part c: programme standards
advertisement

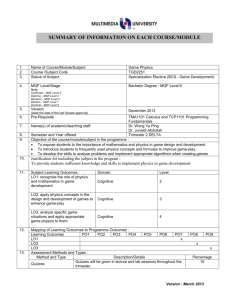
BENGKEL PERSEDIAAN AUDIT PEMATUHAN & OUTCOMEBASED EDUCATION (OBE) 3 APRIL 2014 IPGKTAR KOMEN PANEL PENILAI MQA • Semasa Audit Pematuhan di IPGKTAA dan IPGKTI pada April 2013… • Perkara yang perlu diberi perhatian: • Tahap pemahaman staf akademik berkaitan MQF, SLT, CLO dan PLO masih kurang • Cadangan Penyelesaian: • Latihan untuk staf akademik berkaitan MQF, PLO, CLO wajar diadakan MALAYSIAN QUALIFICATION AGENCY (MQA) Act 679 (Akta MQA 2007) What is MQA? • The Malaysian Qualifications Agency (Agensi Kelayakan Malaysia) or the MQA is a statutory body in Malaysia set up under the Malaysian Qualifications Act 2007 to: o Implement MQF o Accredit HE programmes and qualifications o Supervise and regulate quality and standard of HEP o Establish and maintain MQR RELATED MQA DOCUMENTS Code of Practice for Programme Accreditation (COPPA) Code of Practice for Open and Distance Learning (COPODL) QUALITY ASSURANCE APPLICATION PROVISIONAL ACCREDITATION MQA-01 Part A – General Information on the HEP Part B – Progamme Description Part C – Programme Standards (9) FULL ACCREDITATION MQA-02 Part A – General Information on the HEP Part B – Progamme Description Part C – Programme Standards (9) Part D – Self Review Report (SRR) PART C: PROGRAMME STANDARDS Area 1: Vision, Mission, Educatiponal Goals and Learning Outcomes 1.1 Statement of Programme Aims, Objectives and LOs 1.2 Learning Outcomes Benchmarked Standard (MUST) Enhanced Standards (SHOULD) 7 BS 4 ES 7 (Q + St) 3 (Q + St) CONTOH PART C: PROGRAMME STANDARDS Area 2: Curriculum Design & Delivery 2.1 Academic Autonomy 2.2 Programme Design and TL Methods 2.3 Curriculum Content and Structure 2.4 Management of the Programme 2.5 Linkages with External Stakeholders Benchmarked Standard (MUST) Enhanced Standards (SHOULD) 19 BS 11 ES 18 (Q + St) 10 (Q + St) PART C: PROGRAMME STANDARDS Area 3: Assessment of Students 3.1 Relationship Between Assessment and Learning 3.2 Assessment Method 3.3 Management of Student Assessment Benchmarked Standard (MUST) Enhanced Standards (SHOULD) 11 BS 5 ES 19 (Q + St) 6 (Q + St) PART C: PROGRAMME STANDARDS Area 4: Student Selection & Support Services 4.1 Admission & Selection 4.2 Articulation Regulations, Credit Transfer and Credit Exemption 4.3 Transfer of Students 4.4 Student Supp. Services and Co-curricular Act. 4.5 Student Representation and Participation 4.6 Alumni Benchmark Enhanced ed Standard Standards (MUST) (SHOULD) 21 BS 13 ES 23 (Q + St) 12 (Q + St) PART C: PROGRAMME STANDARDS Area 5: Academic Staff Benchmarked Standard (MUST) Enhanced Standards (SHOULD) 5.1 Recruitment & Management 11 BS 4 ES 5.2 Service and Development 22 (Q + St) 5 (Q + St) PART C: PROGRAMME STANDARDS Area 6: Educational Resources 6.1 Physical Facilities 6.2 Research and Development 6.3 Educational Expertise 6.4 Educational Exchanges 6.5 Financial Allocation Benchmarked Standard (MUST) Enhanced Standards (SHOULD) 12 BS 10 ES 23 (Q + St) 9 (Q + St) PART C: PROGRAMME STANDARDS Area 7: Programme Benchmarked Monitoring and Review Standard 7.1 Mechanisms for Programme Monitoring and Review 7.2 Involvement of Stakeholders (MUST) Enhanced Standards (SHOULD) 5 BS 4 ES 9 (Q + St) 5 (Q + St) PART C: PROGRAMME STANDARDS Area 8: Leadership, Governance and Administration Benchmarked Enhanced Standard Standards (MUST) (SHOULD) 8.1 Governance 8.2 