Generational Differences and Conflicts in the Workplace
advertisement

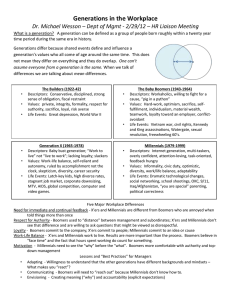
Generations at Work: Generational Differences and Conflicts in the Workplace Presented by Marti Eagleton 10.01.2012 Goals/Objectives Understand each generation’s attitudes towards work ethic, technology, compensation & benefits, and communication; Understand how generational differences can create conflict in the workplace, and, Better appreciate each generation’s contributions to the workforce. From http://citizensforsafetechnology.org What is a generation? A cohort united by a shared coming of age process in which major political, social and/or economic events create a common history and connection with others of the same age. Adwoa K. Buahene and Giselle Kovary Cautions - Not intended to promote ageism, but understanding Not a panacea The Primary Players - Boomers Generation X Millennials (aka Generation Y) Defining Factors - - Historical events Music/books Technology Parental Expectations Values Boomers Generally defined as those born 1946- 1964. Vietnam War, Civil Rights Movement, Space program, the Kennedy and King assassinations Rock & Roll, TV Boomers Grew up in an era of reform. Not afraid of confrontation; challenge established practices Confident, independent, loyal, cynical, work-centric Boomers Motivated by position, perks and prestige Define self-worth by accomplishments “Workaholics” Don’t understand why Gen X and Millennials think they can get ahead without “paying their dues” Fault younger workers for working remotely Competitive Boomers Work is somewhere to go as well as something to do Equate success and commitment with high salaries and long hours Generation X Generally defined as those born 1965- 1981. Sometimes called the “MTV generation” Energy crisis, Chernobyl, Space Shuttle challenger, fall of the Berlin Wall, 1990’s economic boom. Video games, computers. Grunge and hip-hop music. Generation X Cited by the U.S. Census Bureau as the most highly educated generation Smaller than previous generations due to birth decline Initially labeled as insecure, angst-ridden underachievers Now independent, resourceful and selfsufficient Rather than challenge leaders with the intent to replace them, challenge systems and institutions Generation X Dislike being micromanaged and structure work hours. Embrace a hands off management philosophy. Enjoy challenging assignments. Thrive on & seek out diversity, challenge, responsibility and opportunities to give creative input Dislike “meetings about meetings” Generation X Skeptical – grew up in a time of high divorce rates, corporate layoffs and public scandals Saw parents lose hard-earned positions. More willing to change jobs to get ahead than boomers Work to live rather than live to work. Bring fun & humor into the work place Millennials Generally considered to be those born 1982200X. Known by multiple names: Generation Y, Echo Boomers, Generation Me, Trophy Generation, Peter Pan Generation Columbine School shooting, Oklahoma City bombing, dot.com bust, current financial crisis Cell phones, then smart phones. Katy Perry, Miley Cyrus, Justin Bieber. Millennials Most studied generation in history Well-versed in technology, plugged in 24/7 Feel incredible pressure to conform According to Jean Twenge (“Generation Me”), display confidence, tolerance, entitlement, narcissism, rejection of social conventions Millennials Communicate through email, text messaging, instant messaging Prefer webinars to lecture-based presentations Willing to trade high pay for fewer hours and flexible schedules This is often viewed as a lack of commitment, discipline and drive Millennials “No person left behind” – loyal, committed, want to be involved and inclusive Crave attention Seek frequent feedback, praise & reassurance May benefit from being matched with a mentor who can provide 1:1 attention Millennials Lives have always been busy & structured Work is an activity, not a place By the end of this decade, will be the dominant age group in the workforce May be drawn to this field in higher numbers because of their traits Compensation & Benefits Bonuses Vacation Career ladders Other perks Mentoring, Coaching & Supervision Feedback The importance of cross-training Relationships and boundaries Communication Meetings Memos/Emails IM and Texting Recruiting and Retention Job postings Interview process Opportunities for growth and development Managing Teams Communication Expectations Professionalism Dress code Office geography Schedules Other impacts on agencies Social media Texting What can you learn from them? Boomers Gen X Millennials Resources and Additional Reading Generations: The History of America’s Future, 1584 to 2069 (Neil Howe and William Strauss) Generation Me: Why Today’s Young Americans Are More Confident, Assertive, Entitled – And More Miserable Than Ever (Jean M. Twenge) Not Everyone Gets A Trophy: How to Manage Generation Y (Bruce Tulgan) Resources and Additional Reading n-gen People Performance White Paper: http://www.ngenperformance.com/pdf/ white/ManagingGenDivide.Overview.pdf Life Course Associates (Neil Howe): http://www.lifecourse.com/