New Standard on records management
advertisement

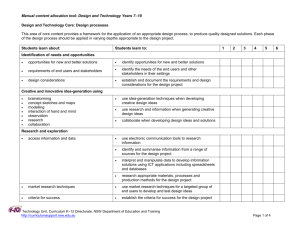
Standard on records management Catherine Robinson Senior Project Officer, Government Recordkeeping Records Managers Forum, 26 November Overview • • • • • Background Drivers for the review of standards Review of 5 standards New Standard on records management Implementing the new standard in 2015 State Records Act 1998 • State Records Authority of NSW has a defined role in approving standards and codes of best practice for records management • Records management is defined in s.13(1) as “all aspects of the making, keeping and disposal of records” • Requirements to consult on proposed standards, they must be approved by the Board, and reviewed Standards and Codes of best practice • Standard on counter disaster strategies for records and recordkeeping systems (2002) • Standard on full and accurate records (2004) • Standard on managing a records management program (2004) • Standard on digital recordkeeping (2008) • Standard on the appraisal and disposal of State records (2007) • Standard on the physical storage of State Records (2012) Code of best practice • AS/ISO 15489 – Records Management Drivers for review • • • • Age of standards Concerns that some standards didn’t assist us in the current recordkeeping environments Issues raised in our 2013 monitoring activity IM Framework in NSW http://finance.nsw.gov.au/ict/information-management-framework • Digital transformation! http://finance.nsw.gov.au/ict/accelerating-digital-government-taskforce Review process • • Review 5 standards rather than just one or two Consultation with public offices about the current standards 5 online surveys in 2 months! • Feedback: • Supportive of standards and many organisations have implemented them Support for a single standard, rather than 5 standards Duplication of requirements across several standards Request to streamline requirements Request for better connections to NSW ICT Strategy Counter disaster strategies standard is out of date Use of plain English, less jargon and should be written for a wide audience Development of a new standard Basis for the next standard • • • • • • One standard, not five! Support both physical & digital records AND support digital records and information management as Government business transitions into fully digital operations Support good information practices in complex business and information environments Build on a strong foundation in the 1st and 2nd generation of standards Consolidate and streamline requirements: 61 minimum compliance requirements have been reduced to 21 minimum compliance requirements New standard has 3 Principles, minimum compliance requirements, and examples of how a public office can demonstrate compliance with requirements. Principle 1: Organisations take responsibility for records and information management Establish governance frameworks: • policy directing how records and information shall be managed • assigning responsibilities • establishing provisions for records and information in outsourcing and service delivery arrangements, and • monitoring records and information management activities, systems and processes. New requirements • Responsibility for ensuring that records and information management is integrated into work processes, systems, and services is allocated to business owners and business units. • Records and information management responsibilities are identified and addressed in outsourced, cloud and similar service arrangements Principle 2: Records and information management support business Taking a planned approach to RM/IM: • undertaking assessment of records and information needs so that the organisation can define key business information • using the assessment to design records and information into processes and systems • considering all operating environments, so that creation and management of records and information needed to support business are considered in all system and service arrangements. Principle 2 contd New requirements • High risk and high value areas of business and the systems, records and information needed to support these business areas are identified. • Records and information management is a designed component of all systems and service environments where high risk and/or high value business is undertaken. • Records and information are managed across all operating environments. Principle 3: Records and information are well managed Effective management of records and information: • underpins trustworthy, useful and accountable records and information • records and information are accessible and retained for as long as they are needed • management extends to records and information in all formats, in all business environments, and in all types of systems. New requirement: • Records and information are kept for as long as they are needed for business, legal and accountability requirements. How will this standard help you? • • • • A tool which will support information assets and resources across the entire organisation Increase visibility of information assets regardless of system (EDRMS, ECM, business systems) and storage location (in the Cloud, in a storage repository) Promote collaboration with ICT Senior Management interest in RM/IM Implementation • • • • New standard will be launched in early March 2015 All public offices will be contacted about the launch of the new standard Implementation guide and updated/new guidance will be available to assist you in implementing the requirements Requirements that have been carried over from the current standards will be mandatory from March 2015; 6 new requirements will commence from December 2015 Thank you! • • catherine.robinson@records.nsw.gov.au tel. 8257 2991