Brain PowerPoint

THE BRAIN AND LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
With support of notes, participants will be able to: describe how learning is related to brain structure and functions offer hypotheses about effective teaching practices based on information about the brain identify misconceptions she/he held and/or the beginnings of new information/knowledge
KEY QUESTIONS
What is learning?
How does the brain “learn”?
How might teachers use information about the brain to support learning for themselves, for children, and for youth?
HOW DOES THE BRAIN
“LEARN”?
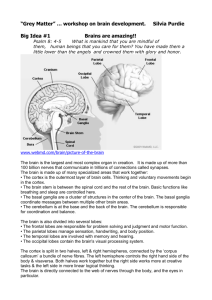
Brain Components
Hemispheres & Lobes
Interior of brain
Cortex
Relationship to learning
Cells
Types of cells
Structure of Neurons
Learning and neurons
EXPLORING BRAIN COMPONENTS,
TEACHING, AND LEARNING
Metaphors old and new
BRAIN AS A RAINFOREST
BRAIN AS A NEIGHBORHOOD
HEMISPHERES
Two cerebral hemispheres - left and right
Connected by corpus callosum
Left hemisphere generally processes information more in parts and sequentially; recognizes positive emotions faster than right hemisphere
Right hemisphere controls gross motor functions but not fine motor functions for right-handers; recognizes negative emotions faster than left hemisphere
Music and arts as right-brain activities OUTDATED!
LOBES
FUNCTIONS OF THE LOBES
Occipital : middle back. Primarily responsible for vision.
Temporal : above and around ears.Primarily responsible for hearing, memory, meaning, and language.
FUNCTIONS OF THE LOBES
Frontal : area around forehead. Purposeful acts like judgment, creativity, problem-solving, planning.
Parietal : top back. Processes sensory and language functions.
INSIDE THE BRAIN
INTERIOR STRUCTURES AND
THEIR FUNCTIONS
Thalamus : key sensory relay station; part of body’s reward system
Hypothalamus : Like a thermostat regulates and influences appetite, hormone secretion, digestion, sexuality, circulation, emotions, sleep
INTERIOR STRUCTURES AND
THEIR FUNCTIONS
Hippocampus : In temporal lobe, strongly involved in learning and memory formation
Amygdala : Critical processor for senses. Plays a role in emotionally laden memories. Contains huge number of opiate receptor sites implicated in rage, fear, and sexual feelings
TYPES OF CELLS
GLIAL CELLS
Greek for “glue”
Most numerous of brain’s cells - 90%
1,000 billion; no cell body
Role - formation of bloodbrain barrier, transport of nutrients, regulation of immune system, remove dead cells, structural support
NEURONS
Adults - 100 billion, half of a two year old
Areas of brain grow new neurons
Healthy neurons continuously firing
Neurons can move
Role Responsible for information processing and converting chemical and electrical signals back and forth
STRUCTURE OF NEURONS
Cell body,axon, dendrites
Myelin sheath, neurotransmitters
Number of combinations est. as a
1 followed by 6.5 million
MILES of 0’s
Earth to Moon and back more than 13 times
LEARNING AND NEURONS
LEARNING AND NEURONS
ANIMATIONS OF NEURONS
FIRING http://www.animate4.com/meditation/brain/neuro/min d/iq/dreams/memory/hypnosis/cerebellum/meditationhypnosis-iq-brain.mpg
http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=713468412
1021483823 http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=-
2349016133121331921&q=Neurons+firing&total=38
&start=0&num=10&so=0&type=search&plindex=3 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ysDGX6bOgAw http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=snO68aJTOpM
KEY FUNCTIONS OF THE
CORTEX
Sense
Integrate
Act
THE CORTEX
MEANING MAKING AND THE
LOBES
STRUCTURE AND LEARNING
IMPLICATIONS OF BRAIN STRUCTURE/FUNCTIONS FOR
LEARNING PROCESS
TRANSFORMATION AND JUSTICE
Information/experience understanding
Past future
Outside inside
Power of other Power of learner
PURPOSE OF THE BRAIN
The purpose of the brain is to ensure survival
Survival is ensured through learning
Learning occurs through the electrical and chemical processing of new, coherent experiences, not through repeating old experiences
That is, people get “smarter,” or
“learn,” by growing more synaptic connections and increasing dendritic branching - INCREMENTAL NOT
FIXED!
Dendritic connections, not brain size, allow us to solve problems
Learning DOES NOT
NECESSARILY mean a change in behavior
Genetic inheritance, damage to the brain, and adverse experiences can interfere with the neurological process of learning
Teaching, learning, and parenting choices can improve learning and capacity
ONE MORE TIME :)
learning changes the brain learning occurs through trying out new things, not through getting the “right” answer - preventing mistakes is not healthy for a growing, adaptive brain repeated electrical stimulation, along with increased input of nutrients, fosters cell growth through dendritic branching and formation of new synapses new synapses usually appear after learning occurs memory is enhanced through relevant, varied, engaging repetition and through applying complex thinking strategies
IDEAS TO CONSIDER
ENRICHED ENVIRONMENTS GROW BETTER
BRAINS
: integrate stories, reading, conversation, movement, music, arts into experiences, provide challenging problem solving, provide opportunities for choice
CHALLENGE
:
The single best way to grow a better brain is through challenging problem solving, critical thinking, relevant projects, complex activities.
FEEDBACK : specific, not general; multi-modal
THE ART OF CHANGING THE
BRAIN -
ZULL
Nutrition
Exercise
Genes
Challenge,language development, and arts
Love
Feedback