e-ProMIS
advertisement

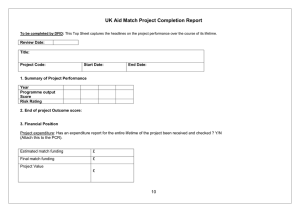
Using Technology in Monitorin g and Evaluation (e-ProMIS) MINISTRY OF DEVOLUTION AND PLANNING. M&E DEPARTMENT WELIME Monitoring & Evaluation Is a management tool for ensuring or determining effectiveness, efficiency, impact and sustainability. It has continuously been improving over time From traditional M&E to Results based M&E In Kenya, M&E was pursued in Ernest from 2004 during the ERS period and now in the vision 2030 period Definations • Monitoring- Is a Continuous function, • Uses systematic methods for collection of data on specified indicators • Evaluation - Systematic and objective assessment of an on-going or completed project, programme or policy (including its design, implementation and results). Foundation for M&E For M&E to be effective, it must approach issues by a specific logic Is this basic logic that allows the tool to identify facts possibly hidden to a casual eye and allow directing on what should be. This is the logic that we intended to get effected through technology. (Logframe) Is a tool for improving the planning, implementation, management, monitoring and evaluation of policies, programmes and projects. It is a way of structuring the main elements and highlighting the logical linkages between them. It helps to identify the expected causal links in the results chain, i.e., inputs + processes – outputs – outcomes - impact What can we use it for? Improving quality of project and program designs by: ■ Summarizing design of complex activities. ■ Assisting the preparation of detailed operational plans. ■ Providing a base for activity review, monitoring, and evaluation. ADVANTAGES: ■ Ensures that decision-makers ask fundamental questions and analyze assumptions and risks. ■ Calls for increased engagement of stakeholders in the planning and monitoring process. ■ When used dynamically, is an effective management tool to guide implementation, monitoring and evaluation. Cont’ DISADVANTAGES: ■ If managed rigidly, stifles creativity and innovation. ■ Training and follow-up are often required. NOTE: Presentation of the Logframe is usually in a vertical and Horizontal flow Vertical Logic Tests whether the sum of activities and lower level results is sufficient to achieve the higher level results. i.e Are all the activities listed under a particular output statement sufficient to achieve the output? Will all outputs listed under a particular outcome be sufficient to achieve the planned outcome? Will the outcomes listed under a strategic result (Goal) be sufficient to achieve the strategic result? Risk in Vertical logic There remains a risk that our assumptions at planning stage could be wrong, e.g. for a conference, Invite 50 people, book a venue, bring facilitators etc does this really mean we have achieved the target of holding a conference!. ……….. Why? The Log frame identifies such critical planning assumptions in order to reduce the risk of failure. Example Logframe Narrative Summary Means of Indicator Verification s Goal Sample survey Purpose/objectiv e /Outcome Improved transport system Outputs Interviews Standard Gauge railway line Observation. Interview Assumption s/ Risks Cont’ Narrative Summary Activities 1.Laying rail tracks Resources Means of Assumptio Indicators Verification ns/ Risks Main Benefit When used dynamically, is an effective management tool to guide implementation, monitoring and evaluation. Only a complete causal analysis will lead to a results framework that would ensure results are achieved and that development partners can identify their roles. Application of Logframe in the system The M&E Module In view of the need to monitor the realization of outcomes at the national level, and by fact that this are closely related to implementation of projects a relation is established between the projects and the targets set at various levels of results i.e output and outcome levels as illustrated. Outcome Outcome indicator Target Project Project weight in relation to the target e.g Improved quality of Education Pupil :teacher ratio 43:1 i 30% ii 25% iii 45% Textbook: pupil ratio 1:3 lower primary 1:2 higher primary i ii i ii Data Entry - M&E Application Reports from the System Locatio Outcome or Indicator baseline target Achiev’. n output