Summary of ECE 3085
advertisement
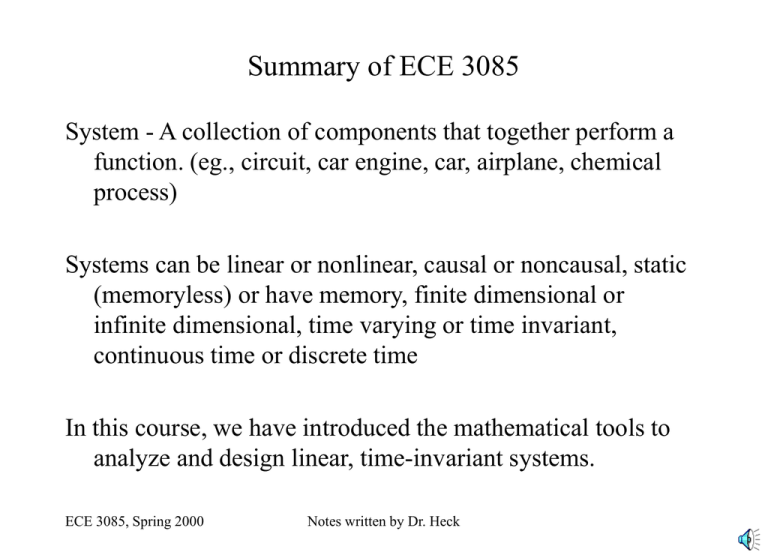
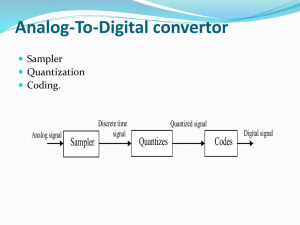
Summary of ECE 3085 System - A collection of components that together perform a function. (eg., circuit, car engine, car, airplane, chemical process) Systems can be linear or nonlinear, causal or noncausal, static (memoryless) or have memory, finite dimensional or infinite dimensional, time varying or time invariant, continuous time or discrete time In this course, we have introduced the mathematical tools to analyze and design linear, time-invariant systems. ECE 3085, Spring 2000 Notes written by Dr. Heck Analysis Tools CONTINUOUS-TIME SYSTEMS DISCRETE-TIME SYSTEMS Laplace Transform Cont. Time Conv. Fourier Transform Z-transform Discrete Time Conv Discrete Time Fourier Transform Solving for response to input X X X X X X Solving for steady state response to sinusoid X X X X X X Understanding filtering characteristics Understanding characteristics of system response (stability, transient behavior, etc) X X X X Transfer function Transfer function ECE 3085, Spring 2000 Notes written by Dr. Heck Control Design Methods • Root Locus - Plot of the closed loop poles as a function of gain (can be used in the s-domain or the z-domain to determine the K that yields desirable closed loop pole positions) • Frequency Response - Bode plot design (not covered in this course, but a common method) • Simulation - after the root locus or the Bode plot methods are used to get an initial design, the system is simulated and the controller can be adjusted for better performance • Implementation - either as an analog circuit or a computer that implements a difference equation ECE 3085, Spring 2000 Notes written by Dr. Heck Digital Control • Mappings - Euler approximation for differentiation, bilinear transformation (or Tustin’s rule or trapezoidal rule), step response matching (or zero order hold) • Direct Method of Design - Map plant to discrete time and do the design directly in the discrete-time domain • Indirect Method of Design - Design the controller in the continuous-time domain, then map it to discrete time • Implementation - computer algorithm implementing a difference equation ECE 3085, Spring 2000 Notes written by Dr. Heck State Space Methods Alternative method to representing systems (as opposed to transfer functions) • Motivation for using: – represents internal model behavior – matrix representation easier for computers to use – easier for multi-input and multi-output systems • What have we learned to do with it? – Put systems into state space form – Solve system response to IC (zero input response) and to the input (zero state response) – Find transfer function ECE 3085, Spring 2000 Notes written by Dr. Heck