Brainstem (Midbrain/Pons) PP
advertisement
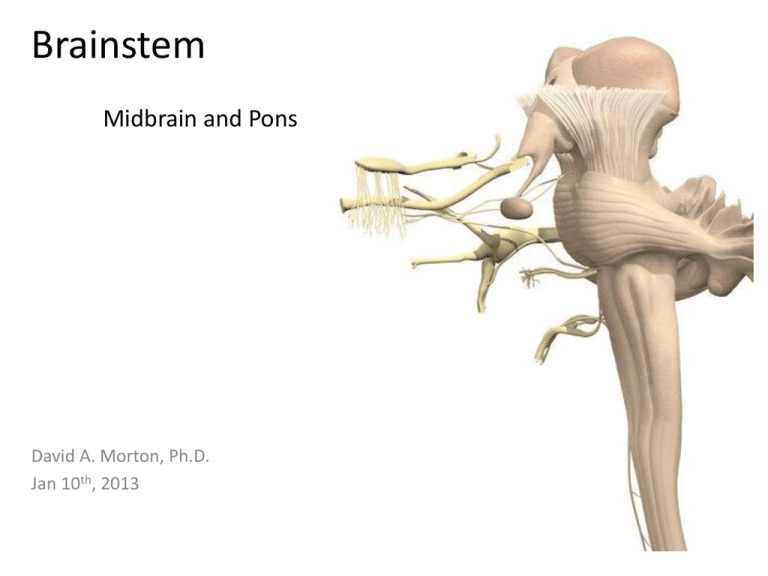
Brainstem Midbrain and Pons David A. Morton, Ph.D. Jan 10th, 2013 Objectives • • • • • • • • • Explain how spinal nerves differ from cranial nerves Name all the cranial nerves and know their components and functions Identify and locate the CN’s associated with the medulla, pons and midbrain Recognize the major internal and external landmarks on the dorsal and ventral surface of the brain stem, so that you can determine if a gross or stained cross section is medulla, pons or midbrain. Identify on a typical cross section all the brain stem nuclei containing motor neurons that end on striated muscle. List the cranial nerves that contain parasympathetic fibers, the location of their nuclei, and their function Explain why cranial nerves are so important in localizing lesions. Name reflexes that test these nerves and brain stem levels. Relate branches of the vertebrobasilar blood supply to the medulla and pons explaining the deficits that would occur with vascular occlusion. Directional terms with Brain Cranial nerve overview CN I – Olfactory nerve Cranial nerve overview CN II – Optic nerve Cranial nerve overview CN III – Oculomotor nerve Cranial nerve overview CN IV – Trochlear nerve Cranial nerve overview CN V – Trigeminal nerve Cranial nerve overview CN VI – Abducens nerve Cranial nerve overview CN VII – Facial nerve Cranial nerve overview CN VIII – Vestibulocochlear nerve Cranial nerve overview CN IX – Glossopharyngeal nerve Cranial nerve overview CN X – Vagus nerve Cranial nerve overview CN XI – Spinal accessory nerve Cranial nerve overview CN XII – Hypoglossal nerve Brain Overview Brainstem • Midbrain • Pons • Medulla Midbrain Pons Medulla Brain Overview Diencephalon • Thalamus • Hypothalamus • Pineal gland Th HTh P Brain Overview • Corpus callosum • Lateral ventricle • 3rd ventricle • Cerebral aqueduct • 4th ventricle LV 3 aq 4 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerve Review Spinal nerve anatomy • Dorsal root • Somatic sensory neurons • Visceral sensory neurons • Ventral root • Visceral motor neurons • Somatic motor neurons Som S Alar VS Sulcus limitans VM SM Basal Spinal cord Internal anatomy of brainstem Som S Alar The fate of the alar and basal laminae VS Sulcus limitans VM • Why are brain stem sensory nuclei lateral to motor nuclei in brainstem? SM Basal Spinal cord Som S Alar VS VM SM BM Basal Medulla Midbrain (mesencephalon) External anatomy: • Quadrigeminal plate • Superior colliculus SC CP IC IV • Inferior colliculus • Cerebral peduncles • CN IV Dorsal view of brainstem Midbrain (mesencephalon) External anatomy: SC • Quadrigeminal plate • Superior colliculus • Inferior colliculus CP • Cerebral peduncles • CN III (arrows) Ventral Rostral midbrain IC CP CP Dorsal view of midbrain Ventral Caudal midbrain Midbrain Oculomotor nucleus Cranial nerve nuclei Edinger-Westphal nucleus • Rostral midbrain • Oculomotor nucleus • Edinger-Westphal nucleus • Caudal midbrain • Trochlear nucleus Motor Sensory Trochlear nucleus Midbrain (Rostral) Internal