Chapter 12 GDP and Growth
advertisement

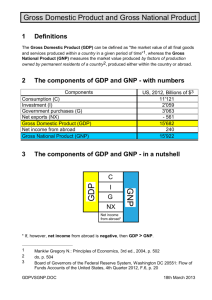
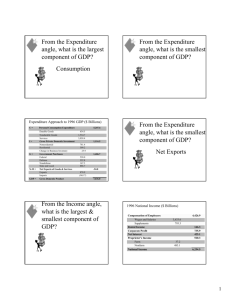
Chapter 12: GDP and Growth Section 1: Gross Domestic Product Section 2: Business Cycles Section 3: economic Growth WRITE ALL BLACK FONT THANGS Section 1: Gross Domestic Product Nation income accounting • A system that collects macroeconomic statistics on production, income, investment, and savings Gross Domestic Product • The dollar value of all final goods and services produced within a country’s boarders in a given year Section 1: GDP types of goods Intermediate goods • Goods used in production of final goods Durable goods • Goods that last for a relatively long time such as refrigerators, cars, and DVD players Nondurable goods • Goods that last a short period of time, such as food, light bulbs, and sneakers Different GDP’s Nominal GDP • GDP measured in current prices Real GDP • GDP expressed in constant, or unchanging, prices Not gdp….. Gross National Product • The annual income earned by U.S. owned firms and U.S. citizens Depreciation • The loss of capital equipment that results form normal wear and tear How we add this up… GDP + income earned outside the U.S. by U.S. firms and citizens – income earned by foreign firms and foreign citizens located in the U.S. = GNP GNP – depreciation of capital equipment = Net Nation Product Net Nation Product – excise taxes = National income Supply and Demand to the Aggregate supply • The total amount of goods and services in the economy available at all possible price levels Aggregate demand • The amount of goods and services in the economy that will be purchased at all possible price levels Section 2: Business Cycles Business cycle • A period of macroeconomic expansion followed by a period of contraction Business cycles Expansion • a period of economical growth as measured by a rise in real GDP • Peak, contraction, trough, expansion • waves ion’s Recession • A prolonged economic contraction Depression • A recession that is especially long and severe Stagflation • A decline in real GDP combined with a rise in price level Government influence over this cycle Only a few ways government can help Taxes Federal Interest Rates Government Spending Section 3: Economic Growth Measuring Economic Growth • We can use GDP to measure standard of living, which relates to material goods. • We cannot use it, however as a complete measure of people’s quality of life. Section 3: Economic Growth Saving and Investment • Income that is not used for consumption is called saving. • The proportion of disposable income that is saved is called the savings rate. Section 3: Economic Growth Technological Progress • Technological Progress is an increase in efficiency gained by producing more output without using more inputs. • Causes of Technological Progress Scientific Research Innovation Scale of the Market Education and Experience Natural Resource Use