Essential Maps
advertisement

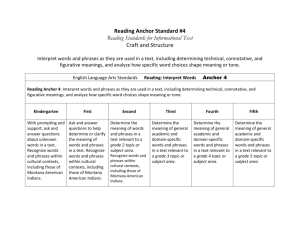
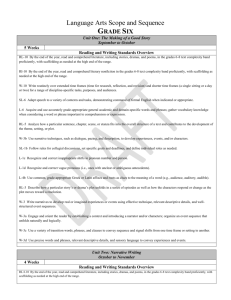
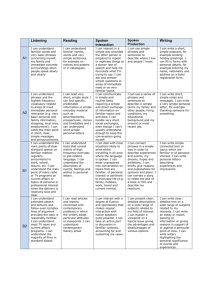
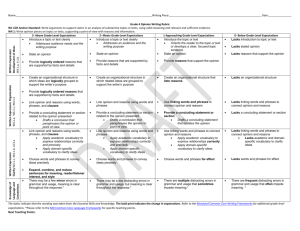
Michael Rush Debra Synatschk June 25, 2011 A Process for Transitioning to the Common Core State Standards Decision Making Process Attained Curriculum Developing a collective understanding of who teaches what and when Constructing a progression of skills Vocabulary is key Collaboration among teachers Aligning assessments to skills Repository for multiple resources Provides a guide for all teachers Demonstrates fidelity of implementation Diary Consensus Master Who creates these maps? What is their purpose? Advantages/Disadvantages? What is their intrinsic value for your teachers? How do you use them? What do you look for when you are using the maps? • • • • Constitute the “critical elements” of the curriculum within and across grade levels Are concept-based Focus on the Securely Held Content (mathematics) and the Core Capacities (ELA) students must truly understand Are developed vertically in order to ensure consistency and alignment Reflect on what is “essential” in the operational curriculum Identify the content and skills that are critical for students to know and be able to do Understand the “whys” for what we teach Match “whys” to the critical elements of the curriculum Curriculum maps, if available, should be used to facilitate the reflection process Discuss and Prioritize What are the concepts that are driving instruction? What is common? What is not essential? How these concepts will be integrated into the curriculum - with consistency? Build a strong verbal and written vocabulary across disciplines Grade 4 Informational Text Determine the meaning of general academic and domain-specific words or phrases in a text relevant to a grade 4 topic or subject area. Where does essential content and skills reside in the standard? What are the learning targets? What is the level of thinking/rigor as students move from grade to grade? How aligned is our vocabulary to the standards? How do we determine the appropriate rigor for standards that cross multiple grades? Grade 2: Determine the meaning of words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 2 topic or subject area. Grade 3: Determine the meaning of general academic and domain-specific words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 3 topic or subject area. Grade 4: Determine the meaning of general academic and domain-specific words or phrases in a text relevant to a grade 4 topic or subject area. Kindergarten: Grade 1: Grade 2: Grade 3: Fluently add and subtract within 5. Demonstrate fluency for addition and subtraction within 10. Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies. By end of Grade 2, know from memory all sums of two one-digit numbers. Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using strategies and algorithms based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. Based on the agreed upon Essential Elements: Establish the content and skills Identify the learning progression within and across grade levels Stop occasionally for vertical review Develop a set of units that incorporate a identified skills Units should be one to two weeks in length Sequence the units over the year As the units are developed, stop occasionally for vertical review Compare prioritized lists of Essential Elements among disciplines to identify commonalities Identify the common elements that cross disciplines Establish an overall sequence for building Essential Maps Mathematics Science NUMBER SENSE & COMPUTATION LIFE SCIENCE Whole Number Animal Life Cycles 1. Count whole numbers up to 1. Identify the stages in an 20 animal's life cycle such as frog, butterfly, bird, and mammal using 2. Identify whole numbers up to 20 appropriate scientific vocabulary. 1.1.1 2. 3. Write whole numbers up to 20 1.1.1 4. Compare whole numbers up to 20 1.1.5 3. Build new mathematical knowledge through problem solving 4. 5. 6. Use math terms and vocabulary: greater than, less than, and equal to 7. Use a number line or hundred chart to show one more and one less Social Studies Civics and Government 2.2.1 - Explain that the United States government is founded on the belief of equal rights for its citizens. (Use specific words and phrases from the text) 2.2.2 - Explain why it is important for a community to have responsible Describe the sequence of the life government. cycle: birth, growth, reproduction 2.2.7 - Explain the consequences of and death. violating laws, including punishment Describe body structures at each of those who do wrong, and the importance of resolving conflicts stage of the life cycle. appropriately. Compare and contrast the body 2.2.4 - Describe how people of structure through the life cycle. different ages, cultural backgrounds and traditions contribute to the community and how all citizens can respect these differences. Use appropriate vocabulary to do the following: - Analyze the need for government (2.2.1) - Classify Government Roles (2.2.2) - Differentiate between right and wrong choices (2.2.7) - Examine jobs of community Leaders (2.2.3) - Analyze contributions of different cultures to society (2.2.4) How do we assess this? In what ways do we know that our students are moving toward the “essential” elements? Are we assessing just the content and skills or are we assessing their understanding? What makes the assessments authentic?