Acad Leadership of the Programme 8.3 Administrative and Management Staff 11 BS 6 ES 19 (Q + St) 6 (Q + St) PART C: PROGRAMME STANDARDS Area 9: Continual Quality Improvement 9.1 Quality Improvement Benchmarked Enhanced Standard Standards (MUST) (SHOULD) 3 BS 2 ES 5 (Q + St) 2 (Q + St) MALAYSIAN QUALIFICATION FRAMEWORK (MQF) MQF in Act 679 (Akta MQA 2007) What is the MQF? MQF* Para 1 MQF is an instrument that develops and classifies qualifications based on a set of criteria that is approved nationally and at par with international practices, and which clarifies the earned academic levels, learning outcomes of study areas and credit system based on student academic load. * The Malaysian Qualifications Agency (2007), The Malaysian Qualifications Framework, Kuala Lumpur. MQF.Roz.Roadshow 3 MAIN FEATURES IN MQF (1) Academic Levels MQF (2) Learning Outcomes (3) Credit System General Principles 3 & 5: Levels of Qualifications & Minimum Graduating Credits Level MGC* Sectors Skills Vocational & Technical Academic 8 80** Doctoral 7 40 30 20 Masters Postgraduate Dip Postgraduate Cert 6 120 60 30 Bachelor Graduate Dip Graduate Cert 5 40 Advanced Diploma Advanced Diploma Advanced Diploma 4 90 Diploma Diploma Diploma 3 60 Certificate 3 2 - Certificate 2 1 - Certificate 1 Note: * MGC = Minimum Graduating Credits MQF.Roz.Roadshow Certificate Certificate General Principle 4: Learning Outcomes (MQF Para 15) – LO Domains 1 4 7 Knowledge 2 Practical Skills Values, attitudes and professionalism Information management and lifelong learning skills 8 Managerial and entrepreneurial skills MQF.Roz.Roadshow 5 3 Social skills and responsibilities Communication, leadership and team skills 6 Problem solving and scientific skills MOE - LO 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Knowledge Practical Skills Thinking and scientific skills Communication skills Social skills, teamwork and responsibility Values, ethics, moral and professionalism Information management and lifelong learning skills Managerial and entrepreneurial skills Leadership skills MQF – Akta 679 * Accreditation is voluntary , but compliance to MQF is mandatory BENEFITS OF ACCREDITATION Accreditation is a status or achievement as a result of quality assessment by MQA. It is a commitment by MQA to all stakeholders in higher education i.e students, parents, employer that the programmes accredited by MQA is quality-assured. (MQA) BENEFITS OF ACCREDITATION 1. Public Service Department (PSD) will use this accreditation status to recognise the qualification for employment in the public service. 2. Professional bodies such as the Board of Engineers Malaysia (BEM) will use the accreditation to recognise engineering graduates for registration as a professional engineers 3. Students in accredited programmes are eligible to apply for loan from funding agencies such as National Higher Education Fund (PTPTN). (MQA) BENEFITS OF ACCREDITATION 4. Graduates are eligible to continue their studies in higher education institutions and obtain credit transfer. However, the final decision lies with the institution concerned. 5. Graduates can be considered for employment in the public sector. In many cases, even private sector employer consider accredited programmes in their selection of graduates for employment. 6. Institutions can franchise their accredited programmes to other institutions, subject to certain conditions. (MQA)