PowerPoint - 4-H Military Partnerships
advertisement

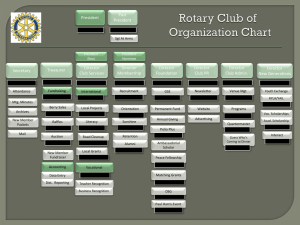
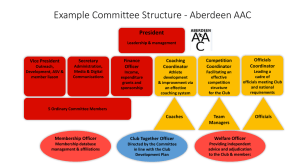
Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers OBJECTIVE Identify 3 ways youth can develop life skills as a 4-H club member. Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers Life Skills Hendricks, P.A. (1998) Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers The Essential Elements In the 4-H Club Belonging Youth help develop an inclusive environment for all club members. Independence Youth see themselves as active participants in the future of their club. Generosity Youth have opportunities to value and practice service to others. Mastery Youth have opportunities to try, make mistakes, and learn. Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers The 4-H Connection The 4-H Pledge The Essential Elements Life Skills Head Independence Thinking, Managing Heart Generosity Relating, Caring Hands Mastery Working, Giving Health Belonging Being, Living Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers Youth Development Objectives Increased: • planning and organizing skills • teamwork, leadership, and social skills • communication and public speaking skills • self - responsibility and decision-making skills • record keeping • management skills and commitment • making new friends. Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers Mastering Maximum Impact ACTIVITY • Small groups of participants Materials • Mastering Maximum Impact of Club Members Worksheet • Pens/pencils In small groups, complete the Mastering Maximum Impact of Club Officers Worksheet. Be ready to share your discussion with the whole group. Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers Life Skills Thinking: • Evaluating relevance • Assessing accuracy • Understanding systems • Thinking critically Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers Life Skills Communication: • Listening • Interpreting • Conveying information • Articulating thoughts and ideas Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers Life Skills Teamwork and Leadership: • Working as a team • Contributing to a group effort • Encouraging others Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers Life Skills Lifelong Learning and Self-direction: • Continually improving capabilities • Setting goals and improving skills • Engaging in mentoring • Learning from one’s mistakes Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers Life Skills Professionalism and Ethics: • Demonstrating accountability • Developing effective work habits • Practicing ethical behavior Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers • How do you feel about focusing on the Essential Elements or life skills when working with clubs? REFLECTION • What do you see as some of the most important Essential Elements/life skills youth can learn through participating in clubs? • What challenges do you think might face club members, officers or the club meeting program in your youth center? • What implications could officers building life skills have on your club? Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers • How will you introduce youth in your program to the idea of participating in a 4-H club? REFLECTION • How will applying the Essential Elements of 4-H and life skills effect the youth and club(s) you work with? • What steps will you take to ensure 4-H members are positively involved as members and officers in your club? • What idea will you take back to help your club run more smoothly and ensure skills are being developed? Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers Key Concepts • 4-H club members and officers can learn and share the Essential Elements with other youth through their leadership • Life skills learned in clubs are skills needed later in life CONCLUSION • Life skills and Essential Elements can be effectively delivered through the club format, especially to youth who serve as club officers • Remember each state and community 4-H program looks a little different. • Contact your local extension agents for assistance on 4-H club officer training materials Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers • Hendricks, P.A. (1998). Developing Youth Curriculum Using the Targeting Life Skills Model, Iowa State University Cooperative Extension, Iowa State University, Ames Iowa. REFERENCE • 4-H 101: The Basics of Starting 4-H Clubs, Retrieved 1/15/12, <www.national4-hheadquarters.gov/library/4H101.pdf> • Positive Youth Development; Developing Life Skills, VRKC: Volunteer Research Knowledge Competency Taxonomy <nextgeneration.4-h.org/volunteerism/vrkc/> Working with 4-H Club Members and Officers • 4-H Club Officers and Committees <ohioline.osu.edu/4h-fact/0014.html> • 4-H Experience & Service Officers Training <www.ca4h.org/Resources/Publications/> REFERENCE • Ohio Workforce Preparedness - Skills for Success, retrieved 8/30/11 <youthsuccess.osu.edu/?page_id=6> • Selecting 4-H Club Officers and Committee Members <www.4-h.org/images/volunteer/VolunteerResources/ Selecting%204-H%20Club%20Officers-Committees.pdf> For more information, visit www.4-Hmilitarypartnerships.org