Make History Come Alive: Economics and Common Core
advertisement

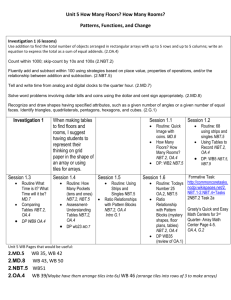
Make History Come Alive: Economics and Common Core Midwest Economic Education Conference May 23-24, 2013 Grant Black UMSL Center for Entrepreneurship and Economic Education Common Core Highlights • • • • • • • Reading and writing across the curriculum Increased emphasis on informational reading Comprehension and collaboration Presentation of knowledge and ideas Content-specific vocabulary Problem solving and reasoning Focused mathematical processes and proficiency Economics and Common Core • • • • • • • • Interdisciplinary connections Analytical thinking and reasoning Problem solving Informational texts Content vocabulary Math applications Data analysis Research Examples • Two elementary curricula using economics to address social studies and Common Core standards – The Louisiana Expansion – Kaleidoscope, USA – pcs.umsl.edu/econed The Louisiana Expansion • Thematic, interdisciplinary unit that brings this historical event to life for students • 8 interactive lessons: stand alone or as a unit • Teaching strategies and activities include: games, plays, creating a timeline, journaling, worksheets, discussions, group presentations, critical thinking, mathematical calculations and reasoning COMMON CORE STANDARDS CORRELATION FOR LOUISIANA EXPANSION Standards/Lessons 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Speaking & Listening SL.4.1a, SL.5.1a Common Core Connections: Reading for Informational Text RI.4.3, RI. 5.3 l l l l l l l l Writing W.4.3, W.5.3 W4.4, W.5.4 •Speaking and listening l l l l l l l l W.4.7, W.5.7 W.4.8, W.5.8 W.4.10, W.5.10 l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l Mathematical Practices •Reading for Informational Text MP.1 MP.2 MP.3 MP.4 MP.5 MP.6 l l l l l l Operations and Algebraic Thinking •Writing 4.OA.3 5.OA.2 l l Numbers and Operations in Base Ten •Math 4.NBT.1, 5.NBT.1 4.NBT.4 4.NBT.5, 5.NBT.5 4.NBT.6, 5.NBT.6 5.NBT.7 l l l l l Measurement and Data 4.MD.2 l Sample Lesson 8: Worth the Trouble? • Students learn about Gross Domestic Product (GDP) • Look at current day GDP for the US and GDP in the 13 states that were part of the Louisiana Territory • Student learn about resources and the circular flow of the economy • Students work in groups to research information about the 13 states GDP Activity • Divide into groups of ~5 • Each group represents a country with its own economy • Each group should name its country • Each group gets an “economy bag” • Each group calculates its own GDP – Calculate market value for each good • Market Value = Quantity x Price – Calculate GDP by adding up market values for all goods • Each group calculates per capita GDP – Per capita GDP = GDP / population Price List • Buttons 15 ₵ • Cotton swabs 10₵ • Pipe cleaners 5₵ • Colored sticks 25₵ • Foam cutouts 30₵ • Toothpicks 2₵ Calculating GDP (Activity 8.1) Good Quantity Produced Price Total Example: Button 2 15₵ 30₵ Our Country’s GDP ___________ GDP Report (Visual 8.1) Country Gross Domestic Product Per Capita GDP Kaleidoscope, USA • Thematic, interdisciplinary unit in which students live history as community developers from colonial period onwards • 12 interactive lessons in 5 units • Students use economics, geography, language arts, science and math skills to develop their own fictitious community from a proprietor colony into an industrialized community and eventually into a community of the future • Teaching strategies and activities include role playing, making choices about colony sites, developing advertisements, writing persuasive letters, predicting the community of the future, and developing land-use graphs COMMON CORE STANDARDS CORRELATION FOR KALEIDOSCOPE Standards/Lessons 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Speaking & Listening SL4.1.a-d, SL.5.1.a-d SL.4.4, SL.5.4 Common Core Connections: RI.4.5, RI.5.5 RI.5.6 RI.5.7 l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l Reading for Literature RL.4.1, RL.5.1 RL.4.2, RL.5.2 RL.4.3, RL.5.3 RL.4.6, RL.5.6 RL.5.9 •Reading for Informational Texts and Literature l l l l Reading for Information RI.4.9, RI.5.9 •Speaking and listening l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l Number & Operations in Fractions 4.NF.3, 5.NF.1, 5.NF.2 4.NF.4, 5.NF.4 l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l l Operations & Algebraic Thinking 4.OA.1, 5.OA.2 4.OA.2, 5.OA.3 4.OA.3 Number & Operations in Base 10 •Writing 4.NBT.5 4.NBT.6, 5.NBT.6 Writing W.5.1.a-d •Math W.5.2.a-e W.4.3.a-e, W.5.3.a-e W.4.4, W.5.4 W.5.5 W.5.6 W.4.7, W.5.7 W.5.9.a-b W.4.10, W.5.10 l l l l l l l l l Sample Lesson: 1650 - Incentives • Students identify resources needed in the colonies • Students explore colonists’ opportunity costs • Students learn about economic incentives and their effect on behavior • Students analyze incentives that motivated people to settle colonies in the 1600s • Students write advertisements, based on particular incentives, to entice particular people to their colony Incentives Activity • Divide into same groups • Each group is the proprietors of a colony • Each group reads one of three vignettes about why some people came to the colonies • Each group answers these questions: – Why may the people be willing to leave their home and move to a new colony? – What opportunity costs may those people have faced by moving to a colony? • Each group develops a written advertisement using the incentives identified in the vignettes to entice people to move to its colony Thanks • Questions? • More information: – UMSL Center for Entrepreneurship and Economic Education – 314-516-5248 – econed@umsl.edu – pcs.umsl.edu/econed