CCNP Network Route -BGP Part
advertisement
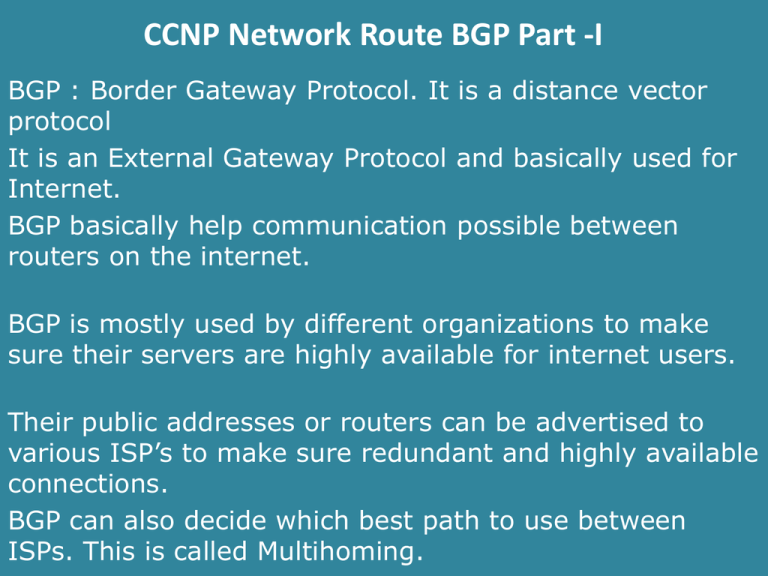
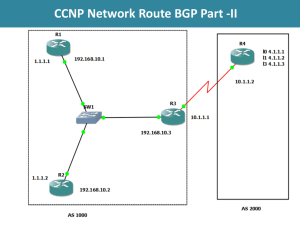
CCNP Network Route BGP Part -I BGP : Border Gateway Protocol. It is a distance vector protocol It is an External Gateway Protocol and basically used for Internet. BGP basically help communication possible between routers on the internet. BGP is mostly used by different organizations to make sure their servers are highly available for internet users. Their public addresses or routers can be advertised to various ISP’s to make sure redundant and highly available connections. BGP can also decide which best path to use between ISPs. This is called Multihoming. CCNP Network Route BGP Part -I BGP runs on TCP and uses port 179. BGP uses TCP because its reliable. BGP only sends an update when a change occurs. BGP is very slow but has the biggest metric & routing table of all protocols. Tuning BGP with attributes is important other wise it will use hop counts for best path irrespective of the bandwidth or speed. There are four kind of packets in BGP. 1. Open: It starts the BGP session 2. Keepalive: Its make sure neighbor is available. 3. Update: It make sure Network is reachable. 4. Notification: If an error occurs it notifies and closes the session. CCNP Network Route BGP Part -I Tables: Three kind of tables: BGP Table: It consist of all BGP routes. Routing Table: It consist of best routes. Neighbor Table: It consist of configured neighbors, because BGP does not configures neighbors automatically so we have to do it manually, however BGP dynamic neighbor is an exception. Please visit www.cisco.com for more info about BGP Dynamic Neighbors. BGP supports two kind of subprotocols. 1. IGBP [ Internal] 2. EBGP [External] CCNP Network Route BGP Part -I Autonomous system: In BGP AS is very important. It basically represents all networks in a specific group. IBGP: is when a neighbor relationship is established between two routers in the same AS or Autonomous System. EBGP: is when a neighbor relationship is established between two routers in different AS. Note: For IBGP its not necessary to form neighbors only if the routers are directly connected. It can form neighbors through routers as well. Transit AS: is when an ISP exchange route through our router running BGP. CCNP Network Route BGP Part -I R1 with IP 192.168.10.1 R2 with IP 192.168.10.2 AS 1000 fro IGBP CCNP Network Route BGP Part -I Basic BGP Configuration: R1(config)#router bgp 1000 Now we have another router R2 and we wish to establish a neighbor relationship with it for that we will use the following command on R1. Note R1 has ip address of 192.168.10.1 and R2 has ip address of 192.168.10.2 R1(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.10.2 remote-as 1000 But at the moment R2 is not configured so if type command: R1(config-router)#do show ip bgp summary It will show the below: BGP router identifier 192.168.10.1, local AS number 1000 BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1 Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 192.168.10.2 4 1000 0 0 0 0 0 never Active Note: Active is not good as it is finding routes and not working CCNP Network Route BGP Part -I Now on R2 we issue the below commands R2(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.10.1 remote-as 1000 R2(config-router)# *Mar 1 00:41:04.675: %BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 192.168.10.1 Up Now if we issue the same command on R1 R1(config-router)#do show ip bgp summary BGP router identifier 192.168.10.1, local AS number 1000 BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1 Neigh V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent 192.168.10.2 4 1000 7 TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/p 7 1 0 0 00:03:06 0 Note: State has changed from Active to a number which is good. CCNP Network Route BGP Part -I To create Neighbors with EGBP we only change AS which will not be the same.