1.1.1 Nature and purpose - SurgeWeb
advertisement

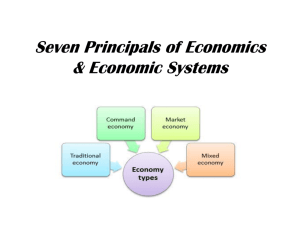
1.1.1 Nature and purpose of economic activity Why did you choose Economics as an A-Level? What other options were there? Why didn’t you choose Economics plus the alternative options? AQA E CON 1: M ARKETS AND MARKET FAILURE 1.1.1 W HAT YOU NEED TO KNOW Candidates should understand that the central purpose of economic activity is the production of goods and services to satisfy needs and wants, and thereby to improve economic welfare They should address the questions of what, how and for whom goods and services should be produced, and consider the role of economic incentives in providing the answers to these questions Candidates should appreciate that economists take a broad view of production and consumption activities including, for example, housework, DIY and benefits derived from the natural environment W HAT DO ECONOMISTS MEAN BY THE ‘ ECONOMIC Explain how the economic problem can be applied to education in the UK. PROBLEM ’? People have unlimited wants However, there aren’t enough resources available to supply all of these wants This creates the economic problem of scarcity The ‘economic problem’ occurs when there are finite resources available to supply infinite wants i.e. scarcity Therefore, choices have to be made Examples of scarcity. Can you add any recent examples that you have seen in the media? E CONOMIC A CTIVITY The central purpose of economic activity is the production of goods and services to satisfy needs and wants. Economic activity will improve economic welfare, the benefit gained by individuals, firms or society in the production of goods and services. Needs are those things required that are essential to maintain survival. Wants are those things that are desired but not The purpose of economic activity is to satisfy the wants and needs of society What is the difference between a want and a need? Are you ever guilty of using the wrong term? Write a list of 4 needs and 4 wants The economic problem tries to answer 3 basic questions: What to produce? How to produce? Who to produce for? W HAT, HOW AND FOR WHOM GOODS AND SERVICES SHOULD BE PRODUCED Economic agents are the individuals and firms that partake in economic activity, the demand for and supply of goods and services. A free market economy is one where firms decide what goods and services to produce with limited intervention from the government. What to produce? How to produce? Economic incentives will provide economic agents with the information required to tell them what goods and services to produce Firms will combine the factors of production (land, labour, capital and enterprise) in order to produce a good or a service For whom to produce? In a free market economy we produce according to demand and supply If there is demand for a product a firm may wish to supply it for a profit T HE Economic incentives are the reasons for economic agents providing goods and services. They include: • Rationing • Signalling • Incentive ROLE OF ECONOMIC INCENTIVES Economic incentives provide the reasons for economic agents to provide goods and services These are based on the price mechanism, the method by which prices for goods and services are achieved The rationing function occurs because increased demand for or reduced supply of a product will lead to a price rise The signalling function occurs because changing prices give a signal to consumers and producers as to whether to leave or enter a market e.g. higher prices suggests that consumers should buy less The incentive function occurs because a consumer or producer is motivated to a course of action e.g. higher prices will incentivise a producer to supply more of a good or service E CONOMISTS TAKE A BROAD VIEW OF CONSUMPTION AND PRODUCTION ACTIVITIES Consumption is the use of a good or a service by a consumer. Production is the provision of a good or service by a producer. Economists include a variety of activities when looking at consumption and production These will include goods and services that have both a financial and non-financial incentive, for example: Financial: Wages earned in a job Buying tickets for a football match Old people’s home Is childcare the same economic activity if undertaken by a parent or paid for in a nursery? Non-financial Benefits from the natural environment e.g. walking on the beach Housework Do It Yourself (DIY) work Q UICK Define the term scarcity. Define the term economic problem. TEST What is the economic problem faced by society? a) How to reduce wants and need b) What, how and for whom to produce goods and services c) How to maximise profits for businesses d) Who to allocate scarce resources to Can you explain your answer? Q UICK TEST The fundamental purpose of economic activity is? a) To increase the supply of renewable resources b) To reduce the use of scarce resources c) Profit maximisation d) The satisfaction of needs and wants Can you explain your answer? T HE N ATURE Take it in turns to pick a term and explain it to the rest of the group. In the study of Economics you will learn a lot of new terminology. Finite resources Infinite wants Wants Needs Economic problem Scarcity AND P URPOSE OF E CONOMIC A CTIVITY Economic welfare Economic agent Free market economy Economic incentives Consumption Production Economic activity Can you pick any two words and explain the relationship between them? T EST YOURSELF 1. What is the purpose of economic activity? 2. State and briefly explain 3 economic incentives. 3. Would an economist view housework as production, consumption or neither? Justify your answer.