LI-TD Kindergarten Magnet Presentation
advertisement
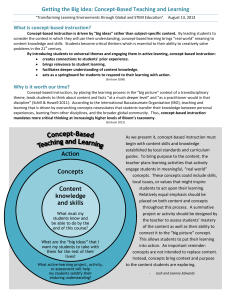
Concept-Based Instruction in the Kindergarten Classroom An Interdisciplinary Unit on Relationships Introductions • Christina Forney LI/TD Magnet Coordinator at Mallard Creek • Sarah Jones LI/TD Magnet Coordinator at Barringer • Kelly Kollar TD Catalyst Teacher at Polo Ridge • Erin Muffler Kindergarten LI Teacher at Barringer • Lauren Teddy K-2 Multi-Age LI Teacher at Tuckaseegee Today’s Objectives 1. Define concept-based instruction. 2. Examine the research behind conceptbased instruction. 3. Discuss why a concept-based unit on relationships is important. 4. Explore the unit. 5. Collaborate with colleagues about implementation. What is Concept-Based Learning? • It approaches content area standards from the perspective of an over-arching concept. Understand Know Be Able to Erickson, H.L. (2008) • Concept and Generalizations- Transferable understandings • Example: Relationships are everywhere. • Factual and Critical Knowledge- Non-Transferable • Example: Understand addition as putting together and adding to. • Skills and Processes- Transfer within and sometimes across disciplines. • Example-Decompose a numbers less than or equal to 10 in more than one way. A Closer Look at Concepts Backwards Planning Concepts/ Knowledge Generalizati ons Skills Patterns can Seasons be found in follow a nature. pattern and change over time. Record observations in a notebook. Compare and contrast pictures. Erickson (2008) and Tomlinson (2003) Concepts vs. Topics Concept Topics Change Weather Patterns Animals Relationships Characters Systems Government Power Grammar Structure Geometry What Does the Research Say about ConceptBased Learning? Concept-Based vs. Topic-Based “Concept-based curricula are more effective than topic-based curricula, for the world of today and tomorrow, because they take teaching and learning to a higher level as students analyze, synthesize and generalize from facts to deeper understanding.” Erickson (2008) The Standards and the Concepts Taba identified patterns of discussion in concept-based learning lessons and found an effective discussion is one in which the teacher remains at the lower levels (facts and topics) long enough for students to acquire enough information before moving them up to the higher levels (concepts). Maker and Sciever (2005) Turn and Talk 1. What is concept-based learning? 2. How could it help your students become better thinkers? A Relationship Unit Why is it important and how will it help me and my LI Kindergarten students this year? What Makes us LI Anyway? • A variety of skills and abilities – This unit is designed to challenge your bright and potentially gifted students at the highest level, while still meeting the standards for all students. • Accelerated, Enriched Curriculum – This unit provides depth and complexity to the common core and state standards. It gives students the conceptual framework to build knowledge. Preparing for Second Grade Testing- Analogies and Relationships • Certifying LI students strengthens the magnet. • LI/TD Magnets tend to have diverse socioeconomic populations and under-represented racial populations. • Exposing students to conceptual learning will provide them will experiences that can build background for the CogAT. • CogAT Quantitative Practice • CogAT Verbal Practice Relationship Unit Planning • UNDERSTAND-Generalizations- The Big Ideas – – – – – – – Relationships are everywhere. Relationships can be helpful or harmful. Relationships can be positive or negative. Relationships can be natural or imposed. Relationships can be correlations (cause and effect). Relationships can cause interdependence. Relationships can cause the exchange of ideas and values. – Relationships are purposeful. Universal Concepts from www.lowellinstitute.com Relationship Unit Planning • How can we study the content-based standards through the concept of Relationships? • KNOW- The Standards – Science • Understand how objects are described based on their physical properties and how they are used. – Social Studies • Explain how families have needs and wants. Explain how jobs help people meet their needs and wants. – Literacy • With guidance and support from adults, explore word relationships and nuances in word meanings. – Math • Understand addition. Practice with Relationships Forced Analogies • How are a hippo and a pencil related? • Benefits- Critical and creative thinking, problem-solving, trains students to look for relationships Practice with Relationships Visual Thinking Strategy Marcy Deutsch from The Art of Autism Quick Write! 3. How could learning Kindergarten standards through the concept of relationships, and in particular analogies, help your students? Answer Garden http://answergarden.ch/64153 Let’s take a closer look at the unit… Really…. Another thing to do!!?? • The lessons should be very easy to implement. All ideas are there and clearly laid out, including prompts, things to consider, and pictures. All worksheets are attached as well. • With a large range of students in the LI program, there is also tips for differentiating lessons! • Lessons correspond to the kindergarten common core state standards. • Lessons tie into curriculum, but can also “stand alone” if the subject is not yet touched upon. Introduction of Unit • Unit is split up into 20 different lessons, approximately 45 minutes in length. • Lessons are set up by: – – – – – – – – Concept Generalization Essential question Common core state standards Lesson Overview Small group/Large group with suggested Tips for differentiation Resources What are the lessons exactly? • Split into 5 different groups- Introduction lessons/conclusion lessons, math lessons, literacy lessons, science lessons, and social studies lessons. • Please consider: – What relationships are being taught in the lesson? – How will these lessons impact the students in your classroom? Let’s Share! 4. Explore the unit. Padlet http://padlet.com/wall/nk2s33hfdy Some resources to help you during and after the unit! Concept Map- Connecting the Content to the Concept Relationships Involve People Can be found Things In my life Friends, family, pets, stores, playground Addition problemsnumbers and signs Are used for Understanding ideas better In School Math, science, literacy, social studies Relationship between matter and what we use it for Friends, teachers, classmates Relationship between money and needs and wants Relationships between words Making life more enjoyable Concept Development • Introductory Lessons for William and Mary • Basic Structure – List – Group – Label – Subsume- combine like groups – Re-group – Re-label – Generalize Building on Relationships • • • • Building Thinking Skills Analogies for Beginners Math Analogies K-2 PETS Collaboration 5.How can you implement this in your classroom? Support for Implementation • Plan to implement second quarter. • Provide feedback to us. • Share and support each other through Edmodo. – Login or sign up at www.edmodo.com – Enter group code • Email Erin Muffler with questions/concerns or post in Edmodo. • • • • • Our Contacts christina.forney@cms.k12.nc.us saraho.jones@cms.k12.nc.us kelly.neelon@cms.k12.nc.us laurene.teddy@cms.k12.nc.us erine.muffler@cms.k12.nc.us Please enjoy this unit and have a great school year!