Suturing Basics
advertisement

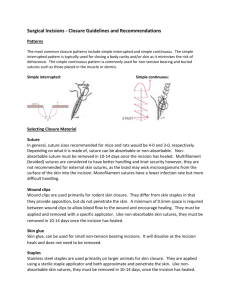
Suturing Basics Terren Trott Objectives • • • • Understand Basic Suturing Anatomy Indications for Suturing Materials and Preparation Suturing Techniques Options to Sutures • Dermabond – Superficial lacerations – Facial lacerations • Staples – – – – Commonly used on the scalp or huge lacerations Faster, lower infection, reduced inflammation Greater tensile strength CI: face, joints, hands • Steristrips • Healing by Secondary Intention – If wound has been open for more than 6 hours Suture Anatomy • Absorbable – Plain gut, FAST gut, vicryl, monocryl • Non-absorbable – Ethilon (Nylon) – Silk – Polypropylene (Prolene) • Monofilament Vs Polyfilament Suturing Preparation • • • • • • Hemostasis Anesthetic Irrigation Exploration Draping Suture selection Hemostasis • • • • Direct pressure and elevation Blood Pressure Cuff Lidocaine with Epinephrine Figure-8 stitch Anesthetic Name Onset Duration Max Dosing Lidocaine 1 – 5 minutes 1.5 – 2 hours 4mg/kg Lidocaine with Epi 1 – 5 minutes 2 – 3 hours 7mg/kg Mepivacaine 1 – 5 minutes 3 hours 5mg/kg Mepivacaine with Epi 1 – 5 minutes 4 – 5 hours 7mg/kg Bupivacaine 10 – 15 minutes ~4 hours 2.5mg/kg Bupivacaine with Epi 10 – 15 minutes ~8 hours 3mg/kg Anesthetic Pearls Epinephrine vasoconstricts Amides: have two ‘I’s in the name, esters have one ‘I’ Infiltrate with anesthetic slowly to reduce the burn Consider digital blocks Bicarb can be used to buffer lidocaine and reduce burning Withdraw on the syringe to make sure you’re not in a vessel What does lidocaine toxicity look like? • Early symtoms – Headache, nausea/vomiting, AMS • Late Symptoms – Seizures – Cardiac Arrythmias: PEA, vtach, torsades • Tx: Sodium Bicarb, IV Lipids Irrigation IRRIGATION IRRIGATION IRRIGATION IRRIGATION IRRIGATION IRRIGATION IRRIGATION Exploration • Radiograph/Ultrasound for foreign bodies • Digital exploration of scalp lacerations for skull fractures • Tendon injuries must be examined through entire course of anatomical range • Missed foreign objects are a common source of Emergency Department litigation Anatomic Site Skin Deep Duration Scalp 5-0, 4-0 Monofilament 4-0 Absorbable 6–8 days Ear 6-0 Monofilament N/A 4–5 days Eyelid 7-0, 6-0 Monofilament N/A 4–5 days Eyebrow 6-0, 5-0 Monofilament 5-0 Absorbable 4–5 days Nose 6-0 Monofilament 5-0 Absorbable 4–5 days Lip 6-0 Monofilament 5-0 Absorbable 4–5 days Face/forehead 6-0 Monofilament 5-0 Absorbable 4–5 days Chest/abdomen 5-0, 4-0 Monofilament 3-0 Absorbable 8–10 days Back 5-0, 4-0 Monofilament 3-0 Absorbable 12–14 days Arm/leg 5-0, 4-0 Monofilament 4-0 Absorbable 8–10 days Hand 5-0 Monofilament 5-0 Absorbable 8–10 daysb Extensor tendon 4-0 Monofilament N/A N/A Foot/sole 4-0, 3-0 Monofilament 4-0 Absorbable 12–14 days Suture Technique Pearls • “Approximate, Don’t Strangulate” • For proper wound eversion, the needle should enter the dermis at 90 degrees • Exit the wound equidistant from the entry site • Reduce tension with deep sutures • No matter how small the laceration, use universal blood precautions • Antibiotics are no substitute for thorough irrigation and cleaning • Shaving hair is a relative contraindication • Use only the minimum number of sutures, excess sutures provide a nidus for infection • Grasp needle ¾ of distance from tip • Use the forceps to grasp under the dermis to prevent crush injury Knot Tying Pearls • Knot throwing: throw as many knows as size suture material • 6-0 throw 6 knots • Knots are tied in opposite directions • Hand tie vs. instrument tie Simple Interrupted • Most commonly used technique to close skin • Attempt to keep all knots on one side • For uncomplicated wound closure Vertical Mattress • Large bite 1 – 1.5 cm from wound edge, cross equidistant to other wound edge. • Reverse the needle • Enter the dermalepidermal junction, 2 – 3mm from wound edge • Advantages: acts as both deep and superficial closure, reducing wound tension Horizontal Mattress • All entry and exit points are equidistant • Advantages: distribution of tension across greater area, improved wound eversion Corner Stitch • Advantages: approximation of corners and stellate lacerations without capillary compromise of the corner Running • Advantages: Faster • Disadvantages: one compromised stitch compromises entire suture Deep Sutures • To decrease tension and approximate tissues • Enter the tissue low and exit high so that the knot ties to the bottom References • http://www.jpatrick.net/WND/woundcare.ht ml