Dr Hafiz Abdullah
advertisement

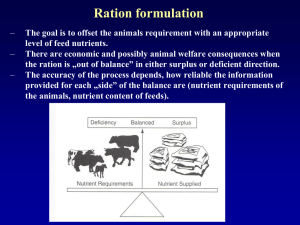
FEEDING TO ENHANCE LIVESTOCK PRODUCTIVITY Prof. Dr. Muhammad Abdullah Dept. of Livestock Production University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Lahore mabdullah@uvas.edu.pk; 0300-6648200 Livestock Productivity Genetics X Environment Adequate feeding levels of a highly nutritional diet are vital for optimal animal performance and well-being. Farm-to-farm variations make it difficult to recommend standard feed levels: ►Animal genetics ►Environmental conditions ►Management practices Goal of a Successful Feeding Programme Optimize Feed milk yield costs represent largest input cost (60-70%) Feeding high producing cows –– a continues challenge Nutrient Requirements Maintenance/Health Growth Milk Production Reproduction Vary with the stage of lactation and gestation A ctivity Priority of Nutrients in the Body Maintenance Growth Lactation Fetal Growth Breeding Body Reserve Why Balanced Ration ? Selection of Concentrate Feeds Availability Cost Nutrient composition (Protein, energy, minerals) General Consideration Oil cakes / Meals Grains By-products Molasses Salt/DCP/MM 20 – 25 % 25 – 30 % 40 – 50 % ~ - 10 % 1 - 2% FEEDING MANAGEMENT Feeding Phases Early lactation—0 to 70 days Peak DM intake (Second 10 Weeks Postpartum) Mid- and late lactation—140 to 305 days (declining milk production) Dry period—60 to 14 days before the next lactation. Transition or close-up period—14 days before to parturition. Events During Different Phases of Lactation Nutrients demand for peak milk yield is high Can not eat to full capacity during early phase Uses body reserves as energy source Rapidly looses body weight Increasing Peak Milk Yield Improve Lactation Performance Milk Yield (lit/day) 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44 Weeks of Lactation Phase 1 Early Lactation—0 to 70 Days Postpartum Feed top quality forage. Make sure the diet contains adequate amounts of CP, DIP and UIP. Increase grain intake at a constant rate after calving. Consider adding fat (0.5 to 0.75 kg /cow/day) to diets. Allow constant access to feed. Minimize stress conditions. Phase 2 Peak DM intake (Second 10 Weeks Postpartum) Feed forages and grain several times a day. Feed the highest quality feeds available. Continue to minimize stress conditions. Phase 3 Mid- to late lactation (140 to 305 days postpartum) Easiest to manage Milk production is declining The cow is pregnant, and nutrient intake will easily meet or exceed requirements Grain feeding should be at a level to meet milk production requirements Lactating cows require less feed to replace a pound of body tissue than dry cows. Phase 4. Dry period (60 to 14 days before parturition) Observe body condition of dry cows and adjust energy feeding as necessary. Meet nutrient requirements and avoid excessive feeding. Change to a transition ration starting 2 weeks before calving. Avoid excess calcium and phosphorus intakes. Limit salt to 25-30 g and limit other sodium-based minerals in the dry cow ration to reduce udder edema problems. Body Condition Scores – Dairy Cows 1 2 BCS: 1 3 BCS: 2 4 BCS: 3 5 BCS: 4 BCS: 5 Feeding in Pregnancy (Last 2 months) 1. 2. Rapid growing foetus Develop body reserves for use in subsequent lactation How; Give rest if in milk (forced drying) Feed concentrate 2 kg/day + good quality fodder, restrict straw Phase 5. Transition period (14 days before to parturition) Provide 3 to 5 kg of grain Increase protein in the ration to between 14 and 15 percent of the ration DM Limit fat in the ration to 100 g. High fat feeding will depress DM intake Maintain 3 to 5 kg hay in the ration to stimulate rumination Remove salt from the ration if edema is a problem Feeding Total Mixed Ration Each bite is nutritionally balance. The roughage-to-concentrate can be varied to regulate nutrient intake. TMR regulates rumen pH and enhance microbial protein synthesis. Minimize feed selection. Increase feed intake. Less labor and feeding operations are readily mechanized. Daily allowance Fodder @ 10% of body weight ~ 40- 60 kg Ration ~ Half of milk production More ration during summer season Water should be available all the time Mineral mixture @ 2% in the ration Flat Rate Concentrate Feeding Do not starve profit out of a good cow Do not feed profit to a poor cow Suggestions Select & mix different ingredients on protein basis for making concentrate mixture) Always add minerals especially take care of Calcium & Phosphorus ratio in the rations Plan your feeding program to raise the peak milk yield Never restrict feed & water soon after parturition Suggestions Avoid large fluctuation in green fodder supply through silage making Make best use of local feeds with relevant supplementation & conservation Improve feeding value of straw through urea treatment for fodder scarcity period THANK YOU