sage update - oct 24 - Canyons Assessment
advertisement

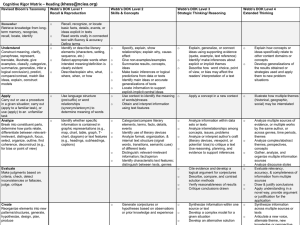
SAGE Update: What do we know now? Leadership Meeting October 24, 2013 Hal Sanderson & Darren Draper Agenda & Objectives Agenda Objectives SAGE Timelines Participants will leave with a clear understanding of district and state timelines SAGE Student View Participants will gain a better understanding of the key features of the testing experience for students SAGE Information for Teachers Participants will leave with a clear understanding of test blueprints and testing time Technology for SAGE Participants will leave with a clear understanding of SAGE technology requirements and receive good news about state technology grant. Next Steps in Communication Participants will understand next steps in communicating SAGE to teachers and parents General SAGE Timeline • Break 2:00-2:15 • End of Session 3:15 • Closing Keynote 3:30-4:30 District SAGE Testing Window • April 21st through May 30th • Six week window What will the SAGE test look like? Student View SAGE Test Information ITEM TYPE STUDENT ACTION Approximately 50% will be multiple choice Students select correct choice out of four choices Approximately 50% will be constructed-response, machine scored Student constructs the answer (drag and drop, hot spot, write an answer) • See SAGE sample questions athttp://Demo.TDS.airast.org/AIRAssessment SAGE Test Item – Hot Spot • See SAGE sample questions athttp://Demo.TDS.airast.org/AIRAssessment See sample questions at http://Demo.TDS.airast.org/AIRAssessment SAGE Test Item – Drag and Drop See sample questions at http://Demo.TDS.airast.org/AIRAssessment SAGE Test Item – Hot Spot See sample questions at http://Demo.TDS.airast.org/AIRAssessment SAGE Test Item – Constructed Response Elementary SAGE Testing Time (Estimated time -- test is untimed) •LANGUAGE ARTS, Grades 3 – 5 Writing - 60 minutes (one or multiple sittings) Reading, Speaking, Listening and Language 90 minutes (Two 45 min sessions) •MATH, Grades 3 – 5; Two 45 min Sessions •SCIENCE, Grades 4 – 5; Two 45 min Sessions Secondary SAGE Testing Time (Estimated time -- test is untimed) •LANGUAGE ARTS, Grades 6 – 11 Writing - 90 minutes (one or multiple sittings) for grades 7 - 11. Grade 6 writing will be 60 minutes. Reading, Speaking, Listening and Language 90 minutes (Two 45 min sessions) •MATH, Two 45 min Sessions (Math 6 through Secondary Math III) •SCIENCE, Two 45 min Sessions (Science 6 – Physics) The SAGE test Information for Teachers SAGE Test Assignment – Grade Based See Handout from the Utah State Office of Education SAGE Test Assignment – Course Based The SAGE test blueprints Available at http://ut.portal.airast.org/resources/?section=1 SAGE Mathematics Blueprint Available at http://ut.portal.airast.org/resources/?section=1 SAGE ELA/Literacy Blueprint Available at http://ut.portal.airast.org/resources/?section=1 SAGE Science Blueprint Available at http://ut.portal.airast.org/resources/?section=1 What is DOK listed in the blueprints? • Depth of Knowledge (DOK) provides a vocabulary and a frame of reference when thinking about our students and how they engage with the core content. • DOK offers a common language to understand "rigor," or cognitive demand, in assessments, as well as curricular units, lessons, and tasks. • DOK levels grow in cognitive complexity and provide educators a lens on creating more cognitively engaging and challenging tasks. • See DOK for each content area. Depth of Knowledge - ELA Hess’ Cognitive Rigor Matrix & Curricular Examples: Applying Webb’s Depth-of-Knowledge Levels to Bloom’s Cognitive Process Dimensions - ELA Revised Bloom’s Webb’s DOK Level 1 Webb’s DOK Level 2 Webb’s DOK Level 3 Webb’s DOK Level 4 Strategic Thinking/ Reasoning Taxonomy Recall & Reproduction Skills & Concepts Extended Thinking o Recall, recognize, or locate Remember Retrieve knowledge from longterm memory, recognize, recall, locate, identify Understand Construct meaning, clarify, paraphrase, represent, translate, illustrate, give examples, classify, categorize, summarize, generalize, infer a logical conclusion), predict, compare/contrast, match like ideas, explain, construct models Apply Carry out or use a procedure in a given situation; carry out (apply to a familiar task), or use (apply) to an unfamiliar task Analyze Break into constituent parts, determine how parts relate, differentiate between relevantirrelevant, distinguish, focus, select, organize, outline, find coherence, deconstruct (e.g., for bias or point of view) o basic facts, details, events, or ideas explicit in texts Read words orally in connected text with fluency & accuracy o Identify or describe literary elements (characters, setting, sequence, etc.) o Select appropriate words when intended meaning/definition is clearly evident o Describe/explain who, what, where, when, or how o Define/describe facts, details, terms, principles o Write simple sentences o Use language structure (pre/suffix) or word relationships (synonym/antonym) to determine meaning of words o Apply rules or resources to edit spelling, grammar, punctuation, conventions, word use o Apply basic formats for documenting sources o Identify whether specific information