userfiles/403/Higher Level Questioning
advertisement

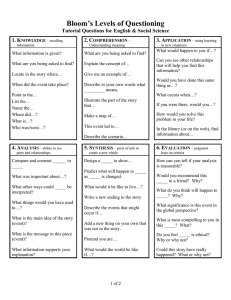
Higher Level Questioning Teachers ask between 300 - 400 questions each day ! Agenda Purpose Question traps How to use Bloom’s to develop questions. Questioning tips Dart Statements I can identify the purpose behind asking questions at a higher level. I can incorporate Bloom’s Taxonomy when developing high level questions. I understand what question space is and can implement this into my own questioning practice. Why do we ask questions in the classroom? On your note card, please list 3 reasons why we ask questions in the classroom. (Individual Activity) Why do we ask questions in the classroom? Share your reasons with the members at your table. Combine, redefine, and / or clarify your responses. Generate one top reason for questioning students. Each table should be prepared to share and chart their responses with the group. What is the purpose for asking questions? To create interest, engage and challenge To check on prior knowledge To check for understanding To focus thinking on key concepts and issues Are you asking the right questions? Are you... Asking too many closed questions Yes or No questions Short answer recall-based questions These are Question Traps How can we avoid these question traps? PLANNING Plan with Bloom’s Taxonomy Knowledge – describe, identify, who, when, where Comprehension – translate, predict, why Application – demonstrate how, solve, try it in a new context Analysis – explain, infer, analysis Synthesis – design, create, compose Evaluation – assess, compare/contrast, judge Three Little Pigs Activity You have a handout in your packet. This handout has questions about the story The Three Little Pigs. Identify the level of Bloom’s associate with each question. Let’s Check It Out! 1._______Application________What would you have done? 2. _______Synthesis_____________Can you think of a different ending? 3.______Knowledge________________What happened in the story? 4._______Application______________What would you have built your home from? 5.______Analysis_____________Give examples of how the third pig showed his cunning? 6.______Comprehension_____________How did the wolf manage to blow down the two homes? 7.______Knowledge____________Why did the three little pigs have to leave home? 8._____Evaluation_______________How would you defend the wolf’s action? 9._______Analysis____________Which part of the story did you like best? PRACTICE IT! On your “Practice It!” handout create a question that is from the lower level of Bloom’s (knowledge, comprehension and application.) These would include simple questions such as "What is the chemical formula for water?" or "Who is the main character in the story?" Now try to build on your lower level questions previously created, by substituting verbs in the question. Create a question from a higher level, (Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation.)Use your Bloom’s Key Words handout to find a list of appropriate verbs to use. Question Tips Plan for Questions Allow suitable response time Ask open questions If you start a lesson with a question, refer back to that question at the end of the lesson Good Teachers Don't Answer Their Own Questions – QUESTION SPACE Remember to Pause for Thinking!!! Q uestion S ilence & Waiting Time P robing A ccepting C larifying & Connecting E laborating & Extending SAY IT AIN’T SO! DID YOU KNOW THOMAS EDISON WAS KICKED OUT OF SCHOOL FOR ASKING TOO MANY QUESTIONS! There are no stupid questions! The students need to feel safe when responding to your question or asking a question of their own. Do you value student’s responses? What did Albert have to say? “In the middle of difficulty lies opportunity. The important thing is not to stop questioning.”