Lesson Planning Documentation PowerPoint
advertisement
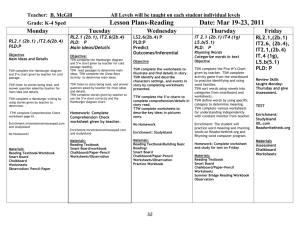
Instructional Planning Documentation Outcomes • Develop an understanding of Instructional Planning Documentation rubric • Understand the process of lesson planning • Be able to develop measurable objectives • Use the lesson plan check list to analyze current lesson plans Fact or Fib • Objectives come from1st page of text book Fib • Objectives are driven by the standards Fact • Objectives and activities are the same thing Fib • Objectives state the learning outcome Fact Fact or Fib • Objectives are not necessary when lesson planning Fib • Daily objectives are not necessary Fib • Standards and objectives are not the same thing Fact • Assessment data is not used in daily lesson plans Fib The teacher designs and plans instruction that develops students’ abilities to meet Arizona’s Academic Standards and District Assessments. TIIES: Instructional Planning Documentation • Based on alignment to state standards and effective use of assessment data, daily written lesson plans are sequential, easy to follow and includes: – – – – Measureable objectives with aligned assessments Essential sub-objectives Modifications and Accommodations Materials/ Resources Needed • Long Range Plans or Pacing Guides include: – Notations of standards that have been taught – Sequenced timeline of standard that remain to be taught. Know Your Target!!! Whole to Parts Rubicon Essential map Standards Pacing Guides and curriculum maps Diary Map Daily Lesson Plans (IEPs, 504s, ELP standards) Assess Consensus Map Long Range Plans TIIES: Instructional Planning Documentation • Based on state standards assessment data and sequential objectives: – Measureable objectives with aligned assessments – Essential sub-objectives – Modifications and Accommodations – Materials/ Resources Needed • Long Range Plans or Pacing Guides – Notations of standards learned – Sequenced timeline of standard that remain to be taught. Where Do My Objectives Come From? • Standards-Common Core, English Language Acquisition Standards • Pacing Guide/Curriculum Map • Assessment Data Whole Objectives W WHAT: CONTENT/ STANDARDS H HOW: PROCESS/ ACTIVITY O OBSERVABLE VERB (s) L LEARNING OUTCOME E EVALUATION W + H + O = L + E = WHOLE OBJECTIVE WHOLE Objective Essential Questions Component Essential questions W 1. 2. What content/ standards need to be taught? What is the essential idea for the PO? What is the time frame and level of understanding of my students ? H 1. 2. What PO am I teaching? What will the students need to able to do to reach the planned level of understanding? What learning multisensory modalities can I use? 3. O What overt verb best describes what I want students to do with the ‘what’ and “how’ of the lesson? L When I combine the what and how of the lesson does it provide a full picture of what students will be able to do by the end of the class? E What assessment, evidence or final product will demonstrate individual levels of proficiency of the objective? Where do the four PLC questions fit within the WHOLE Objective? • What do we expect students to learn? • How will we know what students have learned? • How will we respond to students who aren’t learning? • What will they do if they already know it? Activity vs. Objective • Tables group will sort the strips into two categories: activities and objectives. • When finished be prepared to share the differences between the two categories. Activities Objectives TSW complete problems 1-10 page 24 with w 80% accuracy. TSW demonstrate proficiency in multiplying 2 digit by 2 digit numbers with 80% accuracy by completing pg 24, 1-10. TSW Read the story and answer the questions at the end with 100% accuracy. TSW recall important events and make inferences from a story by answering the questions at the end of the selection with 100% accuracy. TSW do a word sort categorizing words into 2 groups 8 out of 10 times correctly. TSW distinguish the difference between nouns and verbs by doing a word sort with 8 out of 10 correct. TSW work in small groups to compare and contrast characters from a story. Accuracy will be measured by a 4 point rubric. TSW compare and contrast the main characters from a story by creating a Venn Diagram. Accuracy will be measured by a 4 point rubric. Activities Objectives TSW complete problems 1-10 page 24 with w 80% accuracy. TSW demonstrate proficiency in multiplying 2 digit by 2 digit numbers with 80% accuracy by completing pg 24, 1-10. WHAT TSW Read the story and answer the questions at the end with 100% accuracy. WHAT TSW recall important events and make inferences from a story by answering the questions at the end of the selection with 100% accuracy. TSW do a word sort categorizing words into 2 groups 8 out of 10 times correctly. WHAT TSW distinguish the difference between nouns and verbs by doing a word sort with 8 out of 10 correct. TSW work in small groups to compare and contrast characters from a story. Accuracy will be measured by a 4 point rubric. HOW TSW compare and contrast the main characters from a story by creating a Venn Diagram. Accuracy will be measured by a 4 point rubric. Identify Verbs that are difficult to use in WHOLE objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. discuss create match understand summarize in writing review brainstorm talk about Identify verbs that are difficult to use in WHOLE objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. discuss create match understand summarize in writing review brainstorm talk about Why are they difficult? They are not MEASURABLE! Now what am I supposed to do? Identify WHOLE Obj. Components By the end of the lesson, students will demonstrate distributive property of multiplication by building arrays using color tiles. Evidence of proficiency will be measured by a Problem Solving Rubric. WHOLE Obj. Components • By the end of the lesson, students will demonstrate the Distributive Property of Multiplication by (W) building (O) arrays using color tiles. (H) Evidence of proficiency will be measured by a Problem Solving Rubric. (E) • L) - students will demonstrate the Distributive Property of Multiplication (W) by building (O) arrays using color tiles. (H) Let’s look at your lesson plans! • • • • Individually choose an objective from your lesson plans. Determine whether it is an activity or an objective Revise if your objective if needed Share your revisions with your table partners. Sub-Objectives • – – Data driven! Summative and formative assessments Task analyze • Prerequisite knowledge to be successful • Stepping stones to reaching your WHOLE objective Essential Learning Outcome • Math Standard (Gr. 4) – 4.NBT.5 Students will be able to multiply a whole number up to 4 digit by 1 digit and multiply two, 2 digit numbers using strategies based on place value and properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays and/or area models. • Rubicon Skill D: – Solve multiplication equations based on the Multiplication Principle of Counting and justify reasoning using arrays, charts, systematic lists such as tree diagrams. • Daily Objectives: – By the end of the lesson, students will demonstrate the Distributive Property of Multiplication by building arrays using color tiles. Evidence of proficiency will be measured by a Problem Solving Rubric. • Possible Sub-Objectives: – Properties of multiplication – Arrays Let’s Practice • As a group choose one objective from your lesson plans that you brought and identify the appropriate sub-objectives for that lesson. Objective Sub objectives TIIES: Instructional Planning Documentation • Based on state standards assessment data and sequential objectives: – Measureable objectives with aligned assessments – Essential sub-objectives – Modifications and Accommodations – Materials/ Resources Needed • Long Range Plans or Pacing Guides – Notations of standards learned – Sequenced timeline of standard that remain to be taught. Modifications and Accommodations • ALL kids are capable of success NO EXCEPTIONS! • How do I do this? – Modifications- Changing the content or materials for an individual or small group of students – Accommodations- Adjustment made to student participation or teacher actions to enable learning to occur Modifications (What) Accommodation (How) •Moving up or down on Bloom’s Taxonomy based on student need • Adjust material to instructional level (lower level reading material on same topic) Example 1: Students working on 23 digit multiplication and an LD student may need to be working on a single digit multiplication in order to be successful. •Extended time •Frequent breaks •Read, reread, clarify directions •Read out loud the math, writing, science portion of assessments •Take assessments in a small group setting •Enlarge print •Script •Allow verbal responses Example 2: Eighth grade student who reads at a 4th grade level needs content material at a 4th grade reading level. Lesson Plan Checklist What are my objectives for this lesson? (WHOLE and sub-obj.) What assessment data drives this lesson? What materials and resources will I use? (Do I need supplemental materials?) How will I meet the needs of all of my students? (Modifications and Accommodations) What measureable evidence will I use for student learning documentation? Mentor Support My Big Campus- Application Points Use the lesson plan checklist to develop a lesson that you will upload into My Big Campus. Post a question to the group that you would like feedback on in regards to your lesson.