is contained in graphic representations (e.g., map, chart, table, graph, T-chart, diagram) or text features (e.g., headings, subheadings, captions) o Decide which text structure is appropriate to audience and purpose o Specify, explain, show relationships; explain why, cause-effect o Give non-examples/examples o Summarize results, concepts, ideas o Make basic inferences or logical predictions from data or texts o Identify main ideas or accurate generalizations of texts o Locate information to support explicitimplicit central ideas o o Use context to identify the meaning of words/phrases o Obtain and interpret information using text features o Develop a text that may be limited to one paragraph o Apply simple organizational structures (paragraph, sentence types) in writing o Categorize/compare literary elements, terms, facts/details, events o Identify use of literary devices o Analyze format, organization, & internal text structure (signal w ords, transitions, semantic cues) of different texts o Distinguish: relevant-irrelevant information; fact/opinion o Identify characteristic text features; distinguish between texts, genres o o Evaluate o o o o o o o o o o Make judgments based on criteria, check, detect inconsistencies or fallacies, judge, critique Create Reorganize elements into new patterns/structures, generate, hypothesize, design, plan, produce o Brainstorm ideas, concepts, problems, or perspectives related to a topic or concept o Generate conjectures or hypotheses based on observations or prior knowledge and experience o o o o o Explain, generalize, or connect ideas using supporting evidence (quote, example, text reference) Identify/ make inferences about explicit or implicit themes Describe how word choice, point of view, or bias may affect the readers’ interpretation of a text Write multi-paragraph composition for specific purpose, focus, voice, tone, & audience Apply a concept in a new context Revise final draft for meaning or progression of ideas Apply internal consistency of text organization and structure to composing a full composition Apply word choice, point of view, style to impact readers’ /viewers’ interpretation of a text Analyze information within data sets or texts Analyze interrelationships among concepts, issues, problems Analyze or interpret author’s craft (literary devices, viewpoint, or potential bias) to create or critique a text Use reasoning, planning, and evidence to support inferences Cite evidence and develop a logical argument for conjectures Describe, compare, and contrast solution methods Verify reasonableness of results Justify or critique conclusions drawn Synthesize information within one source or text Develop a complex model for a given situation Develop an alternative solution o Explain how concepts or ideas specifically relate to other content domains or concepts o Develop generalizations of the results obtained or strategies used and apply them to new problem situations o Illustrate how multiple themes (historical, geographic, social) may be interrelated o Select or devise an approach among many alternatives to research a novel problem o o o o Analyze multiple sources of evidence, or multiple works by the same author, or across genres, time periods, themes Analyze complex/abstract themes, perspectives, concepts Gather, analyze, and organize multiple information sources Analyze discourse styles o Evaluate relevancy, accuracy, & completeness of information from multiple sources o Apply understanding in a novel way, provide argument or justification for the application o Synthesize information across multiple sources or texts o Articulate a new voice, alternate theme, new knowledge or perspective See Handout © 2009 Karin K. Hess: Hess’ Cognitive Rigor Matrix: Permission to reproduce is given when authorship is fully cited [khess@nciea.org] For full article, go to www.nciea.org Depth of Knowledge – Math/Science Hess’ Cognitive Rigor Matrix & Curricular Examples: Applying Webb’s Depth-of-Knowledge Levels to Bloom’s Cognitive Process Dimensions – Math/Science Revised Bloom’s Webb’s DOK Level 1 Webb’s DOK Level 2 Webb’s DOK Level 3 Webb’s DOK Level 4 Strategic Thinking/ Reasoning Taxonomy Recall & Reproduction Skills & Concepts Extended Thinking o Recall, observe, & recognize Remember Retrieve knowledge from long-term memory, recognize, recall, locate, identify o Understand o o Construct meaning, clarify, paraphrase, represent, translate, illustrate, give examples, classify, categorize, summarize, generalize, infer a logical conclusion (such as from examples given), predict, compare/contrast, match like ideas, explain, construct models Apply Carry out or use a procedure in a given situation; carry out (apply to a familiar task), or use (apply) to an unfamiliar task Analyze Break into constituent parts, determine how parts relate, differentiate between relevant-irrelevant, distinguish, focus, select, organize, outline, find coherence, deconstruct o o o facts, principles, properties Recall/ identify conversions among representations or numbers (e.g., customary and metric measures) Evaluate an expression Locate points on a grid or number on number line Solve a one-step problem Represent math relationships