Activating—Driving Systems of the Brain
advertisement

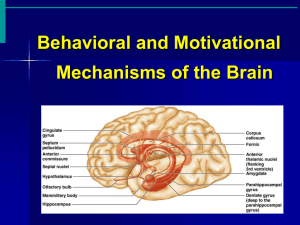
Chapter 58: Behavioral and Motivational Mechanisms of the Brain—The Limbic System and the Hypothalamus Guyton and Hall, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 12 edition Activating—Driving Systems of the Brain • Control of Cerebral Activity by Continuous Excitatory Signals from the Brain Stem a. Reticular excitatory area of the brain stem-sends signals upward and downward b. Downward-to spinal cord reflexes and to maintain tone in the antigravity muscles c. Upward through the thalamus (two signals) 1. Rapid transmission to excite the cerebrum 2. Build up progressively for seconds to minutes Activating—Driving Systems of the Brain Fig. 58.1 Excitatory-activating system of the brain Activating—Driving Systems of the Brain • Excitation by Peripheral Sensory Signals • Increased Activity of the Excitatory Area Caused by Feedback Signals Returning From the Cerebral Cortex • Thalamus is a Distribution Center That Controls Activity in Specific Regions of the Cortex • A Reticular Inhibitory Area is Located in the Lower Brain Stem Activating—Driving Systems of the Brain • Neurohormonal Control of Brain Activity-Three Systems Studied in the Rat a. Norepinephrine system-excitatory and can go to every area of the brain b. Dopamine system-can be both excitatory and inhibitory; goes to specific brain regions c. Serotonin system-inhibitory; goes to specific brain regions Activating—Driving Systems of the Brain • Neurohormonal Systems in the Human Brain a. Same three as in the rat plus b. The acetylcholine system Activating—Driving Systems of the Brain • Neurohormonal Systems in the Human Brain Fig. 58.2 Fig. 58.3 Activating—Driving Systems of the Brain • Other Neurotransmitter and Neurohormonal Substances Secreted in the Brain Neurotransmitter Or Neurohormone Enkephalin ACTH GABA MSH Glutamate Neuropeptide Y Vasopressin Epinephrine Histamine Angiotensin II Endorphins Neurotensin Limbic System • Functional Anatomy of the Limbic System Fig. 58.5 Limbic system showing the key position of the hypothalamus Limbic System • Functional Anatomy of the Limbic System Fig. 58.4 Anatomy of the limbic system Limbic System • Hypothalamus, a Major Control Center for the Limbic System a. Has two-way communicating pathways with all levels of the limbic system; sends output signals in three directions: 1. To the brain stem (mesencephalon, medulla, and pons) and then to the ANS 2. To higher areas of the diencephalon and cerebrum 3. To the infundibulum to control secretions of the anterior and posterior pituitary Limbic System • Hypothalamus, a Major Control Center for the Limbic System b. Vegetative and endocrine control functions of the hypothalamus c. Areas that cause specific activities are not as accurately localized as suggested in the following figures Limbic System Fig. 58.6 Control centers of the hypothalamus Limbic System Fig. 58.7 Coronal view of the hypothalamus Limbic System • Behavioral Functions of the Hypothalamus and Associated Limbic Structures a. Effects caused by stimulation of the hypothalamus 1. Lateral-thirst and eating; increases the general level of activity (possibly rage and fighting) 2. Ventromedial nucleus-satiety, decreased eating, and tranquility 3. Periventricular nuclei-fear and punishment reactions 4. Anterior and posterior hypothalamus-sex drive Limbic System • Behavioral Functions of the Hypothalamus and Associated Limbic Structures b. Effects caused by hypothalamic lesions 1. Bilateral lesions-decrease eating and drinking to zero; extreme passivity 2. Ventromedial areas-excessive eating and drinking; hyperactivity; continuous rage and savagery Limbic System • Reward and Punishment Function of the Limbic System a. Reward centers b. Punishment centers c. Rage-association with punishment centers d. Placidity and tameness Limbic System • Importance of Reward and Punishment on Behavior a. Effect of tranquilizers on reward and punishment b. Importance in learning and memory Specific Functions of Other Parts of the Limbic System • Functions of the Hippocampus a. Role in learning b. Theoretical function • Functions of the Amygdala • Functions of the Limbic Cortex