Ruby Payne Teaching Strategies
advertisement

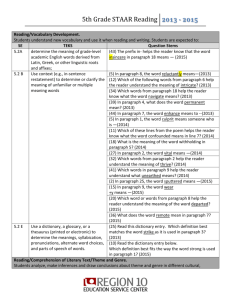
Number of words exposed to Economic group 13 million words Welfare 26 million words Working class 45 million words Professional Fostering Student Engagement What can teachers do to foster student engagement and create positive peer culture? Recent Research on the Achievement Gap with Ronald Ferguson. Harvard Education Letter. November/December 2006. www.edletter.org/current/ferguson.shtml Research shows children from poverty do not understand the “abstract”. Allow the student to sketch his/her understanding of a story, concept, vocabulary word or what they think about a person or idea. Mental Model Beginning Learner •Sensory-based, situated learning •Tied to what is already known Skilled Learner •Abstract respresentational world – formal schooling •Expertise 1. 2. 3. SCIENCE QUESTION/WRITING STEMS How for the Student Question Stem Defining and describing Knowledge • What is (are) ... • Where is (are) ... • Which is (are) ... • How is (are) ... Comprehension • What conclusions can you draw from ... • What observations did you make? Application • Why does ... work? • Sketch your mental model of ... Analysis • Explain how ... Synthesis • How could you explain ... to your friend? • Design a model of ... to represent ... • Write a letter to ... giving a summary of ... • What facts can you compile about ... • Rewrite the definition of ... in your own words. Evaluation • Describe the importance of ... SCIENCE QUESTION/WRITING STEMS How for the Student Question Stem Representing data and interpreting representations Knowledge • Describe what happens when ... Comprehension • Describe what happens when ... • Construct a model to explain your data ... Application • How could you organize your data to help you draw your conclusion? • How could you change the process/procedure to increase/decrease the ... Analysis • How can you sort the parts of ... • What order can you place the data in to make them easier to interpret? Synthesis • How could you compile the data/facts for ... • What plan do you have for collecting your data? • What format will you use to represent your data? Evaluation • What data will you use to evaluate ... • How could you verify the interpretation of your graph/table/map? • What is your interpretation of your data? QUESTION STEMS FOR FIFTH- AND NINTH-GRADE READING 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. In paragraph _____, what does _____ mean? Paragraph _____ is mainly about _____. From the article, the reader can tell … From the passage, the reader can tell … From the paragraph, the reader can tell … From what the reader learns about _____, which statement does not make sense? 7. How does _____ feel? 8. Why is it important … 9. Which of these is the best summary of the selection? 10. Look at this web (flow chart, graph, charts, etc.). Which detail belongs in the empty space? 11. An idea present in both selections is … 12. One way these selections are alike is … 13. One way these selections are different is … 14. Paragraph _____ is important because it helps the reader understand … 15. The reader can tell when _____, he/she will probably … 16. How does _____ feel? QUESTION STEMS FOR FIFTH- AND NINTH-GRADE READING (continued) 17. In paragraph _____, why is _____ sad? (happy, confused, angry, etc.) 18. What is this article mainly about? 19. What can the reader tell about _____ from information in this article? 20. The author builds suspense by … 21. One way this story resembles a fable is that … 22. In paragraph _____, the author uses the word _____ to emphasize _____. 23. Which of the following words is a synonym (antonym) for the word _____ in paragraph _____? 24. What is the overall theme expressed in this article? 25. Which of the following sentences from the article explains the author’s primary conflict? 26. The audience that would probably relate most to the article’s central message would be … 27. Why … 28. How ... SOCIAL STUDIES QUESTION STEM STARTERS Elementary (K–4) 1. What does the map (chart, drawing, timeline, graph) illustrate? 2. Which statement BEST explains (summarizes) _____? 3. What was the main cause of _____? 4. One advantage of _____ is _____. 5. The primary function (purpose, goal, objective) of _____ is _____. 6. Which of the following were consequences of _____? 7. What is the BEST definition of _____? 8. Which of these is a past (current) trend in _____? 9. Approximately when did _____ occur? 10. Which date is associated with _____? 11. Which of these statements explains how _____? 12. What is an example of _____? 13. Which of these would be the BEST solution to _____? SOCIAL STUDIES QUESTION STEM STARTERS Secondary (Grades 5–12) 1. How are different ways of life determined by location? 2. How do/did _____ adapt to their environment? 3. How are/were the roles of the _____ different from the _____? 4. What circumstances led to changes in the lives of _____? 5. What would happen to the _____ civilization if _____? 6. How are the _____ and the _____ similar and different? 7. What connects the grouping? 8. What was the response by _____ to the _____? 9. How did the actions of _____ conflict with _____? 10. How did the _____ feel about _____? 11. What is the correct sequence for the events? READING STRATEGIES •Isosceles Triangle •Scalene Triangle •Rhombus •Vertices Different I saw an isosceles triangle in my refrigerator. I often see a scalene triangle on Kenny’s face. Vertices TOASTIES The Cereal of Winners! My friend the rhombus is known as the “Dancing Wonder.” I found four vertices on a box of cereal. To help students pass the state assessment, a teacher did the following and was very successful. All of her students took a mock test in math. Then they scored their own papers. They made this grid: Questions I got right and could get right again. Questions I did or Questions where I did not do correctly had no clue. but am not sure how to do. PLAN AND LABEL IN MATH MAKING THE GRADE 1. What work have I done well in my English class? a. b. c. d. 2. What work have I done poorly in my English class? a. b. c. d. 3. I was/was not satisfied with my grade in English III last semester. 1st _____ 2nd _____ 3rd _____ Exam _____ Average _____ MAKING THE GRADE (CONTINUED) 4. What grade do I realistically believe that I can earn this semester in English III? 5. What will I do in my English class to earn that grade? a. b. c. SPRING SEMESTER Fourth Grading Period I want to earn ______. Daily 10% Fifth Grading Period Quiz 30% Test 60% I want to earn ______. Daily 10% Quiz 30% Test 60% Quiz 30% Test 60% Sixth Grading Period I want to earn ______. Daily 10% I am/am not satisfied with my grade in English III this semester. 1st _____ 2nd _____ 3rd _____ Exam _____ Average _____ DESCRIPTIVE/TOPICAL Descriptive or topical is the hand. •Use each finger to sort topics or descriptive details. SEQUENCE/HOW-TO For anything sequential use a ladder. •Label sequential steps on a ladder STORY STRUCTURE What you sort for and remember in a piece of fiction are the people, the beginning, the middle, the end, the episode, the problem, the goal, the setting. Use the car as a model for sorting and remembering. Middle Characters Beginning End Problem Goal Setting COMPARE/CONTRAST ADVANTAGES/DISADVANTAGES CAUSE/EFFECT PERSUASIVE REASONS Persuasive: If you use a hamburger, the top bun is the person's position. Each one of those pieces of meat is a piece of support. The bottom bun is a conclusion. KNOWLEDGE RATINGS •Using a graph like the one below, have students list the words in the first column to be studied. They evaluate their knowledge level of each word and check the appropriate box. If they have some idea of the meaning, they write in their guess. • Following discussion or study, they write the definition in their own words. This activity is particularly useful in helping students develop metacognitive (being able to think about one’s own thinking) awareness. Example: Word saline Know Think I know Have heard X GUESS DEFINITION A liquid for contact A salt solution lenses macula a spot or blotch, especially on one's skin torsade a twisted cord PICTURE IT Activity: