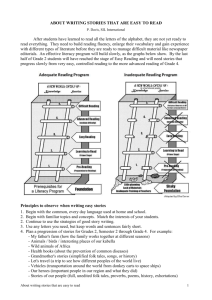
Agenda 01-15-12 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) Sponge Objective: Understanding types of culture Intro: Videos Modeling: Explain Independent Practice Independent Practice: Mash-UP Review Exit Tickets Objective SSSocC1: Students will explain the development and importance of culture. • a. Describe how culture is a social construction. • b. Identify the basic characteristics of culture. • c. Explain the importance of culture as an organizing tool in society. • d. Describe the components of culture to include language, symbols, norms, and values. SSSocC2: Students will evaluate how cultures develop and evolve. • a. Explain cultural change and diversity include ethnocentrism, cultural relevance, folk culture, pop culture, counterculture, subculture, and culture shock. • b. Compare material and non-material culture. • c. Analyze the impact of globalization on US and other world cultures. Reminders • Quiz Thursday over everything covered so far this unit. Sponge: “Well hey there… Welcome to class. Do you know who I am ? How do you know?” Sub-Culture • Groups in society that share values, norms, and behaviors that are not shared by the entire population. Counter-Culture • Groups that reject the major values, norms, and practices of the larger society. Do you know we are? Popular Culture Cultural activities or commercial products reflecting, suited to, or aimed at the tastes of the general masses of people. Sometimes referred to as “Low Culture”. Why? It is very accessible. Seems to be less complex and easy to understand, and therefore available to the masses. High Culture The set of cultural products, mainly in the arts, held in the highest esteem by a culture. Culture of the Elite Not very accessible for most people. Seems more difficult and hard to understand. High vs Low • Who gets to decide? Folk Culture • Folk culture refers to the lifestyle of a culture. Historically, handed down through oral tradition, it demonstrates the "old ways" over novelty and relates to a sense of community. Folk culture is quite often imbued with a sense of place. • Folk Art is not influenced by movements in academic or fine art circles, and, in many cases, folk art does not include work made by professional artists and sold as "high art" or "fine art" to the society's art patrons. What does this picture represent? Independent Practice: Mash Up Activity • Research and find an example of each type of culture discussed today: • Pop-Culture (Low Culture), Counter Culture, Folk Culture, Sub Culture, High Culture, • Explain why each represents this type of culture. • OR create a Mash-UP. – Tell me how your mash-up changes the value of each cultural product