Chapter 4 Lesson 1 and 2 worksheetsx
advertisement

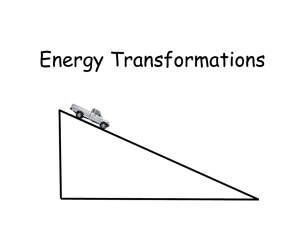
Chapter 4 Lesson 1 and 2 worksheets Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 1 Two books with different masses fall off the same bookshelf. As they fall which has more kinetic energy and why? • The one with the greater mass, because KE=1/2 mv2 Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 2 How can the gravitational potential energy of an object be changed? Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 2 How can the gravitational potential energy of an object be changed? Raise it to a great • height. • Energy is stored in the ch3mical bonds in the food molecules. • No, The energy is stored in the Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 3 How is energy stored in food? is the form of energy stored in food different from the form of energy stored in gasoline? chemical bonds in the octane, gasoline, molecule • Kinetic is the energy Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 4 Contrast potential and kinetic energy. contained in a moving object by virtue of its velocity and mass. • Potential energy is the energy given to an object due to its height. Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 5 Which ball as the greatest potential energy? ___________ the least _________ • Most PE= D • Least PE= C Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 6 A dump truck, a sports car, and a bicycle are traveling at the same velocity. Compare their kinetic energies. • Truck>car>bicycle Chapter 4 Lesson I 7.The only way Ms. Stayner’s 12 year old Honda can go more than 52 mph is to roll down a mountain. If the Honda has a mass of 1300 kg and its velocity is 45 m/s, what is its kinetic energy? Given Work Answer M= 1300 kg V=45 m/s KE= ½ mv2 1,316,250 J KE= ½ (1300) (45)(45) Chapter 4 Lesson I 8.Your physical science textbook is dusty and on a shelf 3 m from the floor. It is sad that you don’t spend quality time with it. If its mass is 1.25 kg, what is its gravitational potential energy? Would the GPE be more or less if the same book were on a shelf 4 m from the ground? Given Work Answer M= 1.25 kg G= 9.8 m/s/s H= 4 m PE= mgh 49 J PE= (1.25) 9.8(4) • The mechanical energy of Chapter 4 Lesson 2 Question 1 Explain mechanical energy and describe the mechanical energy of a roller coaster car immediately before it begins traveling down a long track. any object is the sum of the potential energy and the kinetic energy. At the top of the long track the car has mostly potential energy, which will change to kinetic energy as the car goes down the hill. Chapter 4 Lesson 2 Question 2 What is the law of conservation of energy? • Energy is neither created or destroyed during a change. It remains constant. Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 3 Applying bicycle brakes as you ride down a long hill causes the brake pads and wheel rims to feel warm. Explain. • Friction causes the brake pads to heat up. • In the sun and in the center Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 4 Where do nuclear fusion and fission reactions occur naturally? of the earth. That’s why there is molten rock in the earth’s core. Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 5 How is mass converted into energy in nuclear fission? 5 • Some of the mass in the nucleus is changed to energy. A small amount of mass can create a great amount of energy. This is done according to Einstein’s equation, 2 E=mc Chapter 4 Lesson I • 6. Riley runs the bases with a blazing velocity of 1 .3 m/s with a massive mass of 18 kg. What is his kinetic energy? Given Work Answer M= 18 kg V= 1.3 m/s KE= ½ mv2 15 J KE= ½ (18) (1.3)(1.3) Chapter 4 Lesson I 7Your mom wants you to clean your room which includes doing your yearly dusting. I know it has been since last year that you looked on top of your bookcase. As you climb the 4.25 m to get a look at the top you find the Mt. Dew that you hid from your little brother. The soda, can, and growth of mold combine kg. What is itsAnswer GPE? Given to .78 Work M= 0.78 kg PE= mgh G= 9.8 m/s/s PE= (.78) H= 4.25 m 9.8(4.25) 32 J Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 2 Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 2 Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 2 Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 2 Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 2 Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 2 Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 1 Two books with different masses fall off the same bookshelf. As they fall which has more kinetic energy and why? • The one with the greater mass, because KE=1/2 mv2 Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 1 Two books with different masses fall off the same bookshelf. As they fall which has more kinetic energy and why? • The one with the greater mass, because KE=1/2 mv2 Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 1 Two books with different masses fall off the same bookshelf. As they fall which has more kinetic energy and why? • The one with the greater mass, because KE=1/2 mv2 Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 1 Two books with different masses fall off the same bookshelf. As they fall which has more kinetic energy and why? • The one with the greater mass, because KE=1/2 mv2 Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 1 Two books with different masses fall off the same bookshelf. As they fall which has more kinetic energy and why? • The one with the greater mass, because KE=1/2 mv2 Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 1 Two books with different masses fall off the same bookshelf. As they fall which has more kinetic energy and why? • The one with the greater mass, because KE=1/2 mv2 Chapter 4 Lesson I Question 1 Two books with different masses fall off the same bookshelf. As they fall which has more kinetic energy and why? • The one with the greater mass, because KE=1/2 mv2