7/1 - Andrew Spath

CIVIL SOCIETY IN THE ARAB
WORLD… TOWARDS
DEMOCRACY?
351 – Contemporary Politics of the Middle East
Summer 2010
What is Society?
A system of social interaction that includes culture and social organization
Status (rank in society)
Role (expected behavior associated with a particular status
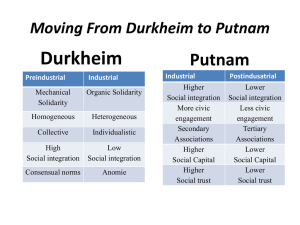
Gemeinschaft and Gesellschaft
Primary and Secondary Associations
What is Civil Society?
Civil society as a set of organized groups/associations, whose members deliberate about social or political issues or act collectively to accomplish common goals.
“the place where a mélange of groups, associations, clubs, guilds, syndicates, federations, unions, parties, and groups come together to provide a buffer between state and citizen.”
Counterweight to the state
TRANSNATIONAL
CIVIL SOCIETY AND
ADVOCACY
NETWORKS
Political society
(e.g., political parties)
CIVIL
SOCIETY
Domestic society
(family, kinship networks)
ECONOMY
STATE
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATIONS AND
TRANSNATIONAL REGIMES: UN, EU,
WTO, WORLD BANK, IMF.
European Union
Source: Jan Kubik, Rutgers University, Comparative Proseminar
Two Examples of Civil Society (1)
Qat Chews in Yemen (Wedeen)
Public Sphere – where people congregate to discuss societal issues and transform discussion into political action
Educated populace, performances of knowledge, enlightened (and critical) debate
help people to develop attachments to the nation outside of the formal institutions of government
Pluralism & inclusivity, but hierarchy
Two Examples of Civil Society (2)
Dewaniya in Kuwait -
place of receiving associates
Gathering place to facilitate discussion & deliberation about important issues, and build consensus
Similar to a ‘town hall’ meeting, but less formal and continuously taking place, and more social
Politics of deliberation, alliance formation, activism, and contention
Locus of pro-democracy movement in 1980s-90s
Locus of nationalist activism during Iraqi occupation
Political Campaigns
Characteristics of Civil Society
Organizations (CSOs)
Secondary group relations, not primary
Openness and inclusivity (public); civil in their behavior
Legally recognized
Produce dense networks of social relationship based on trust and reciprocity (social capital)
**Tolerant and moderate in their claims; Supportive of democratic reform
Networks
What is a network?
A complex set of relationships between individuals and organized groups of individuals
Generates feelings of solidarity
Collective “we” that is often sub-national
Reified by regular associations among individuals
Based on trust and continued associations
Strongest predictor of recruitment into activist organization? knowing someone already involved
Web of Social Affiliations or Social Network
B
A
Some Types of Ties
Professional
C
Family
Romance
Business
D
Some Types of CSOs (Yom reading)
Membership-based Professional Groups
Ex: Lawyer’s organizations (like Bar Association)
NGOs
Ex: Widows for Peace (micro-credit); Iraq Health Aid
Organization (basic nursing skills); require registration
Public Interest Advocates – human rights, watchdogs, thinktanks, etc.
Unions
Ex: Labor Unions exist in most, if not all, Arab states
Regulated by gov’t (public funding; constrains activism)
Informal Social Groups and Networks
Iraqi Youth League in Jordan; Internat’l. Pal. Youth League
What is Democracy?
Minimalist (process) definitions
Substantive definitions (& preconditions)
"democracy is not attained simply by making institutional changes or through elite level maneuvering. Its survival depends also on the values and beliefs of ordinary citizens."
Civic Culture
(Tessler on attitudes)
Pride and emotional investment in the nation & pol. system
Expectation of fair treatment from government authorities
Relative freedoms of speech and expression about political issues
Tolerance toward groups/parties/orgs you disagree with
Valuing of active participation (in local government, parties, & civic associations)
Self-confidence in one's competence to participate in politics
Civic cooperation and trust
Membership in a voluntary association
Social Capital