Running your School on Data
advertisement

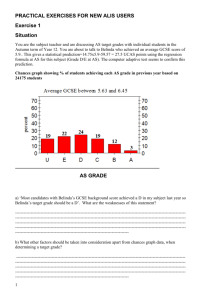
Using CEM Data for Self-Evaluation and Improvement Running Your School on Data 7th June 2011 Peter.Hendry@cem.dur.ac.uk Running your school on data CEM data includes: • • • • • • • School profile bands Baseline test acquired ability data, inc. IPRs Predictive data inc. chances graphs Value-added data Attitudinal data Curriculum assessments (Insight) Software programmes (PARIS) with databases So much data................................! Some key questions: 1. What data is needed? (What data is not needed?) 2. And for Whom is the data ? 3. What does the data mean? (What does the data not mean?) 1. What data do I need? A key first step! e.g. using MidYIS GCSE predictive data for target setting • • • • • Point and/or grade predictions? (e.g. 5.8/grade B) Based on whole cohort? Based on the 75th percentile? Based on prior value-added? The chances graphs? 40 In d ivid u a l C h a n c e s G ra p h fo r A D A M B E C K S M IT H - G C S E E n g lis h M id Y IS S c o re 1 2 1 M id Y IS B a n d A T e a c h e r's A d ju s tm e n t : 0 g ra d e s / le ve ls / p o in ts 34 35 34 30 P e rc e n t 25 Prediction 6.3 A/B 20 17 15 12 10 3 5 0 0 0 0 U G F E 0 D G ra d e C B A A* MidYIS Score 121 MidYIS Band A Prior VA Adjustment : 1 grades / levels 50 45 41 39 40 Prediction 7.4 A*/A 35 Percent 30 25 20 16 15 10 4 5 0 0 0 0 0 U G F E D 0 Grade C B A A* Discussion: setting the targets........... • From your perspective, assess the merit of each type of predictive data and the associated chances graphs • Which type of predictive data would you use to set the targets, and why? • Would your students be involved as part of the target setting process? • Would parents be informed about the process and outcome? • How would you ensure that HoDs were involved to ensure overview the process? 2. CEM data: who is it for? For example: • SMT/SLT: summary data, attitudinal • HoDs: Subject VAD, predictive data • Subject teachers: • FormTutors: • Head of Learning/Year/House: • Parents: • Pupils: and not forgetting: • Governors: • Media: 3. What does the data mean? e.g. value-added data: • The difference between raw and standardised residuals • The use of confidence limits to distinguish between average and statistically significant data, and to allow for small entry subjects • Can ‘zero’ or even ‘negative value-added’ be acceptable? Raw residual Bar chart (MIDYIS and YELLIS only) 0.0 -0.3 Voc Health & Social Care 0.2 SC Religious Studies SC Physical Education -1.0 SC ICT Science: GCSE Additional 0.1 0.1 Science: GCSE Science: Other 0.1 Welsh -0.3 Religious Studies 0.2 0.2 0.2 Physics -0.3 Physical Education 0.3 Music 0.1 Mathematics -0.2 -0.2 ICT 0.3 Home Economics 0.0 History 0.1 0.1 German 1.5 Geography 1.0 French English Literature 0.0 English -2.0 Drama -1.5 -0.1 Design & Technology -0.2 Chemistry 0.5 Business Studies -0.5 Biology Art & Design Average Standardised Residual Standardised Residual Bar Chart 2.5 2.0 99.7% confidence limit 95% confidence limit 0.9 0.1 0.0 -0.2 -0.7 -0.9 ANY VALUE IN THE INNER SHADED AREA IS CONSIDERED TO BE AVERAGE VALUE ADDED -2.5 Raw residual Bar chart (MIDYIS and YELLIS only) 0.0 -0.3 Voc Health & Social Care 0.2 SC Religious Studies SC Physical Education -1.0 SC ICT Science: GCSE Additional 0.1 0.1 Science: GCSE