in words, pictures, or symbols Read, write, compare decimals in scientific notation o Specify and explain relationships (e.g., non-examples/examples; cause-effect) Make and record observations Explain steps followed Summarize results or concepts Make basic inferences or logical predictions from data/observations Use models /diagrams to represent or explain mathematical concepts Make and explain estimates o o Select a procedure according to criteria and perform it o Solve routine problem applying multiple concepts or decision points o Retrieve information from a table, graph, or figure and use it solve a problem requiring multiple steps o Translate between tables, graphs, words, and symbolic notations (e.g., graph data from a table) o Construct models given criteria o Categorize, classify materials, data, figures based on characteristics o Organize or order data o Compare/ contrast figures or data o Select appropriate graph and organize & display data o Interpret data from a simple graph o Extend a pattern o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o Follow simple procedures (recipe-type directions) Calculate, measure, apply a rule (e.g., rounding) Apply algorithm or formula (e.g., area, perimeter) Solve linear equations Make conversions among representations or numbers, or within and between customary and metric measures Retrieve information from a table or graph to answer a question Identify whether specific information is contained in graphic representations (e.g., table, graph, T-chart, diagram) Identify a pattern/trend Evaluate o o o o o o o o o o o o o Make judgments based on criteria, check, detect inconsistencies or fallacies, judge, critique Create o o o o Reorganize elements into new patterns/structures, generate, hypothesize, design, plan, construct, produce Brainstorm ideas, concepts, or perspectives related to a topic o Generate conjectures or hypotheses based on observations or prior knowledge and experience o o o Use concepts to solve non-routine problems Explain, generalize, or connect ideas using supporting evidence Make and justify conjectures Explain thinking when more than one response is possible Explain phenomena in terms of concepts o Relate mathematical or scientific concepts to other content areas, other domains, or other concepts o Develop generalizations of the results obtained and the strategies used (from investigation or readings) and apply them to new problem situations Design investigation for a specific purpose or research question Conduct a designed investigation Use concepts to solve non-routine problems Use & show reasoning, planning, and evidence Translate between problem & symbolic notation when not a direct translation o Select or devise approach among many alternatives to solve a problem o Conduct a project that specifies a problem, identifies solution paths, solves the problem, and reports results Compare information within or across data sets or texts Analyze and draw conclusions from data, citing evidence Generalize a pattern Interpret data from complex graph Analyze similarities/differences between procedures or solutions o Analyze multiple sources of evidence o analyze complex/abstract themes o Gather, analyze, and evaluate information Cite evidence and develop a logical argument for concepts or solutions Describe, compare, and contrast solution methods Verify reasonableness of results o Gather, analyze, & evaluate information to draw conclusions o Apply understanding in a novel way, provide argument or justification for the application Synthesize information within one data set, source, or text Formulate an original problem given a situation Develop a scientific/mathematical model for a complex situation o Synthesize information across multiple sources or texts o Design a mathematical model to inform and solve a practical or abstract situation See Handout © 2009 Karin Hess permission to reproduce is given when authorship is fully cited khess@nciea.org What are the SAGE technology requirements 2014 SAGE Technology • CSD STANDARD. Windows, Macintosh, or Chromebook computers purchased in the last FOUR years can be utilized for SAGE. • iOS Devices. Schools interested in using iPADS will need written approval from Darren Draper by April 15th. According to the State, all IPADS must have external keyboards. • Headphones are required for the SAGE ELA test. Currently the Assessment Department is planning on purchasing inexpensive earbud headphones for each student. This district plan for headphones is subject to change. Do we have a State grant for more technology to help with testing time and instruction? YES! HB 2 – Computer Adaptive Testing (CAT) Funds SAGE-Compatible Computer Labs • We have enough grant money (H.B. 2 General Legislative Session 2013) to provide each school with one new Chromebook lab. • To opt-in, schools need only to provide $1,350 for the cost of a Chromebook cart! How to Opt-In To opt-in to the Chromebook lab Deal O’ the Year, please submit a journal entry: •For $1,350 •To 32 E 048 9932 4791 731 •By November 1st Next Steps SAGE information brochure for teachers SAGE information brochure for parents Chromebook purchase SAGE information for Students with Disabilities