and `table`
advertisement

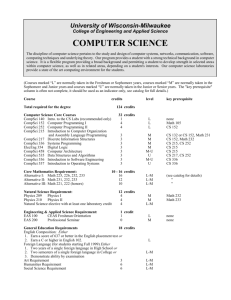
COMPSCI 280 S2 2014
Enterprise Software Development
Connecting an MVC application to a database
Jim Warren, jim@cs.auckland.ac.nz
Today’s learning objectives
To be able to program the key components of a C#/.NET
MVC application for
2
Establishing a database connection
Defining a data model for its tables
Querying the database
Presenting the user a view of the results
To gain familiarity with use of the MVC pattern and its
application to a Web application in practice
COMPSCI 280
The Model-View-Controller approach
Last lecture we introduced the MVC pattern and instantiated a
default Internet Application template for MVC in C#/.NET
Today we want to learn more about the MVC components and
other supporting files of the application so we can integrate the
application with our own database
The Model will define the database connection and
map C# classes to the database tables
The View will be tailored to present information
from a table
The Controller will execute database
queries and return data as parameter to the View
See http://www.asp.net/mvc/tutorials/older-versions/overview/asp-net-mvc-overview
3
COMPSCI 280
Getting MySQL and .NET to play
together
Principles are the same regardless of the database
solution
4
Get the infrastructure (DBMS and its tools)
Set up a database and get its server running
Establish interoperability of the database and the .NET
environment
.NET is proprietary to Microsoft, so they’d prefer you ran
Microsoft SQL Server (‘Express’ version is included Visual
Studio) rather than a competitor such as the free MySQL
Add to your program a ‘connection’
This specifies the running DBMS service, which database (set
of tables, views etc.) you want and your ‘login’ as an authorised
user on that database COMPSCI 280
Specifics
Get MySQL running
I did this by installing XAMPP to get MYSQL, Apache, XAMPP
Control Panel and PHPMyAdmin
Then just start Apache* and MySQL in XAMPP Control Panel
Used PHPMyAdmin to build an employee database with an
employee table, and also to add a user “jim”
Establish interoperability of the technologies
Installed MySQL Connector Net 6.7.5
Did Project/Add Reference/Browse in VS to add the MySql.Web.dll
and MySql.Data.dll from ConnectNet's Assemblies\v4.5
subdirectory
* Apache only needed for PHPMyAdmin - .NET will use Internet Information Server (IIS)
Express to serve the applications Web pages
5
COMPSCI 280
Add a connection
Go into Web.config (from Solution Explorer)
It’s an XML file with project metadata
There’s already a connection defined
It’s used for the user accounts that are built into this project by
default
<connectionStrings>
<add name="DefaultConnection" connectionString="Data Source=
(LocalDb)\v11.0 ... 62020.mdf" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
We’ll put in another ‘add’
The connection name will come up
in the Model
<add name="MySqlConnection"
connectionString="Server=localhost;Database=employee;Uid=jim;Pwd=passw
ord" providerName="MySql.Data.MySqlClient" />
Part of that DLL we got from MySQL
Connector Net
6
COMPSCI 280
The MySQL user we defined (and its
password! – note you can encrypt
part of configuration for security:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/enus/library/ms254494(v=vs.110).aspx
Our Model: Employee.cs
First ‘using’ directive is added for
referencing the DbContext object; next
two are for the ‘key’ and ‘table’
decorators
...
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace MvcLetsConnect.Models
Use that connection we added to the
{
Web.config file
public class EmployeesContext : DbContext
{
public EmployeesContext() : base("MySqlConnection") { }
}
public DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
Our context’s DbSet ‘Employees’
will be a collection of objects of
type Employee
[Table("employee")]
The table in
public class Employee
MySQL is named
{
‘employee’
[Key]
public int IDnum { get; set; }
public string Surname { get; set; }
public string GivenNames { get; set; }
public DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; }
}
Entity Framework can create the table entity definitions
graphically/automatically for SQL server, but still in beta for
MySQL
7
COMPSCI 280
Define properties of
this class with
names matched to
table fields in
MySQL ([Key]
identifies IDnum as
the primary key as
set in MySQL)
Handout 01
Our
Controller
C# moment: the .Format
method of the String class is
handy for laying out output
public ActionResult Index()
{
using (EmployeesContext db = new EmployeesContext())
{
int j = db.Employees.Count();
ViewBag.j = String.Format("We have {0} records.",j);
var data = db.Employees.ToList();
return View(data);
}
The HomeController.cs file includes the handler for the index (home) page
Creating an instance of the Employees context initiates the database
connection
8
Putting it in a ‘using’ statement is tidy – invokes the connection’s dispose method,
which closes the connection when we’re done serving up the page
We can then invoke methods on the Employees collection such as to
.Count() them or assign the whole collection as an enumerable list to be
pointed to by a generic (‘var’) element that we pass to the View
COMPSCI 280
Our
View
Using the Index.cshtml file we display the data
for the user on the home page
The @model keyword in Razor says
that the data passed to the View will
be interpreted as an enumerable list of
Employee objects as defined in the
Model section of the project
...
