PARCC Overview June 2011
advertisement

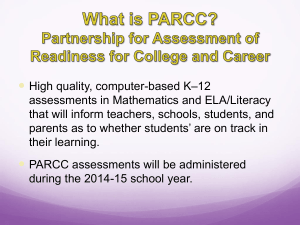
The Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers June 2011 The Common Core State Standards Initiative • Beginning in the spring of 2009, Governors and state commissioners of education from 48 states, 2 territories and the District of Columbia committed to developing a common core of state K-12 standards • In June 2010, the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) were released by NGA and CCSSO • To date, 44 states and the District of Columbia have adopted the Standards • Most states intend to implement the new standards by the 2014-15 school year 2 44 States + DC Have Adopted the Common Core State Standards *Minnesota adopted the CCSS in ELA only The Common Core State Standards Initiative Preparation: The standards are college- and career-ready. They will help prepare students with the knowledge and skills they need to succeed in education and training after high school. Competition: The standards are internationally benchmarked. Common standards will help ensure our students are globally competitive. Equity: Expectations are consistent for all – and not dependent on a student’s zip code. Clarity of purpose: The standards are focused, coherent, and clear. Clearer standards help students (and parents and teachers) understand what is expected of them. Collaboration opportunity: The standards create a foundation to work collaboratively across states and districts, pooling resources and expertise, to create curricular tools, professional development, common assessments and other materials. 4 Key Advances in the Common Core ELA/Literacy Standards Reading • Balance of literature and informational texts • Focus on text complexity and what students read Writing • Emphasis on argument and informative/explanatory writing • Writing about sources (evidence) Speaking and Listening • Inclusion of formal and informal talk Language • Stress on academic and domain-specific vocabulary Address reading and writing across the curriculum 5 • Responsibility of teachers in those subjects • Complement rather than replace content standards in those subjects Key Advances in the Common Core Math Standards Focus and coherence • Focus on key topics at each grade level • Coherent progressions across grade levels Depth over breadth • Allows more time for mastery Balance of concepts and skills • Content standards require both conceptual understanding and procedural fluency Mathematical practices • Foster reasoning and sense-making in mathematics 6 About PARCC Race to the Top Assessment Program Competition • $350 million of Race to the Top Fund set aside for awards to consortia of states to design and develop common K-12 assessment systems aligned to common, college- and career-ready standards • In Sept. 2010, the U.S. Department of Education awarded grants to the Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers (PARCC) and Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium (SBAC) 8 About PARCC • PARCC is an alliance of 25 states working together to develop a common set of K-12 assessments in English and math anchored in what it takes to be ready for college and careers • PARCC is state-led and a subset of PARCC states make up its Governing Board • Collectively the PARCC states educate more than 31 million students — nearly 63% of K-12 students attending American public schools 9 PARCC States Governing Board States 10 Participating States PARCC Governance AZ, AR, DC, FL, GA, IL, IN, LA, MD, MA, NJ, NY, OK, RI, TN Governing Board States Governing Board Chair Massachusetts Commissioner Mitchell Chester Florida Fiscal Agent State US Education Department award is to Florida on behalf of 25 states to oversee budget, procurement, and reporting functions Achieve Project Management Partner 11 Achieve is a bipartisan, non-profit organization that helps states raise academic standards, improve assessments, and strengthen accountability to prepare all young people for postsecondary education, work, and citizenship PARCC Committee Structure Governing Board Deals with major policy issues Steering Committee Technical Advisory Committee (TAC) Responsible for technical and research work Technical Advisors Specific technical advisors appointed as needed 12 Technical Working Groups (TWG) Domain-specific technical advisors, appointed by TAC and Leadership Advisory Committee on College Readiness (ACCR) Advises Governing Board on postsecondary issues Postsecondary Leadership Team Leadership Team (LT) Responsible for operation and management Operational Working Groups (OWG) Responsible for day-today-aspects of specific areas Responsible for postsecondary engagement to advance college readiness Content Leads Groups responsible for aspects of contentspecific areas The PARCC Vision The PARCC Vision for Next Generation Assessments 1. Create high-quality assessments that measure the full range of the Common Core State Standards 2. Build a pathway to college and career readiness for all students 3. Support educators in the classroom 4. Better utilize technology 5. Compare results across districts and states, and determine how students compare to their international peers 14 6. Advance accountability Proposed PARCC Design English Language Arts and Mathematics, Grades 3 - 11 25% 50% 75% 90% PARTNERSHIP RESOURCE CENTER: Digital library of released items, formative assessments, model content frameworks, model instructional supports, student and educator tutorials and sample items, scoring training modules, and professional development materials Through-course ASSESSMENT 1 • ELA • Math Summative assessment for accountability 15 Through-course ASSESSMENT 2 • ELA • Math Required, but not used tor accountability Through-course ASSESSMENT 3 • ELA • Math Through-course ASSESSMENT4 • Speaking • Listening END OF YEAR ASSESSMENT Key advances in the PARCC vision: • • • • Unprecedented collaborative effort across states Anchored in CCSS – and what it takes to be prepared Range of item types that match demands of CCSS Common cut scores/performance levels across states based on evidence of what it takes to be successful • Computer delivered to allow for innovative item types and quick turn around of results 16 Implementation and Instructional Support & Next Steps PARCC’s Implementation Support & Stakeholder Engagement To support state efforts to successfully implement and transition to the Common Core State Standards and next generation assessments by the 2014-15 school year, PARCC will facilitate: – Consortium-wide support for strategic planning and collective problem solving for the implementation of CCSS and PARCC assessments; – Collaborative efforts to develop the highest priority instructional tools; – Multi-state support to build leadership cadres of educators who are deeply engaged in the use of those tools, the CCSS and the PARCC assessments. – Multi-state support to engage the postsecondary community around the design and use of the assessments 18 PARCC Timeline SY 2010-11 SY 2011-12 Launch and design phase Development begins 19 SY 2012-13 SY 2013-14 SY 2014-15 Summer 2015 First year pilot/field testing and related research and data collection Second year pilot/field testing and related research and data collection Full administration of PARCC assessments Set achievement levels, including college-ready performance levels Key Challenges for PARCC Technical Challenges • Developing an interoperable technology platform • Transitioning to an computer-based assessment system • Developing and implementing automated scoring systems and processes • Identifying effective, innovative item types 20 Implementation Challenges • Estimating costs over time, including longterm budgetary planning • Transitioning to the new assessments at the classroom level • Ensuring long-term sustainability • Building on CCSS implementation Policy Challenges • Student supports and interventions • Accountability • High school course requirements • College admissions/ placement • How to change perceptions about what next-gen assessments can and will do The Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers June 2011 www.PARCConline.org