File - Glenview Elementary
advertisement

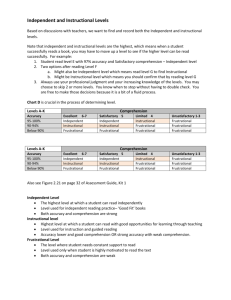
Fountas & Pinnell Benchmark Assessment System Training 2014 Why Are We Doing This? We need to go deeper in comprehension with our students. These Running Records are more insightful into the students’ thinking. Standardizing TLA and making sure that everyone is on the same page is paramount to quality reading instruction. District wants fidelity and consistency in TLA and linking results to drive guided reading instruction. Let’s Take A Look at the Benchmark Assessment System Each level has a fiction and a non-fiction text. Administer 3 times per year: Fall, Winter, Spring. Administration of assessment will determine independent AND instructional levels. Writing component will not be administered the first year. Assessment includes 3 components: accuracy, fluency, and a comprehension conversation with each student. Kits will be distributed to schools with a 2-3 teachers to 1 kit ratio. Students will be assessed past a 44. Schools should use the MNPS Correlation Chart to align with F&P lettered levels. Let’s Take a Closer Look! Inside the Benchmark Assessment System Box Leveled Text – Fiction and Non-Fiction for each level Assessment Guide for Teachers The Continuum of Literacy Learning by levels Assessment Forms Optional Assessments: Student Forms Calculator/Stopwatch – apps also available Student Folders – Set of 30 Recording Forms PD DVD & Assessment Forms CD-ROM Oral Reading Students choose which text they would like to read. Make sure you have all materials prepared and on hand. Students should read text ONLY once! Multiple readings of the same text skews standardization. Read introduction as stated on the form. DO NOT DEVIATE. Deviation skews standardization. Teacher MAY NOT prompt student during TLA. This skews standardization. Teachers may choose to use the F&P calculator which comes with each kit to determine Accuracy Rate and SelfCorrections. Some texts (Levels K-Z) allow students to read a portion of the text aloud and complete the reading of the text silently. Students should read entire text either silently or aloud for comprehension. Calculating the Running Record Errors RW – E ÷ RW = Accuracy (E + SC) ÷ SC = 1: ___ Self Correction – degree of monitoring or checking on understanding. Reconcile text as meaningful and coherent. MSV M = Meaning/Pictures Does it make sense? S = Structure/Syntax Can you say it that way? V = Visual/No pictures Does it look right? Coding, Scoring, & Analysis Consolidation #3 Tutorial Use record form for My Loose Tooth Let’s take a look and discuss: Coding of the TLA Scoring of the TLA Analysis of the TLA Assessing Fluency Levels A-B: No Fluency Key/students may use finger to track. Levels C-Z: 4-point Fluency Key is provided. Teachers should make a note if student uses finger for tracking. Levels J-Z: Optional Reading Rate will not be assessed. Phonetic variations that DO NOT interfere greatly with comprehension or fluency should be judged based on teacher knowledge of student, i.e. EL students. Comprehension Conversation Immediately follows oral reading. Teacher is familiar with the text. Teacher invites student to talk about text. Teacher rates student response by identifying key understandings students should have gained from: within the text beyond the text about the text Prompts are available to help teachers elicit key understandings from readers. Scoring should not be lowered because a student needed a prompt. The student may look back in the book to answer ONLY if the action is initiated by student. Key understandings communicated by the child in the conversation are noted by a checkmark next to that key understanding. Practice Conversation Determining a Student’s Level Students read texts to determine 3 levels: Independent (Easy) Reading Level Instructional Reading Level Frustrational (Hard) Reading Level Determining Independent (Easy) Level Levels A-K Student reads at 95100% accuracy with excellent or satisfactory comprehension. Levels L-Z Student reads at 98100% accuracy with excellent or satisfactory comprehension. Next Step: Move to a higher level text and repeat until student reads at instructional level. Determining Instructional Level Levels A-K Levels L-Z Student reads at 90-94% accuracy with excellent or satisfactory comprehension o Student reads at 95-97% accuracy with excellent or satisfactory comprehension OR OR Student reads at 95100% accuracy with limited comprehension Student reads at 98100% accuracy with limited comprehension Next Step: Move to a higher level text and repeat until student reads at frustrational (hard) level. Determining Frustrational (Hard) Level Levels A-K Student reads below 90% accuracy with any score on comprehension. Levels L-Z Student reads below 95% accuracy with any score on comprehension. Next Step: Move to a lower level text and repeat until student reads at instructional level. Finding a Place to Start Former records Data Warehouse Where-to-Start Word Test Using the Instructional Expectations Chart For the fall benchmark, consider giving the assessment one level BELOW the student’s current level to ensure a successful first read New system will TAKE TIME – plan accordingly by scheduling assessments throughout the window Informal Running Records should be given throughout the semester between formal assessments Entering Data New summary forms provided in the kit: Tri-annual summary form. The class record form provided in the kit may be helpful with grouping. Teacher will still submit grid to Coach. District will still use EXCEL Spreadsheets to track TLA data. Data should be reported and analyzed by teacher and grade level to plan for future instruction. Next Steps: Using the Information to Guide Instruction Each kit includes The Continuum of Literacy Learning – use this text to determine reading behaviors at each level. Teachers may want to use lesson planning templates to plan daily guided reading instruction. Take anecdotal notes during guided reading lessons to use to plan future instruction. Take informal (“on the fly”) running records often. Teacher Reflections Teacher Reflection Tutorial Positives about the new reading assessment Concerns about the new reading assessment