Appendix Lesson Plan #1 Memory
advertisement

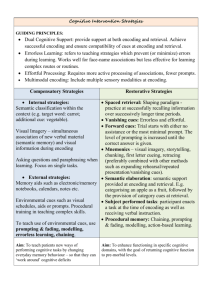
Information Processing Module 20 What is Memory? Process of encoding, storage, and retrieval. Learning that persists over time. Encoding ▫ Get info in Storage ▫ Retain the info Retrieval ▫ Getting the information out In-Class Activity—A Look Into Memory Take out a sheet of paper Write down, in order, all responses that come to mind Ready? What are the names of the seven dwarfs in the story of Snow White? Don’t ask a friend! What are the names of the seven dwarfs in the story of Snow White? Difficult? Why? ▫ Never learned the names (encoding) ▫ Length of time (storage) ▫ Distractions (retrieval) What if you had a list to choose from? Grouchy Sleepy Hopeful Dopey Puffy Lazy Bashful Shorty Doc Gabby Smiley Shy Sniffy Dumpy Pop Cheerful Nifty Wheezy Fearful Jumpy Droopy Wishful Sneezy Grumpy Teach Happy Stubby What are the names of the seven dwarfs in the story of Snow White? The names… ▫ Sleepy, Dopey, Grumpy, Sneezy, Happy, Doc & Bashful Get more names correct with list? Why? ▫ Recall vs. Recognition What are the names of the seven dwarfs in the Disney movie Snow White? Feel like you knew a name but couldn’t recall it? Why? ▫ Tip of the tongue phenomenon ▫ Retrieval failure In-Class Activity – Part 2… Turn your paper over or fold in half Write down the names of the seven dwarfs Easier than before? ▫ Short term memory vs. long term memory Encoding: Getting Information In Automatic Processing ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Time Space Frequency Well-learned material Effortful Processing Encoding: Getting Information In Effortful Processing Ebbinghaus: Rehearsal & Overlearning How do we encode? Serial Position Effect How do we encode? Spacing Effect Distributed vs. Cramming Rehearsal Primacy & Recency What do we encode? Meaningful Information ▫ Personally meaningful ▫ Related to previously learned info Encoded Images ▫ Mental “pictures” ▫ Mnemonics ▫ Kids Please Close Our Front Gate Slowly What do we encode? Organized Information ▫ Chunking ROY G BIV Phone numbers… 867-5309 ▫ Hierarchies This might help you study… Let’s test your encoding! iclicker question According to the serial position effect, when recalling a list of words you should have the greatest difficulty remembering those: A) at the beginning of the list B) at the end of the list C) in the middle of the list D) at the beginning and the end of the list iclicker question You are most likely to automatically encode information about: A) Politicians names B) New phone numbers C) What you did before and after you ate breakfast D) What we learn today 19 Storage: Retaining the Information Sensory Memory Working/ Short-term Memory Long-term Memory Encoding Events Encoding Retrieval Retrieval Storage- Retaining the Information Sensory Memory Fleeting representation unless we attend Lasts for ~ second Iconic & Echoic Storage Working/Short-Term Memory 20 secs – couple minutes “Hold” a limited amount of info (7 +/- 2) No active processing = no short-term memories disappear Storage Long-Term Memory Info stored; can be retrieved Lasts indefinitely Can hold billions of pieces of info Storage- How do we do it? Synaptic Changes Pathway of neural activation creates a stored memory Path reinforced with use 24 Storage Stress Hormones Heightened emotions = stronger memories Boosts activity in memory-forming brain areas More replay= stronger connections Can we take a pill for this? Storage Implicit Memory ▫ Memory for procedures & skill acquisition ▫ Ex: Driving a car ▫ Cerebellum Explicit Memory ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Memory for facts & experiences Ex: Who was your first kiss? Hippocampus-temporary storage site Cortex Retrieval- Getting Information Out 3 Retrieval Types ▫ Recall: generate information ▫ Recognition: identify items ▫ Relearning: learn material for a second time 27 Retrieval Retrieval Cues: Anchor points used to access the info later 28 Retrieval Context Effects Remember better if cues present at encoding are present at retrieval Retrieval Mood-Congruent Memory Recall experiences consistent with current mood 30 Déjà Vu Familiar situation can trigger feelings of “I’ve been here before” Another Activity… 2 volunteers 1 with musical knowledge (majors, private lessons) 1 with little musical knowledge Retrieval & Expertise Expertise Development Central concepts become increasingly elaborated, organized & interconnected Iclicker Question When 80-year-old Ida looked at her old wedding pictures, she was flooded with vivid memories of the early years of her marriage, which she had not thought about in decades. The pictures served as powerful: A) Encoding cues B) Iconic memories C) Implicit memories D) Retrieval cues Iclicker Question Memory of facts is to ________ as memory of skills is to ________. A) Brainstem; Hippocampus B) Explicit Memory; Implicit Memory C) Automatic Processing; Effortful Processing D) Short-term Memory; Long-term Memory So could our memory ever be too good? The women who can’t forget… http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SoxsMMV538U&feature=related Mini-writing #9 You have a friend who is struggling in a class. Now that you know so much about memory, identify 2 effects that we have learned about in class that pertain to memory that could help him. Explain each effect and how each effect would improve his test performance. Effortful processing Serial position effect Meaningfulness Retrieval Cues Sleep Rehearsal Spacing Effect Mnemonics Hierarchies Overlearning Imagery Chunking Context Effects