</hgroup>
@model IEnumerable<MvcLetsConnect.Models.Employee>
@{
ViewBag.Title = "People";
Using C#-like syntax in a Razor code
WebGrid grid = new WebGrid(Model);
block we instantiate an instance of the
}
WebGrid helper on the Model data
<h2>People</h2>
@ViewBag.j
@grid.GetHtml(columns: new [] {
Razor functions put the text
grid.Column("Surname","Last Name"),
of element ‘j’ of the ViewBag
grid.Column("GivenNames","Given Names"),
and the instance of a WebGrid
grid.Column("DateOfBirth","Date of Birth")
into the body of the HTML.
})
9
COMPSCI 280
Each WebGrid Column is
instantiated on an exact
property name of the
Employee class from the
model
The result
10
COMPSCI 280
Handout 02
The result: a closer look
In Chrome, if you right-click and select
‘Inspect Element’ it’ll open a window
showing the HTML (bottom left) and
the CSS styles that have been applied
(bottom right)
11
COMPSCI 280
Handout 02
A closer look (contd.)
The WebGrid and
ViewBag aren’t there
Just as the C# code
has been converted
to CIL for the CLR,
the View’s Razor
syntax has been converted to HTML for the browser to consume
HTML moment: The <table> tag defines the start of a table, with a
<tr> to start each row and a <td> (‘table data’) to start each cell
12
Note that Chrome’s Inspect Element navigation has opened the elements
directly leading to the cell we inspected but, for instance, has the table header
definition (‘thead’) closed
COMPSCI 280
Handout 02
A closer look (contd. again)
If we inspect the ‘Given Names’ column header, we see that the WebGrid helper
did even more for us
13
It built a hyperlink (HTML ‘a’ – for ‘anchor’ – tag) which sends back to the Controller
a request for the page in a different sort order (and the Controller automatically
knows how to handle this, too!)
Note how the Employee class property name (‘GivenNames’) is used in the URL
If we had had more rows, the WebGrid would’ve also built us links for paging the data
COMPSCI 280
Handout 02
Making your mark with style
We can add a style parameter to the constructor for a grid.Column
@grid.GetHtml(columns: new [] {
grid.Column("Surname","Last Name",style:"surname"),
In the Site.css file (under Content in the Solution Explorer) we can create a
corresponding style definition to apply to any element of class surname
And the VS intelli-sense greatly assists writing the CSS code!
}
.surname {
font-style: italic;
width: 150px;
We can also change any HTML tag’s styling for the whole site by editing in
Site.css
E.g. to make all the rows of any table amber (not depicted in next slide)
tr {
}
14
background-color: #ffe030;
COMPSCI 280
Handout 02
Styling result
Chrome has picked up to apply the
style to the content (note how the
Inspect Element tooltip [left] shows
the cell as ‘td.surname’)
The class attribute of each body cell in
the Last Name column has been given
the value we specified
n.b. You’ll probably need to hit
Refresh on your browser to get the
style change to show up
15
COMPSCI 280
Handout 02
Another query syntax: LINQ
Language Integrated Query (LINQ)
Can modify our HomeController.cs to read:
using (EmployeesContext db = new EmployeesContext())
{
var emp = from e in db.Employees
where e.DateOfBirth.Year < 1975
select e;
return View(emp.ToList());
}
Very similar to SQL, but actually part of .NET (i.e. integrated
with the C# language)
16
Differs in leading with ‘from’ and ending with ‘select’ (a better order
for the intelli-sense!)
Note that the class of the objects returned by the query (each row,
the members pointed to by emp) has to align to our @model in the
COMPSCI 280
Handout 02
View definition
Where we’re up to
We’ve now been introduced to the MVC approach in
C#/.NET
And we’ve seen how to connect it to a MySQL database
Now…
17
Work the first labsheet (if you haven’t already)
Look at Assignment 2 (if you haven’t already)
Make a start – use your break time wisely and don’t be afraid to
read ahead into weeks 7 and 8
In weeks 7 and 8 we’ll extend what we can do with MVC in
C#/.NET and get a firmer understanding of what we’ve used so far
COMPSCI 280
Handout 02