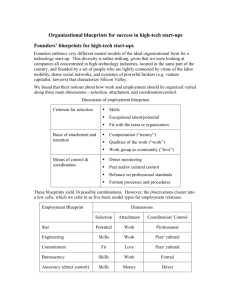
Understanding Basic Blueprint Concepts
advertisement

ESL Resource for Aerospace Pre-Employment: AIR UNIT 1 Brian Briggs Community Colleges of Spokane Press Space Bar to continue What will I learn in this lesson? The definition of a blueprint Important vocabulary and pronunciation The difference between CAD and CAM Common parts of a blueprint Basics of measurement: parts of an inch What is a blueprint? A blueprint is a plan or design which describes how a product should be made. It shows the measurements, dimensions, and materials. In the past, blueprints were drawn by hand on special blue paper. Today, many blueprints are made on a computer using a special program called CAD (Computer Aided Drafting) Reading Blueprints To read a blueprint, it is important to understand the special vocabulary. You must be able to speak the language of blueprints. It is a universal language. Important words to know- Line \ˈlīn\ Dimension \də-ˈmen(t)-shən\ Section \ˈsek-shən\ Process \ˈprä-ˌses\ Geometric positioning \ˌjē-ə-ˈme-trik pə-ˈzi-shəniŋ\ Note \ˈnōt\ Tolerance \ˈtä-lə-rən(t)s\ Material \mə-ˈtir-ē-əl\ Lines give a shape to the object and details about it. Dimensions give the size and location of parts and shapes. How big are the parts? Where do the parts go? Sections show how the object looks inside if it were cut apart. Processes explain how the part is to be produced. Geometric positioning shows exactly how far apart objects should be. Notes should be clearly lettered (printed). Tolerances show exact measurement and dimensions of finished surfaces. Materials are used for making parts. The blueprint also includes information about the weight, strength, and hardness. Some common materials are iron, steel, aluminum, carbon fiber, fiberglass, titanium, and rubber. CAD Computer-Aided Drafting (CAD) is a computer program which helps you draft or draw blueprints on a computer. CAM CAM stands for Computer-Aided Manufacturing. Things you will see on most drawings: Name of the part Quantity (how many are needed) Drawing number Dimensional tolerance Material Measurement Linear or straight line measurement Measured point Reference point Line of measurement Basic size= 7.5 Inch units Drawings might use either inch units, metric units, or both! Fractional parts of an inch 1/64”, 1/32”, 1/16”, 1/8”, 1/4”, 1/2” Decimal (mils) parts of an inch .010”, .050”, .100”, and .500” Metrics Metric dimensions are usually given in millimeters. If you need to change measurements from one system to another, please use a conversion table. Review Go to the quiz and see if you understand the information. Unless otherwise specified, this work by Air Washington is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 United States License.