Science: Other 0.1 Welsh -0.3 Religious Studies 0.2 0.2 0.2 Physics -0.3 Physical Education 0.3 Music 0.1 Mathematics -0.2 -0.2 ICT 0.3 Home Economics 0.0 History 0.1 0.1 German 1.5 Geography 1.0 French English Literature 0.0 English -2.0 Drama -1.5 -0.1 Design & Technology -0.2 Chemistry 0.5 Business Studies -0.5 Biology Art & Design Average Standardised Residual Standardised Residual Bar Chart 2.5 2.0 99.7% confidence limit 95% confidence limit 0.9 0.1 0.0 -0.2 -0.7 -0.9 ANY VALUE IN THE INNER SHADED AREA IS CONSIDERED TO BE AVERAGE VALUE ADDED -2.5 -0 .1 -0 .5 -0 .9 -1 0 .3 0 .3 0 .0 0 .1 0 .2 0 .3 0 .0 0 .0 0 .2 0 .0 0 .6 0 .5 0 .6 0 .5 0 .5 0 .4 0 .3 0 .5 0 .9 0 .8 1 0 A v e ra g e S ta n d a rd is e d R e s id u a l Standardised Residual Bar Chart A ve ra g e S ta n d a rd is e d R e s id u a ls b y S u b je c t M id Y IS Y e a r 7 2 0 0 4 /2 0 0 5 to G C S E 2 0 0 9 2 1 .5 -1 .5 -2 S ta tis tic s S p a n is h S c ie n c e R e lig io u s S tu d ie s P h y s ic a l E d u c a tio n M u s ic M a th e m a tic s L a tin H o m e E c o n o m ic s H is to ry G e rm a n G e o g ra p h y F re n c h E n g lis h L ite ra tu re E n g lis h D ra m a D e s ig n & T e c h n o lo g y B u s in e s s S tu d ie s Bus. & C om m . S y s te m s A rt & D e s ig n A d d itio n a l S c ie n c e Case study: Alis value-added data Four sets of VAD are available! From average GCSE baseline: • all Alis cohort • type of Institution • Syllabus From the baseline test • all Alis cohort SPC Chart with confidence limits: WHOLE SCHOOL All Alis Cohort: Syllabus Institution Using PARIS software: Baseline Test Whole School From your perspective, which set of VAD would you use for the different user groups? (Governors, HoDs, Media, Parents, SMT/SLT...) A final thought.......... 0.5 Additional Science 0.7 Art & Design 0.6 Biology 0.7 Chemistry -0.7 Classical Civilisation 0.2 Design & Technology 0.8 Drama Is it possible to keep adding value at each key stage? English 0.3 English Literature 0.3 0.5 French -0.2 Geography 1.2 German 0.4 History -0.1 Latin 0.2 Mathematics 0.6 Music Average Standardised Residuals by Subject Physical Education MidYIS Year 9 2006/2007 to GCSE 2009 Physics 0.4 0.7 0.5 Religious Studies 0.5 Science 2 0.8 Spanish -3.0 -2.5 -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 Ave rage Raw Re s idual Average Standardised Residual 1.5 0.9 1 0.5 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.4 0.5 0.2 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.5 0.3 0.2 0 -0.2 -0.5 -1 -1.5 -0.6 -0.1 0.6 0.3 0.3 0.5 0.6 2009 A2 2010 A2 2009 2010 • USE ONE YEARS DATA WITH CAUTION! • Better to use three years data as patterns over time are more significant. CEM data is used for: • • • • • • Teachers to help learners Curriculum and staffing decisions Target setting and monitoring pupil progress Inspection evidence Self-evaluation Monitoring changes over time such as pupil ability intake profiles and VAD • Asking the question ‘can we do better?’ i.e. the data is used to aid and to support professional judgement with due consideration to: • • • • Ethos and tradition of ‘my’ institution Accountability Parental expectations Staff training in use of, and ability to cope with, data (data overload) • Management of data: integrating the data into school procedures, storage, retrieval, distribution and access……policy?