anatomy • Tectum • Tegmentum • Central gray matter • Red nucleus • Substantia nigra • Cerebral peduncles Tectum Aq Rn Rostral midbrain Midbrain (Rostral) Internal anatomy • Oculomotor nucleus • Edinger-Westphal nucleus Aq Rostral midbrain Midbrain (Caudal) Internal anatomy • Trochlear nucleus Red nucleus Caudal midbrain Horizontal section Midbrain Functional significance of midbrain: • Visual and auditory reflexes • Coordinates eye movements • Pupillary reflex • Consciousness and arousal (RAS) Midbrain Arterial supply. Branches off the: • Posterior cerebral artery • Basilar artery Pupillary and Accommodation Reflexes Bilateral contraction of sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscles CN II CN III Pons External anatomy: • Basilar pons (pons proper) • Middle cerebellar peduncle (MC) • Basilar artery 4th • 4th ventricle • CNN V, VI, VII, VIII V 4th vent. Pons Horizontal section VI VII VIII 4th Pons Cranial nerve nuclei • Rostral Pons • Trigeminal nucleus • Caudal Pons • Abducens nucleus • Facial nucleus Trigeminal nucleus Abducens nucleus • Sup salivatory nucleus Facial nucleus Sup salivatory nucleus Motor Sensory Pons (Rostral/Mid) Internal anatomy • Trigeminal motor nucleus • Functional significance 4th Ventricle Axons of the sensory part of V Motor nucleus of V Tegmentum R.F. Pons Proper Axons of the motor part of V Pons (caudal) Facial nucleus • Branchial motor nucleus • Innervate muscles of face Pons (caudal) Superior salivatory nucleus • Visceral motor (Para) • Origin of preganglionic parasympathetic neurons Pons (caudal) Abducens nucleus • Origin of Abducens n. (CN VI) • Homolog to ventral horn Pons (caudal) Internal anatomy • Facial nucleus • Superior salivatory nucleus • Abducens nucleus Corneal reflex • Consensual reflex • Sensory: CN V-1 to spinal trigeminal nucleus • Motor: Facial nucleus out to the temporal branch of CN VII Spinal trigem. Nucleus & Tract Corneal Reflex Touch the cornea Semilunar ganglion of CN V Spinal trigeminal nucleus CN V-1 L R Facial motor nucleus Temporal branch of CN VII Blink (Orbicularis occuli muscle) Pons Arterial supply. Branches off the: • Basilar artery • Median and Circumferential branches Match the following reflexes with their associated brainstem level: a. corneal reflex testing? b. Gag reflex testing? c. pupillary light reflex testing? I II III Match the following reflexes with their associated brainstem level: a. corneal reflex testing? I b. Gag reflex testing? III c. pupillary light reflex testing? II You have a patient who cannot look to the right with the right eye or smile or wrinkle the right side of their face. Characterize the lesion as to level, side, structure(s) involved. You have a patient who cannot look to the right with the right eye or smile or wrinkle the right side of their face. Characterize the lesion as to level, side, structure(s) involved. What reflex would be abnormal in a patient with a lesion that included the circled area? What reflex would be abnormal in a patient with a lesion that included the circled area? Abducens nucleus Facial nucleus