Assessment Fairness, Accuracy, and Consistency
advertisement

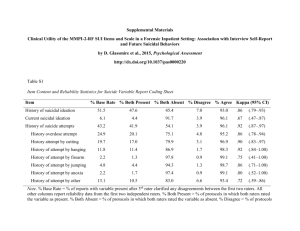
Fairness, Accuracy, & Consistency in Assessment NCATE’s recommendations to reduce bias and ensure fairness to students Fairness “Assess what’s been taught” Candidates should be aware of the knowledge, skills, and dispositions which are measured in the assessments. O Was it taught? O Curriculum map – shows where students learn and practice what is assessed O Do students understand the expectations? O Syllabi containing instructions and timing of assessments O Rubrics/scoring guides shared with students Fairness According to these guidelines, are your program’s assessments FAIR? O Is your curriculum map up to date? O Does the curriculum map link to all professional standards and GSE standards and dispositions? O Does the curriculum map indicate any gaps? O Do syllabi indicate timing of assessments? O Are rubrics/scoring guides shared with students when assigning the work? Accuracy “Assessments measure what they say they measure” Assessments should be aligned with standards and proficiencies they are designed to measure O Are assessments aligned with standards? O Content match O Complexity match O Appropriate degree of difficulty O Is there corroborating evidence? O Is there field input on the assessment? Accuracy According to these guidelines, are your program’s assessments ACCURATE? O Do your program’s assessment types (test, observation) match what is being assessed? O Dispositions = observations O Skills = performance assessment O Which of your assessments “validate” (relate to) other assessments? O Ex. - Work sample to lesson plan assignment O Have you had input from working professionals? Consistency “Assessments produce dependable, trustworthy results” The assessment results should be reliably consistent regardless of time and rater O Are scoring tools sufficiently descriptive? O Language to differentiate between components and between performance levels O Clear descriptors that promote accurate scoring O Students can tell from scoring tool why they were rated at a certain level O Are raters trained? O Agreement between “what a 3 in lesson planning” looks like O Raters understand of the consequences of final scores O Programs have a plan to support/address students with insufficient performance that alleviate rater-pressure Consistency According to these guidelines, are your program’s assessments CONSISTENT? O Does your program consistently use descriptive O O O O O rubrics for major assignments and performance observations? Does your program have regular rater training? Has your program engaged in rubric calibration and moderation activities? Are raters aware of how their assessment’s scores affect the student? Are raters aware of how their assessment’s scores contribute to program review? What is the plan to support struggling students? Avoiding Bias “removing contextual and cultural bias from assessments” The assessment itself and assessment context should be analyzed for factors that would affect performance. O Are clear assessments administered in the proper environment? O Location/equipment O Clear instructions/questions O Have assessments been reviewed for bias? O Racial/ethnic/cultural stereotypes O Disability resource center review O Assignments that favor one group over another Avoiding Bias According to these guidelines, are your program’s assessments BIAS-FREE? O Have all key assessments been reviewed for clarity of expectations? O Have all your assignments been reviewed for accessibility? O Have all your assignments been scrutinized for cultural bias and stereotypes? O Has your program analyzed student outcomes according to sub-groups to determine if consistent scoring bias exists? GSE Rubric Guidelines Developed by the Assessment Committee - 2010 O 4 levels of competency: Unsatisfactory, Emerging, Proficient, Exemplary O In ascending order from left to right O If numbers are used: 1-4 from left to right States values, beliefs and assumptions about priorities for resource allocation. NEEDS IMPROVEMENT (1) Statement of values, beliefs and assumptions is absent EMERGING (2) PROFICIENT (3) EXEMPLARY (4) Statement of values, beliefs, and assumptions is vague, too general or contrived. Statement of values, beliefs, and assumptions is clearly defined and specific. Statement of values, beliefs, and assumptions is clear, specific, convincing, and includes personal experience that promotes clarity. Rubric Moderation O Process of strengthening consistency O Develops inter-rater reliability through shared examination and discussion of student work. O Involves all/many raters O Process O Recruit raters for a two-hour session O Provide 4 samples of work O Provide rubric and have raters “score” each sample O Discuss as a group why the raters chose the scores O Debrief about what was learned, what remains unanswered. Rubric Calibration O Process of strengthening consistency O Develops inter-rater reliability by setting expectations of what the scores mean regarding student work. O Involves all/many raters O Process O Recruit raters for a two-hour session O Provide 4 samples of work that have been pre-scored (anchor O O O O papers), at least one at a low, medium, and high level of performance Discuss rubric areas and expectations for each level and component before scoring begins Provide rubric and have raters “score” each sample with your discussion in mind. Have raters compare the scores they assigned to the “anchor” papers Debrief about what was learned, what remains unanswered. Next Steps O How is your program doing in providing fair, accurate, consistent, bias-free assessments to students? O What work needs to be done in your program to ensure quality assessments are used? O What do you need to be able to accomplish this?