Costa levels - PowerPoint
advertisement

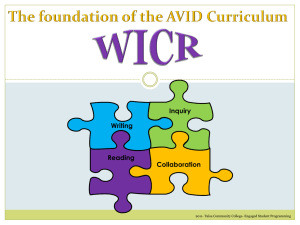
2011- Tulsa Community College- Engaged Student Programming 3 LEVELS OF QUESTIONING • Level 1 – Define • Level 2 – Analyze • Level 3 – Apply 2011- Tulsa Community College- Engaged Student Programming Extend Recall Paraphrase Rewrite Locate Find Repeat Restate Describe Remember Recognize Record Label List Discuss Name Define Tell Review Memorize Match Explain Express Generalize Report Show understanding State Give examples Identify Summarize 2011- Tulsa Community College- Engaged Student Programming Ask Level 1 questions to identify what students know • What do you know? • What did you record from your class notes about the lecture? • What is a formula or mnemonic device that will help you identify the steps necessary to solve the problem? Examples • What is a gene? • Define irony. • When did the American Revolution begin? 2011- Tulsa Community College- Engaged Student Programming Practice Imply Operate Compute Criticize Relate Illustrate Dramatize Use Differentiate Translate Experiment Analyze Debate Question Distinguish Change Pretend Discover Solve Categorize Contrast Compare Demonstrate Examine Interpret Prepare Infer Diagram 2011- Tulsa Community College- Engaged Student Programming Ask Level 2 questions to begin processing the information gathered, make connections and create relationships. • Can you break down the problem into smaller parts? • What can you infer from what you read? • Can you find a problem/question similar to this in the textbook to use as an example? • What is the relationship between ___ and ___? Examples • Compare and contrast genes and chromosomes. • Diagram and order the stages of photosynthesis. • Analyze the causes of the American Revolution. 2011- Tulsa Community College- Engaged Student Programming Predict Value Judge Justify Apply Measure Decide Rate Assess Choose Select Estimate Conclude Support Prove Model Summarize Multiple solutions Teach Check Solve Evaluate Explain Hypothesize Real-life 2011- Tulsa Community College- Engaged Student Programming Ask Level 3 questions to apply knowledge acquired and connections made to predict, judge, hypothesize or evaluate. • How do you know the solution is correct? How could you check your answer? • Is there more than one way to solve the problem? • How do you interpret the message of the text? • Is there a real life situation where this can be applied or used? • How would you teach this to a friend? Examples • Apply the Pythagorean theorem to the find the measurement of this triangle. • If there were a Constitutional amendment that prohibited ownership of weapons by citizens, how might American society be affected? • Imagine you were a soldier fighting in the Civil War. How would you feel? 2011- Tulsa Community College- Engaged Student Programming • Reword the question using other words from the same Costa level. • Construct a new question using words from higher or lower Costa levels. • Use several level one questions to create a level two or three question. • Relate ideas from the question to: a personal experience, a movie, to the “big” questions of life, or random words (to find “hidden connections”). • If you don’t know how to answer the question, develop a new question that you predict will have a similar answer but is easier to discuss. Example: Change “What caused the Civil War?” into “Compare and contrast the North and the South before the Civil War.” 2011- Tulsa Community College- Engaged Student Programming Steps to a successful tutorial session (Costa levels in parenthesis) 1. Read individual questions aloud (1) and evaluate their Costa level (3). 2. Develop level one questions into a level two or three question (3). 3. Brainstorm possible answers to the question (3). 4. Evaluate the brainstormed ideas (3) and discuss how well they answer the question (1). 5. Summarize this process (3). 6. Repeat as time allows. 2011- Tulsa Community College- Engaged Student Programming