Costa`s Level of Inquiry
advertisement

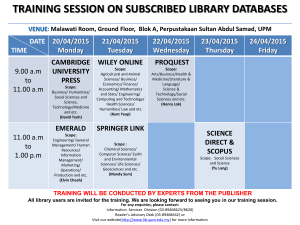
A Learners Guide Inquiry is an important part of any classroom. Inquiry-based learning focuses on the student as learner, developing skillful, open-ended questioning skills. Being able to recognize different levels of questions is beneficial for all students, whether it is in math, humanities, science, or any other class. Dr. Art Costa developed the three levels of questions used in inquiry in the classroom. Truly understanding the three levels of questions explained in the following slides is critical for student success. It will make you a better student, not only at GMS but in high school and when you are enrolled in college. Level One Questions are “Text Explicit.” This means that you can point to one correct answer right in the text. These questions are basic comprehension questions and require little if any real thought. Words found in these questions include: define observe describe name identify recite note list Questions are often written using the words: Who What Where When Who is the protagonist in The Hunger Games? (Humanities) What was the first battle of the American Revolution? (Humanities) Define tangent. (Math) List the steps in photosynthesis. (Science) What are the primary and secondary colors on the color wheel? (Art) Where is stage left and stage right? (Drama) Level Two Implicit.” This Questions are “Text means that readers infer answers from what the text implicitly states, finding answers in several places in the text. Another way to say this is that you make a judgment or conclusion using evidence from what you have read. Words found in these questions include: analyze group synthesize compare/contrast infer sequence Questions are often written using the words: How Why Compare and contrast Percy and Annabeth in Percy Jackson and the Lightening Thief. (Humanities) Analyze the causes of the American Revolution. (Humanities) Compare the square root of 49 to the square root of 64. Which is greater? (Math) Diagram and order the life stages of a milkweed bug. (Science) Why did the Roman Empire eventually fall? (Humanities) Level Three Questions are “Experience Based.” This means that readers must think beyond what the text states. Answers to the questions are based on your prior knowledge and experiences and will not be the same as other student’s answers. Words found in these questions include: evaluate judge apply speculate imagine predict hypothesize Questions are often written using the words: Could Should Would Predict how Katniss Everdeen will change if she survives. (Humanities) Could you survive as a 13 year old male in Sparta.? How would you be successful? (Humanities) Apply the Pythagorean theorem to the find the measurement of this triangle. (Math) Diagram the stages of photosynthesis and predict how long each takes. (Science) Evaluate the use of light in Monet’s Giverny series of paintings. (Art) Level 1 (the lowest level) requires you to gather information. Level 2 (the middle level) requires you to process the information. Level 3 (the highest level) requires you to apply the information. There are one-story intellects, two-story intellects, and three-story intellects with skylights. All fact collectors who have no aim beyond their facts are one-story people. Two-story people compare, reason, generalize, using the labor of fact collectors as their own. Three-story people idealize, imagine, predict—their best illumination comes through the skylight. AVID Tutor/Student www.mrkash.com Guide